Industries such as e-commerce, online gaming, and on-demand audio and video streaming require high access speed and quality. To improve the experience of end users, you can use Global Accelerator (GA) together with Content Delivery Network (CDN). Global Accelerator (GA) leverages Alibaba Cloud's premium Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) bandwidth and global transmission network. In conjunction with CDN, it helps you build a global CDN back-to-origin network and ensures comprehensive acceleration of dynamic content.
Scenarios
A web service is deployed on Alibaba Cloud in the US (Silicon Valley) region. The domain name of the service is www.<YOURDOMAIN>.fun. The forwarding port is HTTP port 80. Most clients are located in China (Hong Kong). When clients in China (Hong Kong) access the web service in US (Silicon Valley), issues such as high network latency, network jitter, and packet loss frequently occur due to unstable cross-border Internet connections.
You can deploy CDN for your web service. CDN improves the user experience by caching content on edge nodes. You can also connect CDN to Global Accelerator (GA). GA leverages Alibaba Cloud's premium BGP bandwidth and global transmission network to accelerate back-to-origin delivery for CDN, ensuring high-speed delivery of dynamic content worldwide.

Prerequisites
Applications are deployed on the origin server.
In this example, the Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 operating system is used. NGINX and Netcat are used to build a web page that includes dynamic time display and static images to simulate the server.
You have added an A record to point the service domain name
www.<YOURDOMAIN>.funto the public IP address of the origin server.This topic uses Alibaba Cloud DNS as an example to describe how to configure DNS records. For more information about how to configure DNS records, see Add DNS records. If you use a third-party DNS service, refer to the user guide provided by the service provider.
You have activated the CDN service.
Procedure
Step 1: Configure a GA instance
In this example, a pay-as-you-go standard GA instance is used.
On the page of the GA console, click Create Standard Pay-as-you-go Instance.
In the Basic Instance Configuration step, configure the basic information and click Next.
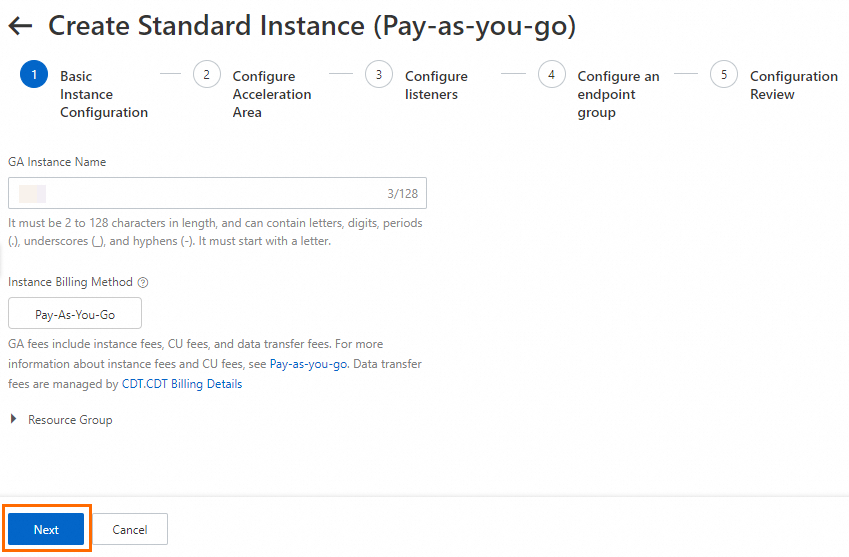
In the Configure Acceleration Area step, add an acceleration region, allocate bandwidth to the region, and then click Next.
In this example, the Acceleration Region parameter is set to China (Hong Kong), and the ISP Line Type parameter is set to BGP (Multi-ISP). You can use the default values for other parameters or modify the parameters based on your business requirements. For more information, see Add and manage acceleration areas.
ImportantIf the acceleration regions include regions in the Chinese mainland, you must apply for an ICP number for the domain name to provide services.
If you specify a small value for the maximum bandwidth, throttling may occur and packets may be dropped. Specify a maximum bandwidth based on your business requirements.
In the Configure listeners step, configure the forwarding protocol and the port, and then click Next.
In this scenario, set the Protocol parameter to HTTP and the Port parameter to 80. You can use the default values for other parameters, such as the Other listener parameter configurations, or modify them as needed.

On the Configure endpoint group page, configure the backend services for the endpoints, and click Next.
In this scenario, set Region to US (Silicon Valley), Backend Service Type to ECS, and Backend Service to the target ECS instance. Then, read and select Compliance Commitments Regarding Cross-border Data Transfers. For other endpoint group parameters, keep the default values or modify them as needed.


In the Configuration Review step, confirm the configurations for Global Accelerator and click Submit.
On the Instances page, find the created GA instance and obtain the CNAME assigned to the GA instance in the CNAME column.
Step 2: Configure CDN
On the Domain Names page of the CDN console, click Add Domain Name.
On the Domain Name Information configuration wizard page, configure Business Information and Origin Servers.
Configure Business Information.
In this scenario, in the Business Information section, set Region to Global (Excluding the Chinese Mainland) and Domain Name to Accelerate to your business domain name, such as
www.<YOURDOMAIN>.fun. You can use the default values for the other parameters or modify them as needed. For more information about domain name configuration, see Add an accelerated domain name.
Configure Origin Servers.
In the Origin Servers section, click Add Origin Server. In the Add Origin Server dialog box, select the type of the origin server, enter the address, and then click OK.
In this example, for Origin Info, select the Site Domain type and enter the CNAME of GA. Set Weight to 100. You can keep the default values for other parameters or modify them as needed. For more information about how to configure origin information, see Add an accelerated domain name.

Select Compliance Warranty Regarding Cross-border Data Transfers and click Next.
On the Recommended Configurations page, you can configure features for the domain name, such as cache expiration time, bandwidth cap, and page optimization, and then click Configure, or directly click Skip.
In this scenario, in the Cache Expiration Time section, find the default cache rule, click Modify in the Actions column, and set Object to /dynamic and Expire In to 0 seconds to fetch dynamic content from the origin. For more information about the recommended configurations, see Recommended Configurations (Optional).

On the Domain Names page, find the added domain name and obtain the CNAME assigned by CDN in the CNAME column.
Step 3: Configure DNS records
After the domain name is added, you must create a DNS record of the domain name to the CNAME assigned by CDN. Then, requests that are sent to the domain name can be forwarded to CDN for acceleration.
To avoid conflicts between the existing A record and the CNAME record, you can set different DNS request sources or resolution lines for the records. In this example, you can add a CNAME record for the China (Hong Kong) region to perform a test. If the test is successful, you can gradually apply the CNAME record to other regions or switch to the default line.
On the Public Zone page, find the domain name that you want to use and click Settings in the Actions column.
NoteFor a domain name that is not registered with Alibaba Cloud, you must add the domain name to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console before you can configure DNS records.
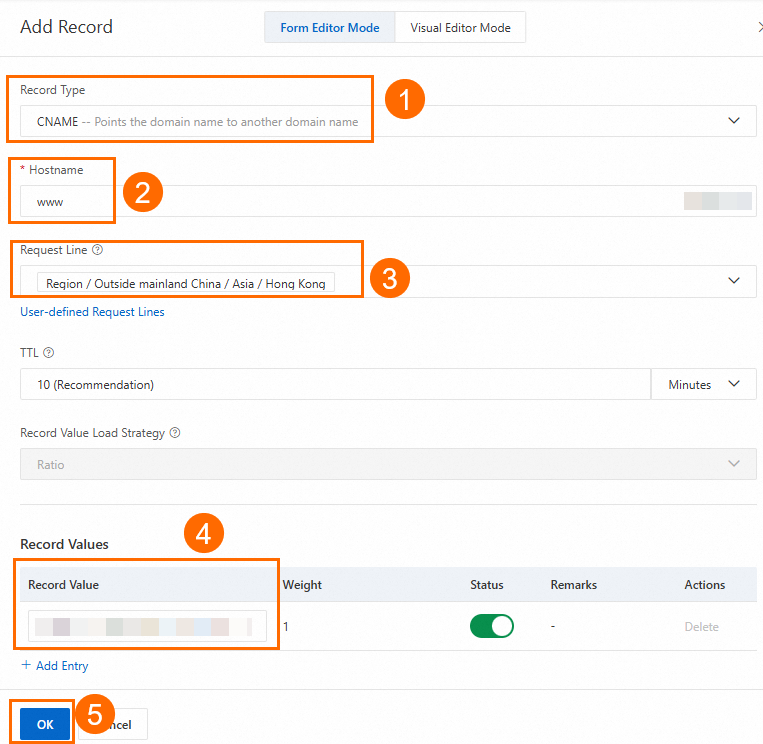
On the DNS Settings page, click Add Record, configure a CNAME record, and then click OK.
In this scenario, Record Type is set to CNAME, Host Record is set to www, Query Source is set to China (Hong Kong), and Record Value is set to the CDN CNAME. For other DNS record parameters, you can use the default values or modify them as needed.
Step 4: Test access
On a computer in the acceleration region (in this topic, China (Hong Kong)), use the developer tools in your browser to access www.<YOURDOMAIN>.fun and view the loading time of each resource on the current webpage.
Check the network latency after GA and CDN are configured.

Check the network latency when only CDN is configured.
You can change the origin site of CDN from the CNAME of GA to the public IP address of the origin server, delete the endpoint group from GA, and then perform a test.

Check the network latency when GA and CDN are not configured.
You can disable the accelerated domain name in CDN, disable the CNAME record in DNS, and then perform a test.

Compare the results:
The test data shows that after CDN is used, the access latency of static content (
test.png) is reduced. After GA is configured with CDN, the access latency of dynamic content (dynamic) is further reduced.Scenario
Static content
test.pngTime consumed (ms)
Dynamic content
dynamicTime consumed (ms)
Comparison
Scenario 1: Use GA and CDN
5
228
Compared with Scenario 2, the access speed of dynamic content is 50.5% faster.
Scenario 2: Use CDN only
5
461
Compared with Scenario 3, the access speed of static content is 98.1% faster.
Scenario 3: GA and CDN are not used
261
474
/
The acceleration performance varies based on your actual business tests.
References
Pay-as-you-go GA fees include GA instance fees, capacity unit (CU) fees, and data transfer fees. For more information, see Billing of pay-as-you-go GA instances.
When you use GA and CDN to accelerate origin fetches, CDN traffic (or bandwidth) fees are incurred. For more information, see CDN billing overview.