Why am I seeing 'duplicate key value violates unique constraint' errors or missing data when querying logical partitioned tables in Hologres V4.0.0-4.0.8?
In V4.0, the multi-partition flush optimization for logical partitioned tables has a bug in its cluster index implementation. This bug can cause corrupted indexes within AliORC files (data files of column-oriented tables). This can lead to two main problems:
Missing data: Queries may fail to find existing data because of the incorrect clustering index.
Duplicate primary keys: During data updates, Hologres may fail to locate existing records, leading to new records being inserted instead. This violates the primary key constraint and results in data duplication.
This bug only occurs if all three of the following conditions are met:
Your Hologres instance version is between 4.0.0 and 4.0.8.
The table is a logical partitioned table of column-oriented or hybrid row-columnar storage.
The table has an explicitly defined clustering key.
Solutions
Upgrade instances
Upgrade your instance to V4.0.9 or later.
In V4.0.9, if a query attempts to use an incorrect index, the query fails and returns the following error message:
clustered_index size [x] incorrect.
Check tables with index problems
Run the following SQL statements for each database to detect tables with corrupted indexes.
WITH logical_partition_tables AS ( SELECT DISTINCT p1.table_namespace, p1.table_name FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p1 WHERE p1.property_key = 'logical_partition_columns' AND EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p2 WHERE p2.table_namespace = p1.table_namespace AND p2.table_name = p1.table_name AND p2.property_key = 'orientation' AND p2.property_value IN ('column', 'row,column', 'column,row') ) ), tables_with_pk AS ( SELECT l.table_namespace, l.table_name, p.property_value AS pk_expr FROM logical_partition_tables l JOIN hologres.hg_table_properties p ON l.table_namespace = p.table_namespace AND l.table_name = p.table_name WHERE p.property_key = 'primary_key' ), partition_cols AS ( SELECT l.table_namespace, l.table_name, p.property_value AS part_expr FROM logical_partition_tables l JOIN hologres.hg_table_properties p ON l.table_namespace = p.table_namespace AND l.table_name = p.table_name WHERE p.property_key = 'logical_partition_columns' ), all_partitions AS ( SELECT t.table_namespace, t.table_name, t.pk_expr, pc.part_expr, part.partition FROM tables_with_pk t JOIN partition_cols pc ON t.table_namespace = pc.table_namespace AND t.table_name = pc.table_name CROSS JOIN LATERAL ( SELECT partition FROM hologres.hg_list_logical_partition( (t.table_namespace || '.' || t.table_name)::TEXT ) ) AS part ), split_kv AS ( SELECT table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition, TRIM(SPLIT_PART(kv, '=', 1)) AS col_name, TRIM(SPLIT_PART(kv, '=', 2)) AS col_val FROM all_partitions, UNNEST(STRING_TO_ARRAY(partition, '/')) AS kv ), final_where AS ( SELECT table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition, STRING_AGG( FORMAT('%I = %L', col_name, col_val), ' AND ' ORDER BY col_name ) AS where_clause FROM split_kv GROUP BY table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition ) SELECT FORMAT( '-- Check PK duplicates in %I.%I, partition: %s' || E'\n' || 'SELECT %s, COUNT(1) FROM %I.%I WHERE %s GROUP BY %s HAVING COUNT(1) > 1;', table_namespace, table_name, partition, pk_expr, table_namespace, table_name, where_clause, pk_expr ) AS detection_sql FROM final_where ORDER BY table_namespace, table_name, partition;The above SQL commands return several other SQL statements, which can be run to check whether any tables in the current database have incorrect indexes.
Sample result:
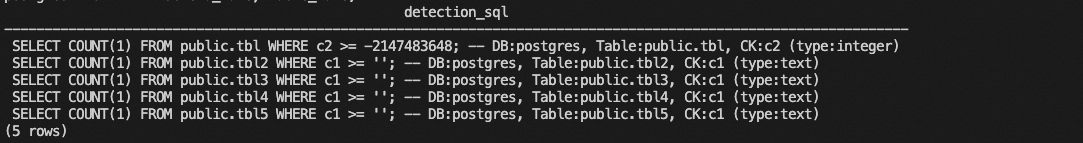
Run the SQL statements. If they execute successfully, the indexes are correct. If a
clustere_index size mismatcherror occurs, the index is corrupted. For tables identified in the error message, perform a full compaction to fix the incorrect index files:SELECT hologres.hg_full_compact_table('schema.table_name','max_file_size_mb=1, reclaim_deleted_data_space = false');After compaction, the index is rebuilt correctly. You can run the preceding check statements again for the affected table to verify the fix.
Check tables with duplicate primary keys
For logical partitioned tables, duplicate primary keys can occur. This problem can manifest as a
duplicate key value violates unique constrainterror or as multiple records for the same primary key. Run the following code:WITH logical_partition_tables AS ( SELECT DISTINCT p1.table_namespace, p1.table_name FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p1 WHERE p1.property_key = 'logical_partition_columns' AND EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p2 WHERE p2.table_namespace = p1.table_namespace AND p2.table_name = p1.table_name AND p2.property_key = 'orientation' AND p2.property_value IN ('column', 'row,column') ) ), tables_with_pk AS ( SELECT l.table_namespace, l.table_name, p.property_value AS pk_expr FROM logical_partition_tables l JOIN hologres.hg_table_properties p ON l.table_namespace = p.table_namespace AND l.table_name = p.table_name WHERE p.property_key = 'primary_key' ), partition_cols AS ( SELECT l.table_namespace, l.table_name, p.property_value AS part_expr FROM logical_partition_tables l JOIN hologres.hg_table_properties p ON l.table_namespace = p.table_namespace AND l.table_name = p.table_name WHERE p.property_key = 'logical_partition_columns' ), all_partitions AS ( SELECT t.table_namespace, t.table_name, t.pk_expr, pc.part_expr, part.partition FROM tables_with_pk t JOIN partition_cols pc ON t.table_namespace = pc.table_namespace AND t.table_name = pc.table_name CROSS JOIN LATERAL ( SELECT partition FROM hologres.hg_list_logical_partition( (t.table_namespace || '.' || t.table_name)::TEXT ) ) AS part ), split_kv AS ( SELECT table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition, TRIM(SPLIT_PART(kv, '=', 1)) AS col_name, TRIM(SPLIT_PART(kv, '=', 2)) AS col_val FROM all_partitions, UNNEST(STRING_TO_ARRAY(partition, '/')) AS kv ), final_where AS ( SELECT table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition, STRING_AGG( FORMAT('%I = %L', col_name, col_val), ' AND ' ORDER BY col_name ) AS where_clause FROM split_kv GROUP BY table_namespace, table_name, pk_expr, partition ) SELECT FORMAT( '-- Check PK duplicates in %I.%I, partition: %s' || E'\n' || 'SELECT %s, COUNT(1) FROM %I.%I WHERE %s GROUP BY %s HAVING COUNT(1) > 1;', table_namespace, table_name, partition, pk_expr, table_namespace, table_name, where_clause, pk_expr ) AS detection_sql FROM final_where ORDER BY table_namespace, table_name, partition;These commands return several other SQL statements, which can be run to check whether any tables in the current database have duplicate primary keys.
Sample results:
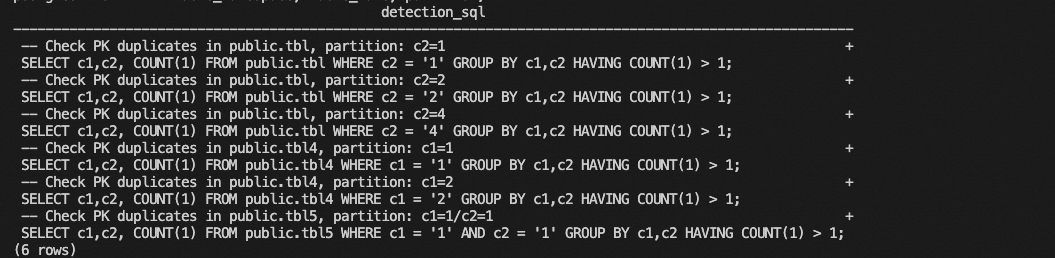
If running the returned SQL commands returns data, duplicate primary keys exist. Perform a full compaction and remove duplicate primary keys.
-- Step 1 select hologres.hg_full_compact_table('schema.table_name','max_file_size_mb=1'); -- Step 2 call public.hg_remove_duplicated_pk('schema.table_name','max_file_size_mb=1'); -- Note: If running hg_remove_duplicated_pk returns a 'Query exceed memory limit' error, the data volume is too large to handle. In this case, remove duplicates by partition. The SQL comments from the previous step show the partitions that contain duplicate data. call public.hg_remove_duplicated_pk('schema.table_name_1', 'dt_int=1'); call public.hg_remove_duplicated_pk('schema.table_name_2', 'dt_text=''A''');After the operation is complete, the duplicate data is removed. You can run the preceding check statements again for the corresponding table to verify the fix.
Check tables with potential problems
If the previous checks pass without issues, you may choose to conduct additional checks on tables lacking a clustering key. Such tables are susceptible to duplicate primary keys, and real-time queries following write-backs can encounter cluster index size mismatch errors. To address these potential risks, use the following SQL commands to identify potentially affected tables, and then execute a full compaction on them.
SELECT FORMAT( 'SELECT hologres.hg_full_compact_table(%L, ''max_file_size_mb=1''); -- Table: %I.%I (has logical partition but NO clustering_key)', table_namespace || '.' || table_name, table_namespace, table_name ) AS compact_sql FROM ( SELECT DISTINCT p1.table_namespace, p1.table_name FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p1 WHERE p1.property_key = 'logical_partition_columns' AND EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM hologres.hg_table_properties p2 WHERE p2.table_namespace = p1.table_namespace AND p2.table_name = p1.table_name AND p2.property_key = 'orientation' AND p2.property_value IN ('column', 'row,column') ) ) AS tables_missing_ck ORDER BY table_namespace, table_name;The preceding SQL statements generate full compact commands.
Sample results:

Execute the commands during off-peak hours.