This topic describes how to configure rule-based custom DNS resolution.
Prerequisites
You have added the domain name that you want to use for custom DNS resolution. For more information, see Add a domain name.
Procedure
Log on to the EMAS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resolution Management > Custom Resolution.
Click Add Custom Resolution, and set Policy Type to Rule-based Policy.
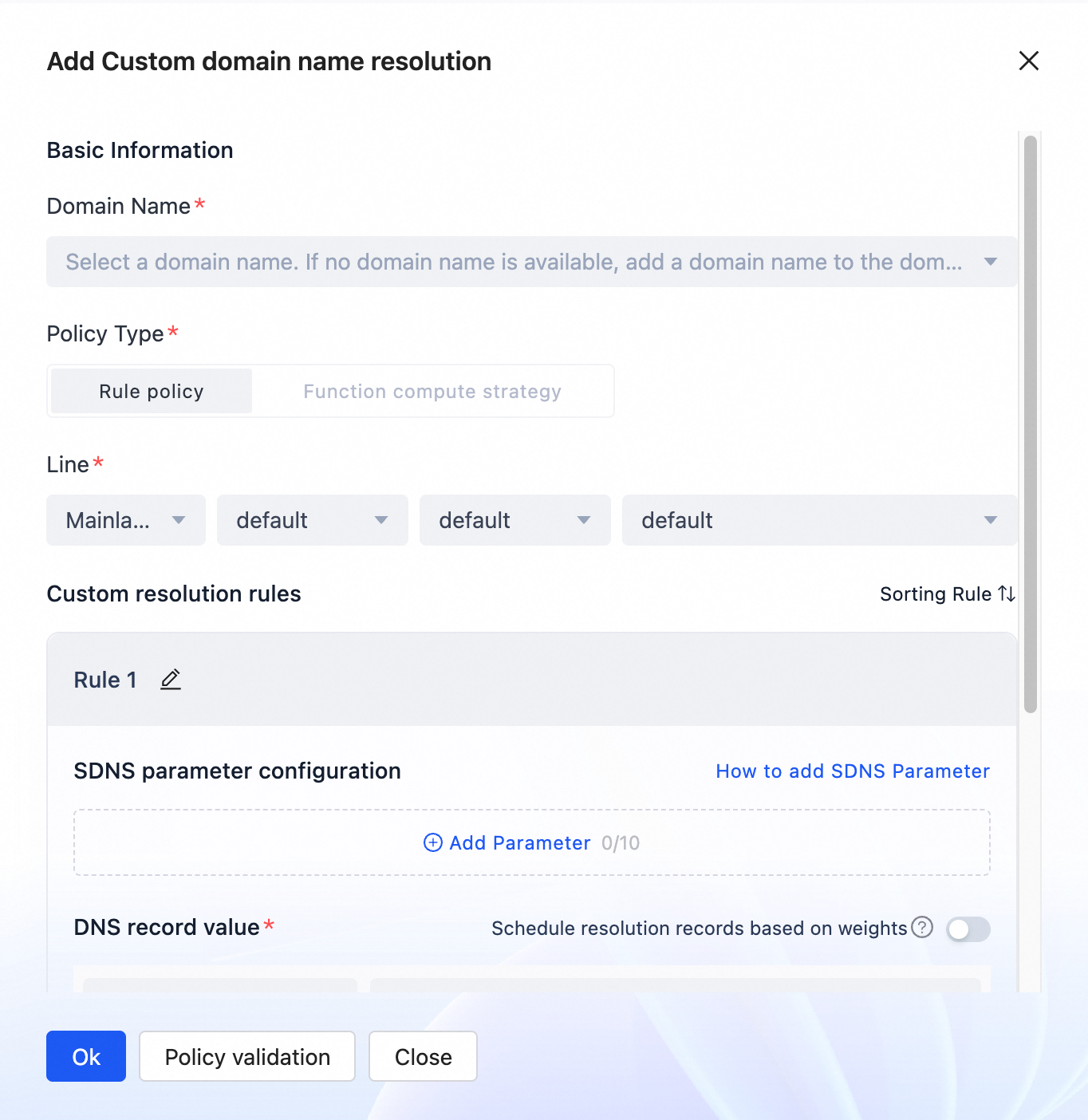
Configure the following parameters:
Basic information
Parameter
Description
Domain Name
The domain name for which you want to configure custom DNS resolution, such as www.aliyun.com.
NoteThe domain names in the drop-down list are sourced from the domain names that you have added in Domain Name Management. If the domain name that you want to use is not in the drop-down list, add it in Domain Name Management and then add a custom DNS record for it.
To add a custom DNS record for a subdomain of a wildcard domain name, such as a.aliyun.com for *.aliyun.com, you must first add a.aliyun.com to the domain name list, and then add a custom DNS record for it.
The domain name you want might not appear in the drop-down list for the following reasons:
The domain name is not in the domain name list. Add the domain name in Domain Name Management.
The domain name is a subdomain of a wildcard domain name. Add the subdomain to the domain name list.
A custom DNS record already exists for the domain name. Manage the domain name in the custom DNS record list.
Line
Configure lines based on carrier and location.
Lines in the Chinese mainland: Configure lines by Carrier > Region > Province.
Carrier: Specify a carrier, such as China Telecom. If you set Carrier to Default, the line covers all carriers.
Region: Regions are divided geographically, such as Northeast, North China, and East China. Provinces belong to their corresponding regions. If you set Region to Default, the line covers all regions.
Province: Specify a province, such as Beijing or Hebei. If you set Province to Default, the line covers all provinces.
Lines outside China: This takes effect when the location is set to Outside China. Configure lines by Continent > Country or Area.
You can select a continent, such as Asia, Europe, or South America. You can also select a specific country or area within a continent, such as Japan or the United Kingdom.
If you set Continent, Country, or Area to Default, the line covers all areas within the selected scope.
NoteFor users in the same location under the same domain name, the line priority is: Carrier > Geographic Location > Default. For example, the priority order is: China Telecom-North China-Beijing > China Telecom-North China-Default > Default-North China-Beijing > Default-Default-Default.
For example, if two rule-based policies exist for the same domain name with lines set to China Telecom-North China-Beijing and China Telecom-North China-Default, users of China Telecom in Beijing use the rule-based policy for the China Telecom-North China-Beijing line.
Custom parsing rules
A rule-based policy can contain up to 10 custom DNS resolution rules.
Parameter
Description
Rule Name
The name of the rule. The name can describe the purpose of the rule, such as scheduling by SDK version.
Rule Sorting
You can adjust the order of the rules. The rules are matched sequentially from top to bottom. The order determines which rule is hit first. After you adjust the order, the rules are matched in the new order.
SDNS Parameter Settings
Matches the SDNS parameters carried in the resolution request from the client to determine whether the rule is hit. If a match is found, the DNS record value in the rule is returned. For more information about the matching logic, see Matching logic for rule-based policies.
Parameter Name: The name of the SDNS parameter. The name must be 2 to 64 characters in length.
Parameter Value: The value of the SDNS parameter. The value must be 1 to 64 characters in length.
NoteA rule can contain up to 10 SDNS parameters.
You can add SDNS parameters to the resolution API. For more information, see Pass custom resolution parameters from a client .
DNS Record Value
A collection of return values for custom DNS resolution. Each record value represents a DNS record in the record set. This parameter is required.
Record Type: The type of the returned DNS record value. A and AAAA records are supported.
Record Value: The returned record value.
You can add multiple record values. If weighting is disabled, the added record values are merged and returned together.
You can also schedule based on weight. To do this, enable scheduling by weight. After you enable weighting, you can set a weight for each record value. The weight can range from 1 to 100. A load balancing algorithm returns a suitable record value based on the weights.
NoteA rule can contain up to 10 record values.
TTL
Required. The validity period of the custom DNS record. A shorter validity period causes the DNS record cache in the HTTPDNS SDK to expire faster. This increases the frequency at which the HTTPDNS SDK requests new DNS records.
Policy validation
On the page for adding a rule-based policy, you can validate the rules as shown in the following figure:
In the policy validation window, enter the relevant parameters to verify that the policy works as expected.

Matching logic for rule-based policies
The following figure shows the resolution flow for a rule-based policy. Parameters in the request are used to match a specific rule. The rules are matched sequentially from top to bottom. If a rule is hit, the matching process stops and the result for that rule is returned. If no rules are hit, the result from the authoritative server is returned.

The matching logic for parameters in a single rule is as follows:
A match occurs if the request parameters fully match the parameters configured in the rule. A full match means that the request parameters must contain all parameters that are configured for the rule.
If no parameters are configured in the rule, the rule is considered a match.
Parameters within a single rule are evaluated with a logical AND.
The following examples describe the matching logic:
Assume that the domain name for custom DNS resolution is www.example.com
Example 1
Rule A parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
Rule B parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Rule C parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
Request parameters:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Matching result:
In Example 1, the request parameters fully match Rule B. The HTTPDNS server returns the record value from Rule B.
Example 2
Rule A parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
bizType | app |
Rule B parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Rule C parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
Request parameters:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Matching result:
In Example 2, because the parameters in a rule are evaluated with a logical AND, the request parameters fully match Rule B. The HTTPDNS server returns the record value from Rule B.
Example 3
Rule A parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
bizType | car |
Rule B parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
bizType | car |
region | hangzhou |
Parameter settings for Rule C:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
region | shanghai |
Request parameters
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
bizType | car |
region | hangzhou |
Matching results:
In Example 3, the request parameters match Rule A based on the principles of full match and first-match priority. As a result, the HTTPDNS server returns the record value from Rule A.
Example 4
Rule A parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
Rule B parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
bizType | car |
region | hangzhou |
Rule C parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
region | shanghai |
Request parameters:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Matching result:
In Example 4, based on the principles of full match and first match priority, the request parameters do not hit any rule. The HTTPDNS server returns the query result from the authoritative server.
Example 5
Rule A parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
Rule B has no parameters configured.
Rule C parameter settings:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | Android |
bizType | car |
region | shanghai |
Request parameters:
Parameter name | Parameter value |
osType | iOS |
Matching result:
In Example 5, based on the principles of full match and first match priority, the request parameters match Rule B. The HTTPDNS server returns the record value from Rule B.
What to do next
After you configure rule-based custom DNS resolution, see Overall workflow to complete the subsequent steps.