This topic describes how to create, edit, delete, copy, and rename SQL queries in HoloWeb. The SQL window is suitable for interactive short queries. It is not suitable for offline jobs such as importing or exporting large data volumes. It does not support SQL execution exceeding 60 minutes.
Prerequisites
Instances are logged in. For more information, see Log on to an instance.
Feature Entry
-
Log on to the Hologres Management Console.
-
In the navigation pane on the left of the top menu bar, select the desired region.
-
You can click Go to HoloWeb to go to the HoloWeb development page.
-
On the HoloWeb development page, in the top menu bar, click .
Create an SQL Query
After you access the SQL Editor page through the feature entry, perform the following operations:
-
In the navigation pane on the left, right-click My SQL Queries, and select Create SQL Query.
Click
 to create a temporary SQL query window and execute SQL commands. After execution, click Save as needed to retain the content of the current SQL window.
to create a temporary SQL query window and execute SQL commands. After execution, click Save as needed to retain the content of the current SQL window. -
In the Create SQL Query dialog box, configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Job Name
The name of the new SQL query.
Folder
The location where the new SQL query is stored.
The default folder is My SQL Queries. You can also store it in an existing folder.
New Folder
The location where the new SQL query is stored. You can choose to store it in a new folder.
Instance Name
Select the target instance name.
Database Name
The database name under the current Hologres instance.
-
Click OK to complete the creation.
You can also use standard PostgreSQL language for development in the SQL editor.
 Note
NoteSQL queries are case-insensitive for table and field names. To perform a term query for tables with exact case-sensitive names, enclose the table name in double quotation marks.
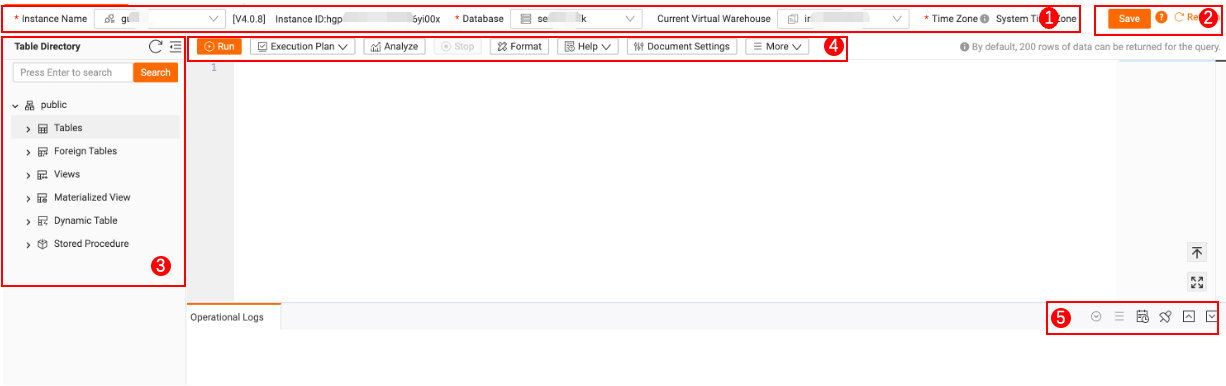
Area
Description
①
Displays the target instance name, instance ID, database, current compute group, and current time zone for the current SQL execution.
②
-
Save the content of the current SQL window.
-
Refresh the SQL editor page.
③
All table information under the current target database:
④
-
Run: Run SQL commands.
-
Stop: Stop running SQL commands.
-
Format: Format SQL commands.
-
Help: View data types, function references, and SQL parameter documentation.
-
Document Settings: Supports editor settings, SQL parameters, and time zone settings.
-
More: Supports importing or exporting SQL, or accessing DataService Studio in DataWorks for SQL development.
⑤
-
 : Search operational logs.
: Search operational logs. -
 : Close all logs, jump to the last page of logs, and display logs.
: Close all logs, jump to the last page of logs, and display logs. -
 : Save logs.
: Save logs. -
 : Pause log scrolling.
: Pause log scrolling. -
 and
and  : Adjust the log display area.
: Adjust the log display area.
Note-
HoloWeb supports SQL execution for a maximum of 60 minutes. If execution exceeds 60 minutes, a timeout message appears:
cancel query due to timeout, queryTimeout setting is: 3600s. -
If you set the `statement_timeout` parameter to be greater than 60 minutes, this parameter does not take effect for SQL statements in HoloWeb. For information about how to set `statement_timeout`, see Modifying Active Query Timeout.
-
Other Operations
-
Access the SQL Editor page through the feature entry.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, click My SQL Queries. Find the target SQL query and perform the following operations:
NoteIf the target SQL query is in a folder, enter the target SQL query name in the search box below Query.
-
Edit an SQL query: Double-click the target SQL query. Enter the SQL statement to execute in the SQL editor.
-
Delete an SQL query: Right-click the target SQL query, and click Delete SQL Query Task.
-
Copy an SQL query: Right-click the target SQL query, and click Copy SQL Query Task. Paste the copied SQL statement into other SQL query windows as needed.
-
Rename an SQL query: Right-click the target SQL query, and click Rename. Rename the SQL query as needed.
-