This topic describes the syntax of array functions and operators. This topic also provides examples on how to use the functions and operators.
The following table describes the array functions and operators that are supported by Simple Log Service.
Function or operator | Syntax | Description | Supported in SQL | Supported in SPL |
[x] | Returns the element whose index is x in an array. This operator is equivalent to the element_at function. | √ | × | |
array_agg(x) | Returns an array that consists of all values of the x field. | √ | × | |
array_distinct(x) | Removes duplicate elements from an array. | √ | √ | |
array_except(x, y) | Calculates the difference of two arrays. | √ | √ | |
array_intersect(x, y) | Calculates the intersection of two arrays. | √ | √ | |
array_join(x, delimiter) | Concatenates the elements of an array into a string by using a specified delimiter. If the array contains a null element, the null element is ignored. Important The array_join function can return up to 1 KB of data. If the size of the data to return exceeds 1 KB, the data is truncated. | √ | √ | |
array_join(x, delimiter, null_replacement) | Concatenates the elements of an array into a string by using a specified delimiter. If the array contains a null element, the null element is replaced with the value of the null_replacement parameter. Important The array_join function can return up to 1 KB of data. If the size of the data to return exceeds 1 KB, the data is truncated. | √ | √ | |
array_max(x) | Returns the maximum value in an array. | √ | √ | |
array_min(x) | Returns the minimum value in an array. | √ | √ | |
array_position(x, element) | Returns the index of a specified element in an array. The index starts from 1. If the specified element does not exist, the function returns 0. | √ | √ | |
array_remove(x, element) | Removes a specified element from an array. | √ | √ | |
array_sort(x) | Sorts the elements in an array in ascending order. If the array contains a null element, the null element is placed at the end. | √ | √ | |
array_transpose(x) | Transposes a matrix and returns a new two-dimensional array that consists of the elements in the matrix. The elements are located by using the same indexes. | √ | × | |
array_union(x, y) | Calculates the union of two arrays. | √ | × | |
cardinality(x) | Counts the number of elements in an array. | √ | √ | |
concat(x, y…) | Concatenates multiple arrays into one array. | √ | × | |
contains(x, element) | Checks whether an array contains a specified element. If the array contains the specified element, the function returns true. | √ | × | |
element_at(x, y) | Returns the element whose index is y in an array. | √ | × | |
filter(x, lambda_expression) | Filters elements in an array based on a lambda expression and returns elements that match the lambda expression. | √ | √ | |
flatten(x) | Transforms a two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array. | √ | × | |
reduce(x, lambda_expression) | Returns the sum of the elements in an array based on a lambda expression. | √ | √ | |
reverse(x) | Reverses the elements in an array. | √ | √ | |
sequence(x, y) | Returns an array of elements within a specified range. The elements are consecutive and incremental. The incremental step is 1, which is the default value. | √ | √ | |
sequence(x, y, step) | Returns an array of elements within a specified range. The elements are consecutive and incremental. The incremental step is a custom value. | √ | √ | |
shuffle(x) | Shuffles the elements in an array. | √ | √ | |
slice(x, start, length) | Returns a subset of an array. | √ | √ | |
transform(x, lambda_expression) | Transforms each element in an array by using a lambda expression. | √ | √ | |
zip(x, y...) | Merges multiple arrays into a two-dimensional array. Elements that have the same index in the input arrays form a new array in the two-dimensional array. | √ | √ | |
zip_with(x, y, lambda_expression) | Merges two arrays into one array by using a lambda expression. | √ | × |
Subscript operator
The subscript operator returns the element whose index is x in an array. This operator is equivalent to the element_at function.
Syntax
[x]Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is the index of an element in the array. The index starts from 1. The value of this parameter is of the bigint type. |
Return value type
The data type of the specified element.
Examples
Return the first element in the value of the number field.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
* | SELECT cast(json_parse(number) as array(bigint)) [1]Query and analysis results

array_agg function
The array_agg function returns an array that consists of all values of the x field.
Syntax
array_agg (x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of an arbitrary data type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Return an array that consists of all values of the status field.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_agg(status) AS arrayQuery and analysis results

array_distinct function
The array_distinct function removes duplicate elements from an array.
Syntax
array_distinct(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Remove duplicate elements from the value of the number field.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
*| SELECT array_distinct(cast(json_parse(number) as array(bigint)))Query and analysis results

array_except function
The array_except function calculates the difference of two arrays.
Syntax
array_except(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Calculate the difference of the [1,2,3,4,5] and [1,3,5,7] arrays.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_except(array[1,2,3,4,5],array[1,3,5,7])Query and analysis results

array_intersect function
The array_intersect function calculates the intersection of two arrays.
Syntax
array_intersect(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Calculate the intersection of the [1,2,3,4,5] and [1,3,5,7] arrays.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_intersect(array[1,2,3,4,5],array[1,3,5,7])Query and analysis results

array_join function
The array_join function concatenates the elements of an array into a string by using a specified delimiter.
Syntax
If you use the following syntax, the function concatenates the elements of an array into a string by using a specified delimiter. If the array contains a null element, the null element is ignored.
array_join(x, delimiter)If you use the following syntax, the function concatenates the elements of an array into a string by using a specified delimiter. If the array contains a null element, the null element is replaced with the value of the null_replacement parameter.
array_join(x, delimiter,null_replacement)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of an arbitrary array type. |
delimiter | The value of this parameter is the delimiter that is used to concatenate elements. You can specify a string for this parameter. |
null_replacement | The value of this parameter is the string that is used to replace a null element. |
Return value type
The varchar type.
Examples
Concatenate the elements of the [null, 'Log','Service'] array into a string by using spaces and replace the null element with Alicloud.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_join(array[null,'Log','Service'],' ','Alicloud')Query and analysis results

array_max function
The array_max function returns the maximum value in an array.
Syntax
array_max(x) Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. Important If an array contains a null element, the function returns null. |
Return value type
Same as the data type of the elements in the parameter value.
Examples
Return the maximum value in an array.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
*| SELECT array_max(try_cast(json_parse(number) as array(bigint))) AS max_numberQuery and analysis results

array_min function
The array_min function returns the minimum value in an array.
Syntax
array_min(x) Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. Important If an array contains a null element, the function returns null. |
Return value type
Same as the data type of the elements in the parameter value.
Examples
Return the minimum value in an array.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
*| SELECT array_min(try_cast(json_parse(number) as array(bigint))) AS min_numberQuery and analysis results

array_position function
The array_position function returns the index of a specified element in an array. The index starts from 1. If the specified element does not exist, the function returns 0.
Syntax
array_position(x, element)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
element | The value of this parameter is an element in the array. Note If the element is null, the function returns null. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Return the index of 45 in the [49,45,47] array.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_position(array[49,45,47],45)Query and analysis results

array_remove function
The array_remove function removes a specified element from an array.
Syntax
array_remove(x, element)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
element | The value of this parameter is an element in the array. Note If the element is null, the function returns null. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Remove 45 from the [49,45,47] array.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_remove(array[49,45,47],45)Query and analysis results

array_sort function
The array_sort function sorts the elements in an array in ascending order. If the array contains a null element, the null element is placed at the end.
Syntax
array_sort(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Sort the elements in the ['b', 'd', null, 'c', 'a'] array in ascending order.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_sort(array['b','d',null,'c','a'])Query and analysis results

array_transpose function
The array_transpose function transposes a matrix and returns a new two-dimensional array that consists of the elements in the matrix. The elements are located by using the same indexes.
Syntax
array_transpose(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array(double) type. |
Return value type
The array(double) type.
Examples
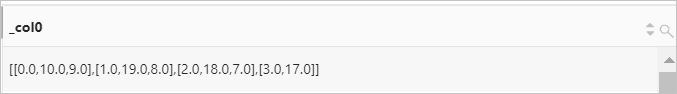
Create a two-dimensional array from elements that are located by using the same indexes in a different two-dimensional array. For example, in the [0,1,2,3], [10,19,18,17], and [9,8,7] arrays, 0, 10, and 9 are located by using the index 1. This way, the new array [0.0,10.0,9.0] is formed.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_transpose(array[array[0,1,2,3],array[10,19,18,17],array[9,8,7]])Query and analysis results
array_union function
The array_union function calculates the union of two arrays.
Syntax
array_union(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Calculate the union of the [1,2,3,4,5] and [1,3,5,7] arrays.
Query statement
* | SELECT array_union(array[1,2,3,4,5],array[1,3,5,7])Query and analysis results

cardinality function
The cardinality function counts the number of elements in an array.
Syntax
cardinality(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Count the number of elements in the value of the number field.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
*| SELECT cardinality(cast(json_parse(number) as array(bigint)))Query and analysis results

concat function
The concat function concatenates multiple arrays into one array.
Syntax
concat(x, y…)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Concatenate the ['red','blue'] and ['yellow','green'] arrays into one array.
Query statement
* | SELECT concat(array['red','blue'],array['yellow','green'])Query and analysis results

contains function
The contains function checks whether an array contains a specified element. If the array contains the specified element, the function returns true.
Syntax
contains(x, element)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
element | The value of this parameter is an element in an array. |
Return value type
The Boolean type.
Examples
Check whether the value of the region field contains cn-beijing.
Sample field
region:["cn-hangzhou","cn-shanghai","cn-beijing"]Query statement
*| SELECT contains(cast(json_parse(region) as array(varchar)),'cn-beijing')Query and analysis results

element_at function
The element_at function returns the element whose index is y in an array.
Syntax
element_at(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is the index of an element in the array. The index starts from 1. The value of this parameter is of the bigint type. |
Return value type
An arbitrary data type.
Examples
Return the second element in the value of the number field.
Sample field
number:[49,50,45,47,50]Query statement
* | SELECT element_at(cast(json_parse(number) AS array(varchar)), 2)Query and analysis results

filter function
The filter function filters elements in an array based on a lambda expression and returns elements that match the lambda expression.
Syntax
filter(x, lambda_expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
lambda_expression | The value of this parameter is a lambda expression. For more information, see Lambda expressions. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Return the elements that are greater than 0 in the [5,-6,null,7] array by using the x -> x > 0 lambda expression.
Query statement
* | SELECT filter(array[5,-6,null,7],x -> x > 0)Query and analysis results

flatten function
The flatten function transforms a two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array.
Syntax
flatten(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Transform the two-dimensional array [array[1,2,3,4],array[5,2,2,4] into a one-dimensional array.
Query statement
* | SELECT flatten(array[array[1,2,3,4],array[5,2,2,4]])Query and analysis results

reduce function
The reduce function returns the sum of the elements in an array based on a lambda expression.
Syntax
reduce(x, lambda_expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
lambda_expression | The value of this parameter is a combination of an initial value, the lambda expression that you want to use, and the processing method of the lambda expression result. For more information, see Lambda expressions. |
Return value type
The bigint type.
Examples
Return the sum of the elements in the [5,20,50] array.
Query statement
* | SELECT reduce(array[5,20,50],0,(s, x) -> s + x, s -> s)Query and analysis results

reverse function
The reverse function reverses the elements in an array.
Syntax
reverse(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Reverse the elements in the [1,2,3,4,5] array.
Query statement
* | SELECT reverse(array[1,2,3,4,5])Query and analysis results

sequence function
The sequence function returns an array of elements within a specified range. The elements are consecutive and incremental.
Syntax
If you use the following syntax, you must use the default incremental step, which is 1.
sequence(x, y)If you use the following syntax, you can specify a custom incremental step.
sequence(x, y, step)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the bigint or timestamp type. UNIX timestamps and date and time expressions are supported. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the bigint or timestamp type. UNIX timestamps and date and time expressions are supported. |
step | The value of this parameter is an incremental step. If the values of the x and y parameters are date and time expressions, the value of the step parameter is in one of the following formats:
|
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Example 1: Return the even numbers from 0 to 10.
Query statement
* | SELECT sequence(0,10,2)Query and analysis results

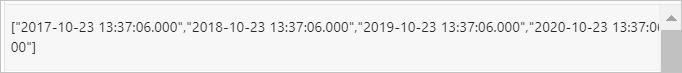
Example 2: Return the dates from October 23, 2017 to August 12, 2021 at the incremental step of 1 year.
Query statement
ww* | SELECT sequence(from_unixtime(1508737026),from_unixtime(1628734085),interval '1' year to month )Query and analysis results
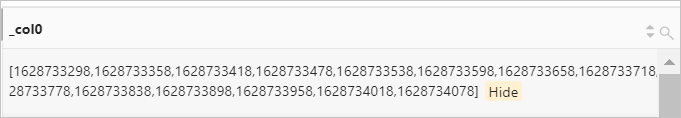
Example 3: Return the UNIX timestamps from 1628733298 to 1628734085 at the incremental step of 60 seconds.
Query statement
* | SELECT sequence(1628733298,1628734085,60)Query and analysis results
shuffle function
The shuffle function shuffles the elements in an array.
Syntax
shuffle(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
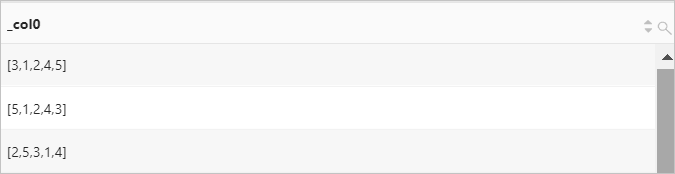
Examples
Shuffle the elements in the [1,2,3,4,5] array.
Query statement
*| SELECT shuffle(array[1,2,3,4,5])Query and analysis results
slice function
The slice function returns a subset of an array.
Syntax
slice(x, start, length)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
start | The value of this parameter is the index at which Simple Log Service starts to extract elements.
|
length | The value of this parameter is the number of elements in the subset that you want to obtain. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Return a subset of the [1,2,4,5,6,7,7] array from the third element. The subset consists of two elements.
Query statement
* | SELECT slice(array[1,2,4,5,6,7,7],3,2)Query and analysis results

transform function
The transform function transforms each element in an array by using a lambda expression.
Syntax
transform(x, lambda_expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
lambda_expression | The value of this parameter is a lambda expression. For more information, see Lambda expressions. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Add 1 to each element in the [5,6] array and return a new array.
Query statement
* | SELECT transform(array[5,6],x -> x + 1)Query and analysis results

zip function
The zip function merges multiple arrays into a two-dimensional array. Elements that have the same index in the input arrays form a new array in the two-dimensional array.
Syntax
zip(x, y...) Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Merge the [1, 2,3], ['1b', null, '3b'], and [1, 2,3] arrays into a two-dimensional array.
Query statement
* | SELECT zip(array[1,2,3], array['1b',null,'3b'],array[1,2,3])Query and analysis results

zip_with function
The zip_with function merges two arrays into one array by using a lambda expression.
Syntax
zip_with(x, y, lambda_expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
y | The value of this parameter is of the array type. |
lambda_expression | The value of this parameter is a lambda expression. For more information, see Lambda expressions. |
Return value type
The array type.
Examples
Use the (x, y) -> x + y lambda expression to add the elements in the [1, 2] and [3, 4] arrays and return a new array.
Query statement
SELECT zip_with(array[1,2], array[3,4],(x,y) -> x + y)Query and analysis results
