When you connect a device to IoT Platform by using a Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) gateway, you can enable two-way verification between the device and IoT Platform to verify the identity of the device. This topic describes how to connect a device to IoT Platform by using X.509 certificate-based two-way verification. In this example, an MQTT gateway whose Authentication Type parameter is set to One-party Verification and Enable X.509 certificate-based Device Verification parameter is set to Yes is created and sample Java code is provided.
Prerequisites
An Exclusive Enterprise Edition instance is purchased. In this example, an Exclusive Enterprise Edition instance is purchased in the China (Shanghai) region. For more information, see Purchase an Enterprise Edition instance.
Certificates that are required to perform two-way verification are prepared.
In this example, the following certificate files are used:
root-ca.crtroot certificate file,server.keyserver-side private key file,server.crtserver-side certificate file,client.keydevice-side private key file, andclient.crtdevice certificate file.
Background information
IoT Platform provides MQTT gateways and allows you to use X.509 certificates and custom certificates to verify and connect devices to IoT Platform for communication. This helps IoT Platform meet the requirements of various IoT business scenarios.
For more information about verification and communication between MQTT gateways and devices, see MQTT gateways.
Preparations
In this example, Java is used to develop a program. A Java development environment that meets the following requirements is prepared:
Operating system: Windows 10 (64-bit)
Java Development Kit (JDK): JDK 8
Integrated development environment (IDE): IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition
Create a gateway and add a device
Create an MQTT gateway: In the Add Gateway dialog box, set the Server Certificate parameter to the content of the
server.crtfile, the Private Key of Server Certificate parameter to the content of theserver.keyfile, and the Device Root Certificate parameter to the content of theroot-ca.crtfile. Then, configure other parameters, as shown in the following figure.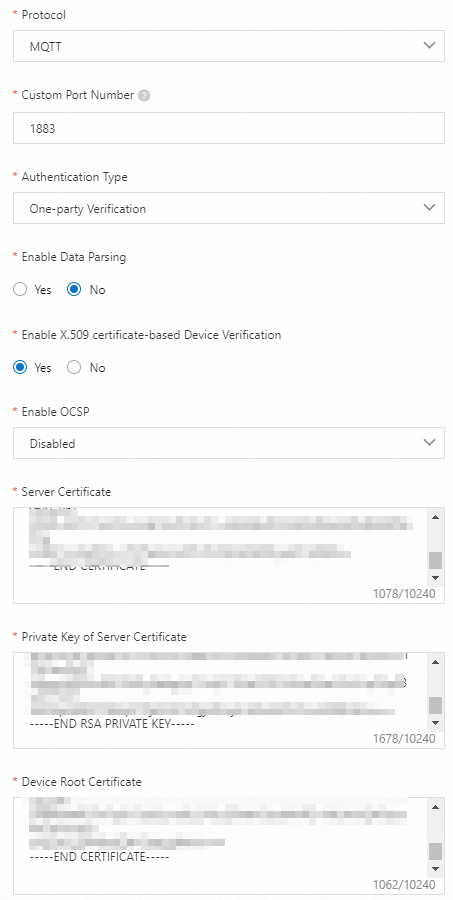
On the Gateway page, copy the URL in the Gateway URL column of the gateway.

Add a device to the MQTT gateway product. In this example, a device whose MQTT Username parameter is set to
device01and whose MQTT Password parameter is set tohello456is added.
Develop a device program
Download the aiot-java-dual-auth-demo code package and decompress the code package.
Open IntelliJ IDEA and import the
aiot-java-demosample project from the code package.Add Maven dependencies to the
pom.xmlfile. In this example, the following dependencies are used:<dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.paho</groupId> <artifactId>org.eclipse.paho.mqttv5.client</artifactId> <version>1.2.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.paho</groupId> <artifactId>org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3</artifactId> <version>1.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.bouncycastle</groupId> <artifactId>bcpkix-jdk15on</artifactId> <version>1.47</version> </dependency>The
/src/main/java/com/aliyun/iotdirectory of the project contains the following program files that are required to perform two-way verification:SslUtil.java: reads device certificates.Mqtt5TlsApp.java: connects devices to IoT Platform.
In the
pom.xmlfile of the project, click Load Maven Changes to download dependency packages.In the
/src/maindirectory of the project, create a folder namedresources.In the
/src/main/resourcesdirectory of the project, import the following certificate files:root-ca.crtthat contains the root certificate,client.keythat contains the device-side private key, andclient.crtthat contains the device certificate.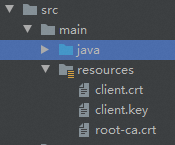
In the
/src/main/java/com/aliyun/iot/SslUtil.javafile of the project, modify the key that is used to generate a certificate.ImportantThe value
123456that is specified for theclientKs.setKeyEntry()function indicates a key that is used to generate a certificate. Change the value based on your business scenario....... // Replace 123456 with an actual key value. clientKs.setKeyEntry("private-key", key.getPrivate(), "123456".toCharArray(), new java.security.cert.Certificate[]{clientCertificate}); ......Open the
/src/main/java/com/aliyun/iot/Mqtt5TlsApp.javafile of the project and modify the device connection parameters....... // MQTT connection parameters String userName = "device01"; String password = "hello456"; String clientId = "test01_client1"; // The path in which the root directory is stored. String caCertPath = "src/main/resources/root-ca.crt"; // The path in which the device certificate is stored. String clientCertPath= "src/main/resources/client.crt"; // The path in which the device-side private key is stored. String clientKeyPath="src/main/resources/client.key"; // The URL of the MQTT gateway. String broker = "ssl://iot-*******.igw.iothub.aliyuncs.com:1883"; ......Parameter
Example
Description
userName
device01The value of the MQTT Username parameter of the added device.
password
hello456The value of the MQTT Password parameter of the added device.
clientId
test01_client1(Optional) The ID of the client. The client ID must be 1 to 64 characters in length. We recommend that you use the MAC address or serial number (SN) of the device as the client ID.
caCertPath
src/main/resources/root-ca.crtThe project path in which the
root-ca.crtdevice root certificate file is stored.clientCertPath
src/main/resources/client.crtThe project path in which the
client.crtdevice certificate file is stored.clientKeyPath
src/main/resources/client.keyThe project path where the
client.keydevice-side private key file is stored.broker
ssl://iot-*******.igw.iothub.aliyuncs.com:1883The endpoint of the MQTT gateway to which you want to connect the device. Format:
ssl://${Gateway endpoint}:${Port number}.Replace
${Gateway endpoint}and${Port number}with the endpoint of the custom port number of the gateway URL that you saved.Run the
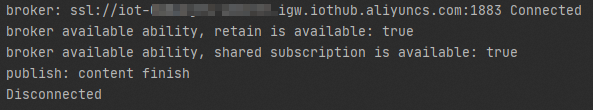
Mqtt5TlsApp.javaprogram file to perform two-way verification between the device and IoT Platform.NoteIn this example,
Thread.sleep(20000);is added to theMqtt5TlsApp.javafile. The Thread.sleep(20000); code terminates the Mqtt5TlsApp.java program and disconnects the device from IoT Platform 20 seconds after the program runs. In actual scenarios, you can write custom code to connect or disconnect devices.The following figure shows the result. After the device passes verification, the device is connected to IoT Platform.