Simple Log Service provides the real-time consumption feature that allows you to consume data in real time by using SDKs. This topic describes the real-time consumption feature, including the concept, benefits, scenarios, billing, and consumers.
Real-time consumption
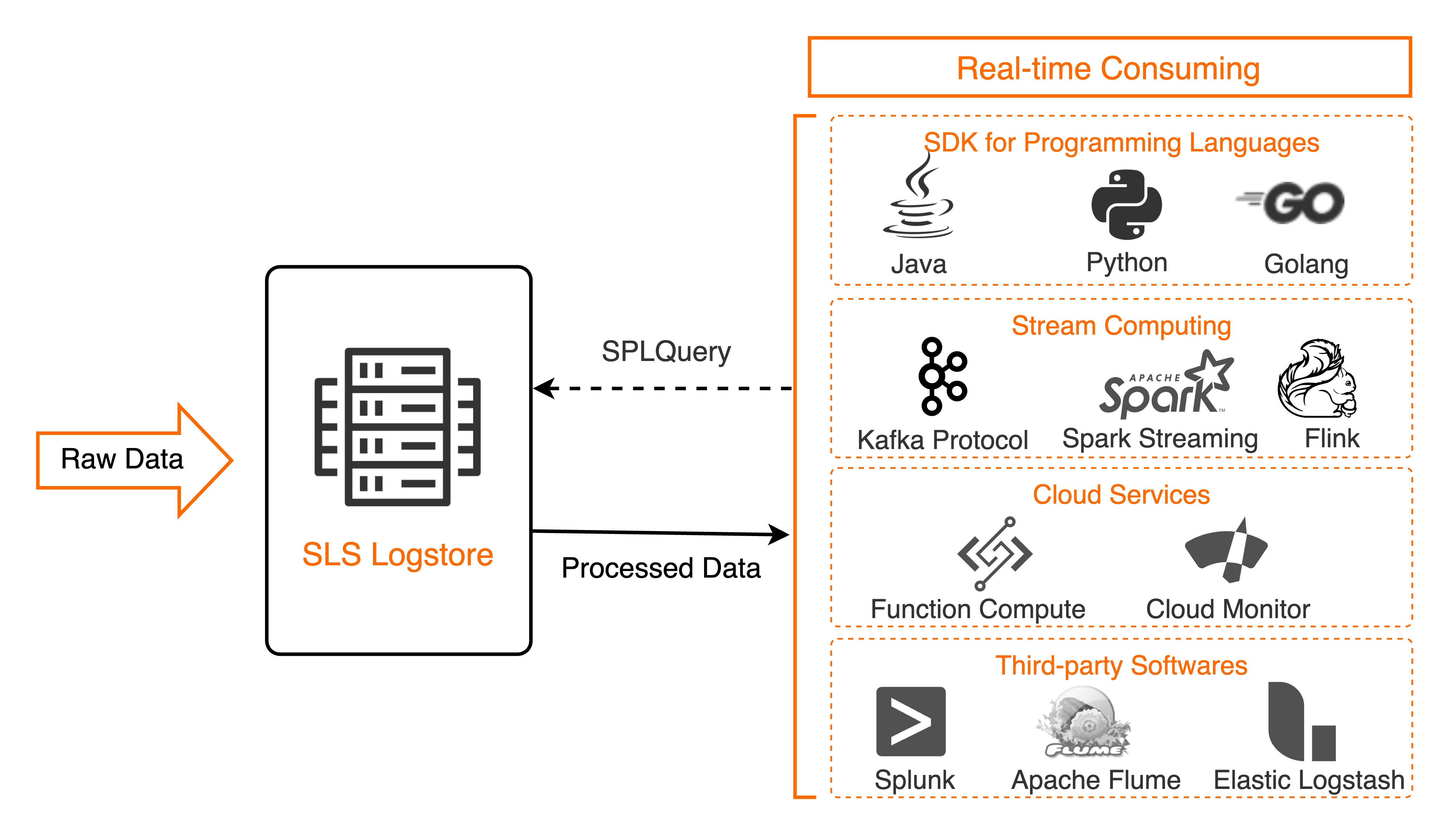
Real-time consumption refers to log data consumption by entities in real time by using SDKs. The entities include third-party software, applications in various programming languages, cloud services, and stream computing frameworks. This feature reads and writes full data based on the first in, first out (FIFO) order. This feature works in a similar manner as Apache Kafka. Real-time consumption allows you to use Simple Log Service Processing Language (SPL) statements to process data. Then, Simple Log Service the processing results. For more information, see SPL overview.
Both the real-time consumption feature and the query and analysis feature are used to read data. For more information about the differences between the two features, see What are the differences between LogHub and LogSearch?
Scenarios
Real-time consumption is suitable for scenarios such as stream computing and real-time computing. Real-time consumption is time-sensitive and implements data consumption within seconds. You can configure a custom data retention period.
Benefits
Real-time consumption provides the following benefits:
Centralized data storage
Simple Log Service centrally stores log data that is collected from different machines. This allows you to consume the collected data in real time by using SDKs.
Data classification and management
Simple Log Service supports data classification and management. This allows different applications and services to consume different types of data in different projects in real time.
Billing
If your Logstores use the pay-by-ingested-data billing mode, you are not charged for real-time consumption. However, if data is pulled over a public Simple Log Service endpoint, you are charged for read traffic over the Internet. The traffic is calculated based on the size of data after compression. For more information, see Billable items of pay-by-ingested-data. For information about how to check the billing mode of a Logstore, see Manage a logstore.
If your Logstores use the pay-by-feature billing mode, you are charged for real-time consumption based on multiple billable items, such as read and write traffic and requests. For more information, see Billable items of pay-by-feature.
Consumers
The following table describes the consumers that are supported by real-time consumption.
Type | Consumer | Description |
Third-party software | Flume | You can use Flume to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Flume to consume log data. |
Logstash | You can use Logstash to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Logstash to consume log data. | |
QRadar | Security information and event management (SIEM) systems, such as IBM QRadar, can consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time over HTTPS or Syslog. For more information, see Ship logs to a SIEM system over HTTPS and Ship logs to a SIEM system over Syslog. | |
Applications in various programming languages | Applications in various programming languages | Applications that are developed in programming languages such as Java, Python, and Go can consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service as consumers or consumer groups. For more information, see Consume log data by using Simple Log Service SDK and Use consumer groups to consume logs. |
Stream computing frameworks | Flink | You can use the stream computing framework Flink to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Flink to consume data. |
Spark | You can use the stream computing framework Spark to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Spark Streaming to consume log data. | |
Cloud services | Function Compute | You can use Function Compute to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Function Compute to consume log data. |
Blink | You can use Realtime Compute for Apache Flink to consume data that is collected by Simple Log Service in real time. For more information, see Use Realtime Compute for Apache Flink to consume log data. |