Overview
Global Traffic Manager (GTM) helps enterprises achieve nearby access to application services and load balancing in high-concurrency scenarios. It also provides the health check feature for application services and implements fault isolation or failover based on health check results. This allows enterprises to build active zone-redundancy and geo-disaster recovery services in a flexible and efficient manner. For more information about how GTM works, see Principles.
If you have not purchased the GTM service, click here to purchase it.
Features
This section provides an overview of the features in GTM. For more information about the features, see Features.
1. Address pool management
GTM allows you to group the IP addresses or domain names that are used to access application services into address pools for management. An address pool contains a group of IP addresses or domain names that are used to access the same application service. The IP addresses or domain names in an address pool belong to the same Internet service provider (ISP) or reside in the same region. You can configure more than one address pool for a GTM instance. This way, requests from different regions can be forwarded to the nearest access points by using different address pools. If a primary address pool set is unavailable, GTM switches to a secondary address pool set.
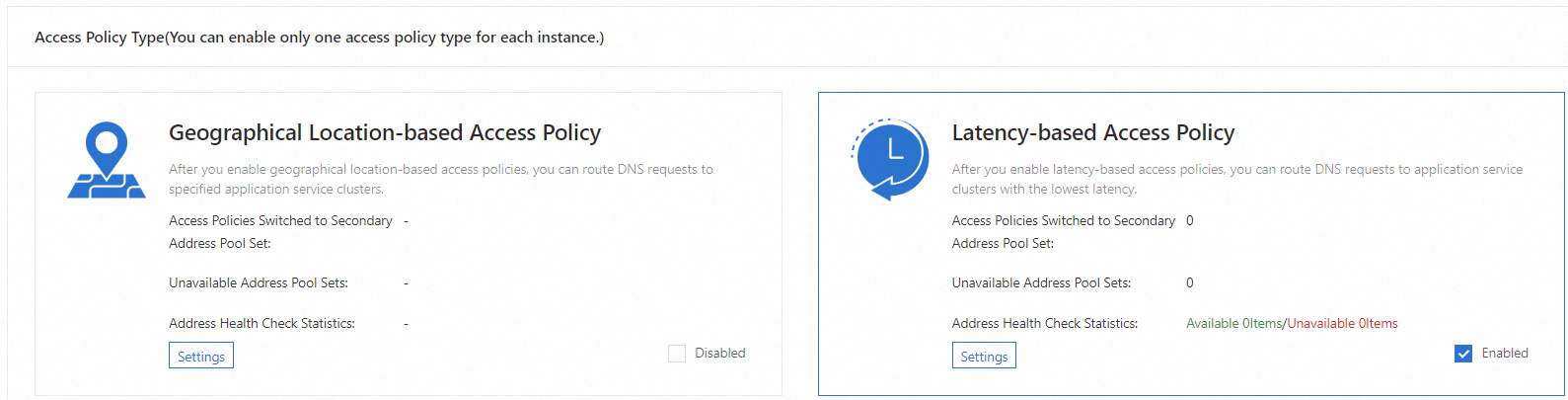
2. Access policy
Access policies allow enterprises to manage global traffic with ease. You can configure traffic scheduling policies to define address pools based on which requests from different networks or regions are resolved. This way, users can connect to the nearest access points and the loads can be automatically switched between the primary and secondary servers for fast failover. GTM supports two types of access policies. You can configure only one type of access policy for each instance.
Access policy based on geographical locations: Users from different regions or networks can access services from the nearest access points. This way, network access is accelerated.
Access policy based on access latency: GTM detects the access latency between the location of a user and the region in which the application service is deployed. Then, GTM routes the request initiated by the user to the application server cluster that has the lowest latency.
3. Health check
The health check feature allows you to perform health checks on the IP addresses in address pools based on Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), TCP, HTTP, or HTTPS. This helps you monitor the availability of your application services in real time.
4. DNS failover
If the health check feature detects that a primary address pool set is unavailable, GTM switches to a secondary address pool set. Then, the secondary address pool set is used to respond to Domain Name System (DNS) requests from users. This way, GTM reduces the risk of business interruption and ensures stable operation of business.
Architecture
GTM consists of the control layer and the resolution layer:
The control layer provides external services based on the console and OpenAPI, and implements the features of adding, deleting, modifying, querying, and storing various data such as DNS resolution data, configuration data, monitoring data, and log data. The control layer is deployed in China (Zhangjiakou).
The resolution layer provides external services by using the DNS server clusters that are deployed around the world. The resolution layer receives the DNS records distributed from the control layer and responds to the query requests for the DNS records. The resolution layer covers the major continents and regions around the world.
Join us
DingTalk group: 36335002029