To process data or train a model, you must first prepare a dataset. AI Asset Management provides powerful features to create and manage datasets. Its version management allows you to precisely reproduce experiments, track data versions, and record data lineage. If a new version causes issues, you can quickly roll back to a previous version to ensure business continuity.
Overview
AI Asset Management lets you manage basic and labeled datasets. A basic dataset typically contains large volumes of raw information and is primarily used to pre-train models to capture broad features and patterns. A labeled dataset contains human-annotated data with specific labels and is primarily used for model fine-tuning and evaluation to improve model performance on specific tasks.
Item | Basic dataset | Labeled dataset |
Definition | Raw, unlabeled data. | Human-annotated data |
Data processing | Data cleaning, deduplication, and more. | Data labeling, validation, and more |
Scenarios |
|
|
Go to the Datasets page
Log on to the PAI console.
In the upper-left corner, select the region where your workspace is located.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Workspaces. Click the name of the workspace that you want to open.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose AI Asset Management > Datasets.
Create a basic dataset
On the Custom Datasets tab, click Create Dataset and select Basic for Dataset Type. You can create a dataset from Object Storage Service (OSS) or File Storage (General-purpose NAS, Extreme NAS, CPFS, and AI-CPFS).
Storage type is Object Storage Service (OSS)
Parameter | Description |
Content Type | Select the data type, such as image, text, audio, video, table, or general. Specifying a type allows the system to filter datasets for future labeling tasks. |
Owner | Select the dataset owner. Only workspace administrators can configure this parameter. |
Import Format/OSS Path | |
Default Mount Path | The default path for mounting the data. This is often used in DSW and DLC:
|
Enable Version Acceleration | You can enable dataset version acceleration when you set Import Format to Folder. Key settings include:
|
Storage type is file system
Parameter | Description |
Content Type | Select the data type, such as image, text, audio, video, table, or general. Specifying a type allows the system to filter datasets for future labeling tasks. |
Owner | Select the dataset owner. Only workspace administrators can configure this parameter. |
File System | Select a file system that corresponds to the Storage Type. |
Mount Target | Configure a mount target to access the file system. |
File System Path | Specify the path to your data in the file system. For example, |
Default Mount Path | The default path for mounting the data. This is often used in DSW and DLC:
|
Enable Version Acceleration | If the Storage Type is General-purpose NAS, Extreme NAS, or CPFS, you can enable dataset version acceleration. The key parameters are described as follows:
|
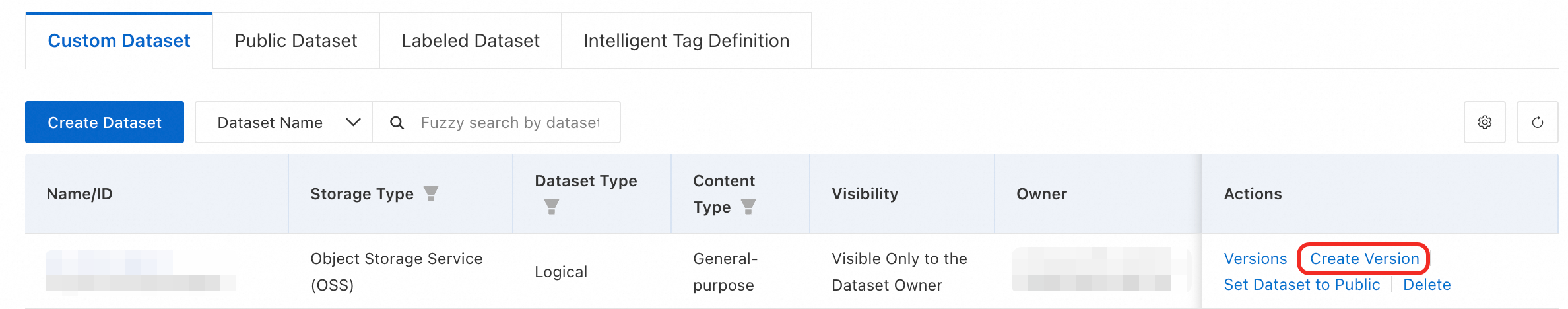
Create a basic dataset version
On the Custom Datasets tab, click Create Version in the Actions column for the target dataset.
Note:
The dataset name, storage type, and data type are inherited from the V1 version and cannot be changed.
The system automatically generates the dataset version, which is read-only.
For other parameter settings, see the descriptions in the Create a basic dataset section.
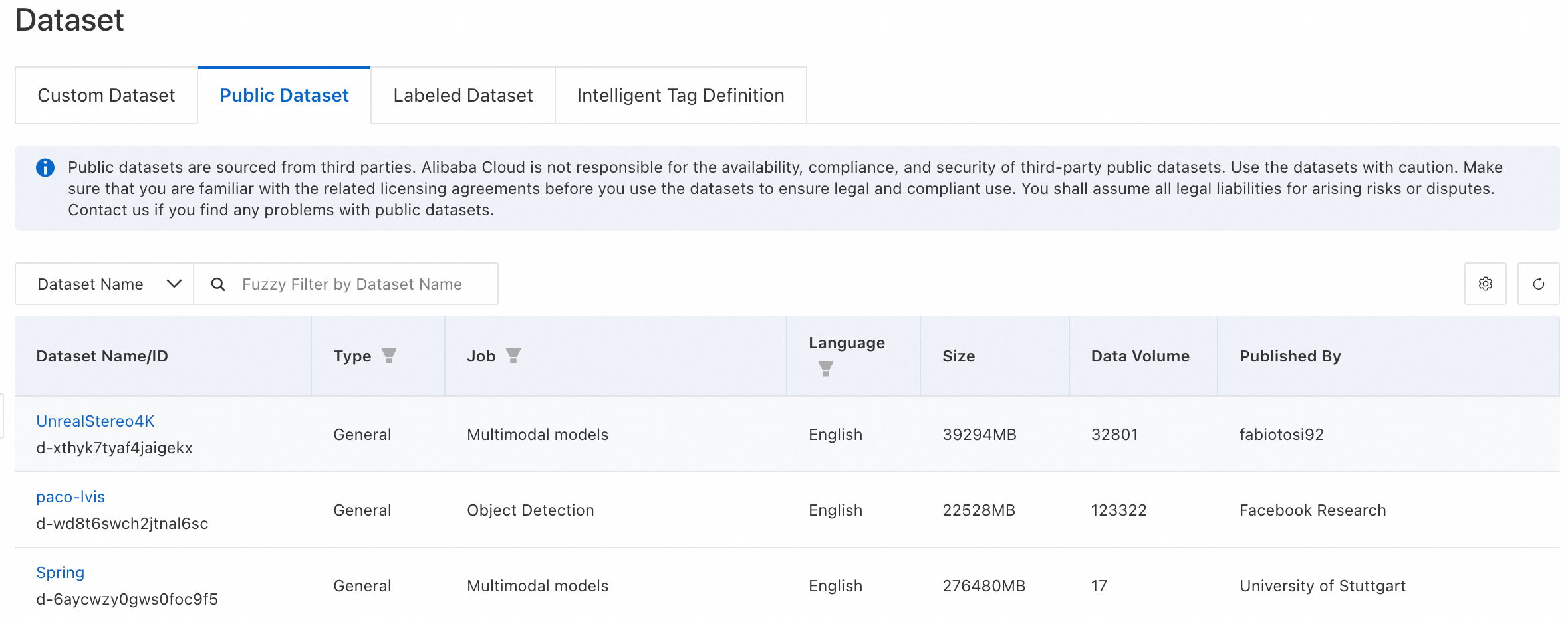
View public datasets
The system provides a variety of built-in public datasets, such as MMLU, CMMLU, and GSM8K. On the Public Dataset tab, you can click a dataset name to view its basic information.
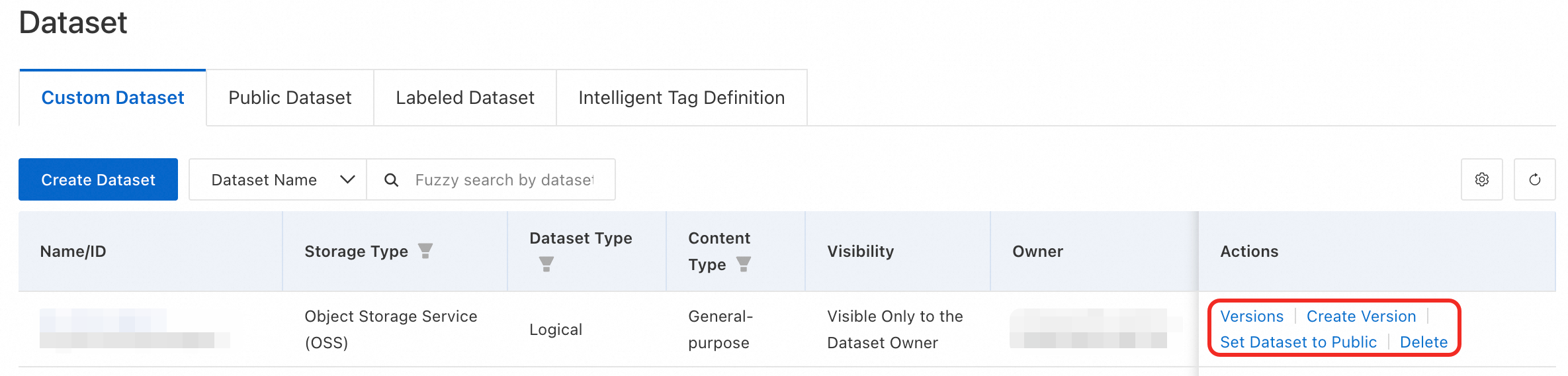
Manage datasets
For custom datasets, you can view the list of versions, create a new version, set a dataset to public, or delete it. For labeled datasets, you can view their data, set them to public, or delete them.
Note:
For a dataset with its Visibility set to Dataset Owner, you can click Set Dataset to Public to share the dataset within the workspace. This allows all workspace members to view the dataset. Once public, a dataset cannot be made private again. Proceed with caution.
If a RAM user receives an access denied error when trying to view dataset data, you must grant permissions to the RAM user.
Deleting a dataset might affect running tasks that depend on it. Important: Deleting a dataset is irreversible. Proceed with caution.