Simple Log Service allows you to collect metric data from hosts by using Logtail. The metric data includes CPU, memory, load, disk, and network data. This topic describes how to use Logtail to collect metric data from hosts.
Prerequisites
A project and a Metricstore are created. For more information, see Create a project and Create a Metricstore.
Limits
Windows servers are not supported.
Metric data about GPUs and hardware status cannot be collected.
Only Linux Logtail V0.16.40 and later can collect host metric data. If you have installed an earlier version of Logtail on your server, you must update Logtail to a supported version. For more information, see Install Logtail on a Linux server.
Procedure
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
In the Import Data section, click the Monitoring Data tab. Then, click Host Monitoring Data.
Select the project and Metricstore. Then, click Next.
Create a machine group.
If a machine group is available, click Use Existing Machine Groups.
If no machine groups are available, perform the following steps to create a machine group. In this example, an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance is used.
On the ECS Instances tab, select Manually Select Instances. Then, select the ECS instance that you want to use and click Create.
For more information, see Install Logtail on ECS instances.
ImportantIf you want to collect logs from an ECS instance that belongs to a different Alibaba Cloud account than Simple Log Service, a server in a data center, or a server of a third-party cloud service provider, you must manually install Logtail. For more information, see Install Logtail on a Linux server. After you manually install Logtail, you must configure a user identifier for the server. For more information, see Configure a user identifier.
After Logtail is installed, click Complete Installation.
In the Create Machine Group step, configure the Name parameter and click Next.
Simple Log Service allows you to create IP address-based machine groups and custom identifier-based machine groups. For more information, see Create an IP address-based machine group and Create a custom identifier-based machine group.
Select the new machine group from Source Server Groups and move the machine group to Applied Server Groups. Then, click Next.
ImportantIf you apply a machine group immediately after you create the machine group, the heartbeat status of the machine group may be FAIL. This issue occurs because the machine group is not connected to Simple Log Service. To resolve this issue, you can click Automatic Retry. If the issue persists, see What do I do if no heartbeat connections are detected on Logtail?
In the Configure Data Source step, configure the Configuration Name and Plug-in Configuration parameters. Then, click Next.
inputs is required and is used to configure the data source settings for the Logtail configuration.
ImportantYou can specify only one type of data source in the inputs parameter.
{ "inputs": [ { "detail": { "IntervalMs": 30000 }, "type": "metric_system_v2" } ] }Parameter
Type
Required
Description
type
string
Yes
The type of the data source. Set the value to metric_system_v2.
IntervalMs
int
Yes
The interval between two consecutive requests. Unit: milliseconds. The value must be greater than or equal to 5000. We recommend that you set the value to 30000.
What to do next
Query and analysis
After metric data is collected, you can query and analyze the data on the query and analysis page of the Metricstore. For more information, see Query and analyze metric data.
For more information about host metrics, see Metrics.
Visualization on Simple Log Service
Simple Log Service automatically creates a host monitoring dashboard in the project. In the dashboard, you can view query and analysis results, configure alerts, and perform other operations.
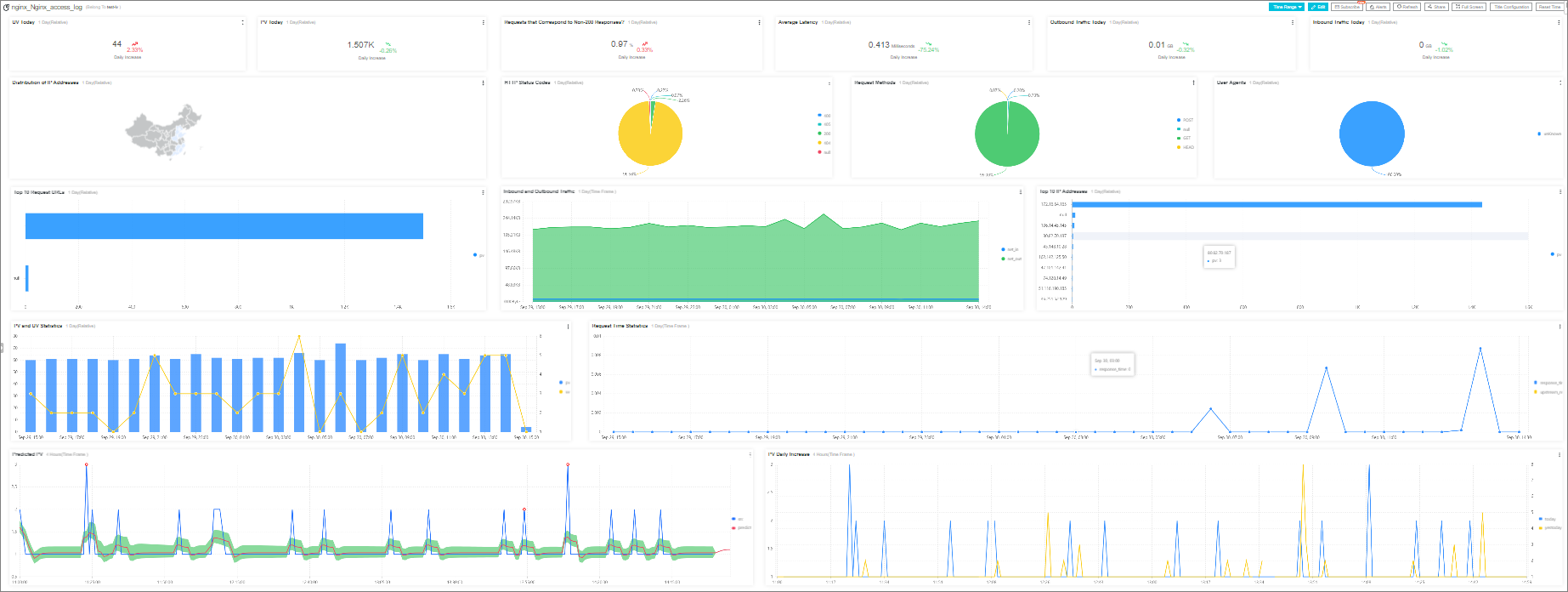
Visualization on Grafana
Simple Log Service provides a Grafana dashboard template for host metric data. You can view query and analysis results on a Grafana dashboard. For more information, see Use Prometheus to collect Kubernetes metric data. For more information about the Grafana dashboard template, see 1 Host metric monitoring of Simple Log Service v2020.08.08.
Metrics
The following tables describe metrics, including the metrics that are related to CPUs, memory, loads, disks, and networks.
CPU-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
cpu_count
The number of CPU cores.
N/A
2.0
cpu_util
The CPU utilization. The CPU utilization equals one minus the sum of the idle, wait, and steal counters.
Percent (%)
7.68
cpu_guest_util
The guest counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends on processes of the normal priority.
Percent (%)
0.0
cpu_guestnice_util
The guest_nice counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends on processes of the niced priority.
Percent (%)
0.0
cpu_irq_util
The irq counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends serving hardware interrupt requests.
Percent (%)
0.0
cpu_nice_util
The nice counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends on user-mode processes of the niced priority.
Percent (%)
0.0
cpu_softirq_util
The softirq counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends serving software interrupt requests.
Percent (%)
0.06
cpu_steal_util
The steal counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends running other operating systems in a virtual environment.
Percent (%)
0.0
cpu_sys_util
The system counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends on kernel-mode processes.
Percent (%)
2.77
cpu_user_util
The user counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends on user-mode processes of the normal priority.
Percent (%)
4.84
cpu_wait_util
The iowait counter of Linux. This counter indicates the percentage of the time that the CPU spends idling when outstanding disk I/O requests exist.
Percent (%)
0.11
Memory-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
mem_util
The memory usage.
Percent (%)
51.03
mem_cache
The amount of the memory that is allocated but unused.
Byte
3566386668.0
mem_free
The amount of the unused memory.
Byte
177350084.0
mem_available
The amount of the available memory.
Byte
3699885553.0
mem_used
The amount of the used memory.
Byte
4041510463.0
mem_swap_util
The swap usage.
Percent (%)
0.0
mem_total
The memory size.
Byte
7919128576.0
Disk-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
disk_rbps
The amount of data that is read from the disk per second.
Byte/s
8376.81
disk_wbps
The amount of data that is written to the disk per second.
Byte/s
247633.58
disk_riops
The number of read operations completed on the disk per second.
Read/s
0.22
disk_wiops
The number of write operations completed on the disk per second.
Write/s
43.39
disk_rlatency
The average read latency.
ms
2.83
disk_wlatency
The average write latency.
ms
2.15
disk_util
The I/O usage of the disk.
Percent (%)
0.27
disk_space_usage
The percentage of the used disk space.
Percent (%)
9.12
disk_inode_usage
The percentage of the used index node (inode) space.
Percent (%)
1.18
disk_space_used
The amount of the used disk space.
Byte
11068512238.59
disk_space_total
The total amount of the disk space.
Byte
126692061184.0
disk_inode_total
The total number of inodes.
N/A
7864320.0
disk_inode_used
The number of used inodes.
N/A
93054.78
Network-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
net_drop_util
The percentage of discarded packets to all packets.
Percent (%)
0.0
net_err_util
The percentage of error packets to all packets.
Percent (%)
0.0
net_in
The amount of data that is received per second.
Byte/s
8440.91
net_in_pkt
The number of packets that are received per second.
Packet/s
40.83
net_out
The amount of data that is sent per second.
Byte/s
12446.53
net_out_pkt
The number of packets that are sent per second.
Packet/s
39.95
TCP-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
protocol_tcp_established
The number of established connections.
N/A
205.0
protocol_tcp_insegs
The number of received packets.
N/A
4654.0
protocol_tcp_outsegs
The number of sent packets.
N/A
4870.0
protocol_tcp_retran_segs
The number of re-sent packets.
N/A
0.0
protocol_tcp_retran_util
The percentage of re-sent packets to sent packets.
Percent (%)
0.0
System-related metrics
Metric
Description
Unit
Example value
system_boot_time
The system startup time.
s
1578461935.0
system_load1
The average system load every minute.
N/A
0.58
system_load5
The average system load every 5 minutes.
N/A
0.68
system_load15
The average system load every 15 minutes.
N/A
0.60