This topic describes the syntax of conditional expressions. This topic also provides examples on how to use the expressions.
The following table describes the conditional expressions that are supported by Simple Log Service.
Expression | Syntax | Description | Supported in SQL | Supported in SPL |
CASE WHEN condition1 THEN result1 [WHEN condition2 THEN result2] [ELSE result3] END | Classifies data based on specified conditions. | √ | √ | |
IF(condition, result1) | If condition evaluates to true, result1 is returned. Otherwise, null is returned. | √ | √ | |
IF(condition, result1, result2) | If condition evaluates to true, result1 is returned. Otherwise, result2 is returned. | √ | √ | |
COALESCE(expression1, expression2, expression3...) | Returns the first non-null value of multiple expressions. | √ | √ | |
NULLIF(expression1, expression2) | Evaluates whether the values of two expressions are the same. If the values are the same, null is returned. Otherwise, the value of the first expression is returned. | √ | × | |
TRY(expression) | Captures errors that occur during the invocation of an expression and ensures that Simple Log Service can continue to query and analyze data even if errors occur. | √ | √ |
CASE WHEN expression
The CASE WHEN expression classifies data.
Syntax
CASE WHEN condition1 THEN result1
[WHEN condition2 THEN result2]
[ELSE result3]
ENDParameters
Parameter | Description |
condition | The value of this parameter is a conditional expression. |
result1 | The result that is returned. |
Examples
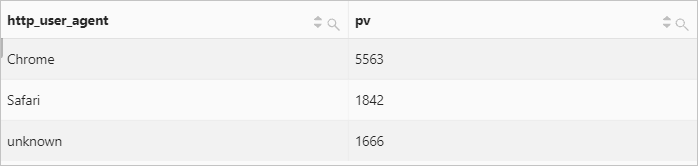
Example 1: Extract browser information from the value of the http_user_agent field. Then, classify the information into Chrome, Safari, and unknown types and calculate the number of page views (PVs) for the three types.
Query statement
* | SELECT CASE WHEN http_user_agent like '%Chrome%' then 'Chrome' WHEN http_user_agent like '%Safari%' then 'Safari' ELSE 'unknown' END AS http_user_agent, count(*) AS pv GROUP BY http_user_agentQuery and analysis results
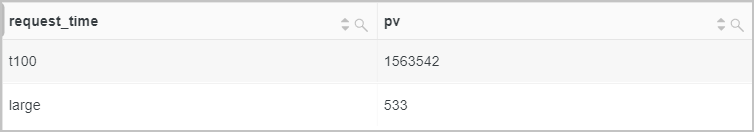
Example 2: Query the distribution of requests that are sent at different points in time.
Query statement
* | SELECT CASE WHEN request_time < 10 then 't10' WHEN request_time < 100 then 't100' WHEN request_time < 1000 then 't1000' WHEN request_time < 10000 then 't10000' ELSE 'large' END AS request_time, count(*) AS pv GROUP BY request_timeQuery and analysis results
IF expression
The IF expression classifies data. This expression works in a similar manner to the CASE WHEN expression.
Syntax
If condition evaluates to true, result1 is returned. Otherwise, null is returned.
IF(condition, result1)If condition evaluates to true, result1 is returned. Otherwise, result2 is returned.
IF(condition, result1, result2)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
condition | The value of this parameter is a conditional expression. |
result | The result that is returned. |
Examples
Calculate the proportion of requests whose status code is 200 to all requests.
Query statement
* | SELECT sum(IF(status = 200, 1, 0)) * 1.0 / count(*) AS status_200_percentagQuery and analysis results

COALESCE expression
The COALESCE expression returns the first non-null value of multiple expressions.
Syntax
COALESCE(expression1, expression2, expression3...)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
expression | The value of this parameter is an expression of an arbitrary type. |
Examples
Calculate the ratio of the expenses of the previous day to the expenses of the same day in the previous month.
Query statement
* | SELECT compare("Expenses of the previous day", 604800) AS diff FROM ( SELECT COALESCE(sum(PretaxAmount), 0) AS "Expenses of the previous day" FROM log )Query and analysis results
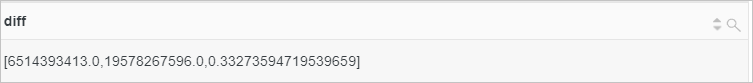
The value 6514393413.0 indicates the expenses of the previous day.
The value 19578267596.0 indicates the expenses of the same day in the previous month.
The value 0.33273594719539659 indicates the ratio of the expenses of the previous day to the expenses of the same day in the previous month.
NULLIF expression
The NULLIF expression evaluates whether the values of two expressions are the same. If the values are the same, null is returned. Otherwise, the value of the first expression is returned.
Syntax
NULLIF(expression1, expression2)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
expression | The value of this parameter is a valid scalar expression. |
Examples
Evaluate whether the values of the client_ip and host fields are the same. If the values are different, the value of the client_ip field is returned.
Query statement
* | SELECT NULLIF(client_ip,host)Query and analysis results

TRY expression
The TRY expression captures errors that occur during the invocation of an expression and ensures that Simple Log Service can continue to query and analyze data even if errors occur.
Syntax
TRY(expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
expression | The value of this parameter is an expression of an arbitrary type. |
Examples
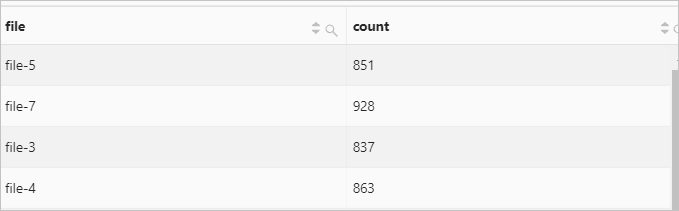
If an error occurs when the regexp_extract expression is invoked, the TRY expression captures the error and Simple Log Service continues to query and analyze data. The query and analysis results are returned.
Query statement
* | SELECT TRY(regexp_extract(request_uri, '.*\/(file.*)', 1)) AS file, count(*) AS count GROUP BY fileQuery and analysis results