This topic describes how to configure instance isolation in the Function Compute console.
Limits
Request isolation and session isolation are supported only for functions that use an instance type with two or more vCPUs.
You cannot enable request isolation and session isolation at the same time.
After you enable request isolation, the system automatically sets the concurrency per instance to 1. This ensures that each function instance can process only one request at a time. Any previously configured concurrency value greater than 1 is ignored.
Asynchronous task requests do not support session isolation.
Procedure
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click Create Function.
In the dialog box that appears, select a function type. On the Create Function page, locate the Isolation and Affinity section. Configure the parameters as described below and then click Create.
Request isolation
For Instance Isolation, select Request Isolation.
Session isolation
For Instance Isolation, select Session Isolation.
When you enable session isolation, session affinity is also automatically enabled. You must also configure the session affinity parameters.
NoteUnlike with session affinity, when you enable session isolation, the number of concurrent sessions per instance is automatically set to 1 and cannot be changed.
When session isolation is enabled, session affinity is also enabled.
This means that requests from the same client are routed to the same function instance, and that instance can serve requests only from that specific client.
MCP SSE affinity
Configuration item
Description
Example
Session Affinity Type
Select MCP SSE Affinity. Based on the MCP SSE protocol specifications, the system ensures that client requests that carry the same SessionId are always routed to the same instance to implement affinity.
MCP SSE Affinity
SSE Path
The path for initiating an SSE connection request.
/sse
Number of Concurrent Sessions per Instance
After you enable session isolation, the number of concurrent sessions per instance is automatically set to 1 and cannot be changed.
1
HeaderField affinity
Configuration item
Description
Example
Session Affinity
Select HeaderField Affinity. Session affinity is implemented based on the value of a specified field in the HTTP request header.
HeaderField affinity
Header Name
The header name used to pass the client ID for affinity. For example, if you want to pass `mySessionId` as the affinity ID and the Header Name is `x-custom-affinity-header`, you must include the following header and value in your HTTP call:
x-custom-affinity-header: mySessionId.x-custom-affinity-header
Number of Concurrent Sessions per Instance
After you enable session isolation, the number of concurrent sessions per instance is automatically set to 1 and cannot be changed.
1
Session Lifecycle
The entire process from session creation and use to final destruction. If the Session Lifecycle is exceeded, the server automatically destroys the session and no longer guarantees affinity.
21600 seconds
Session Idle Timeout
If a user performs no operations for a period of time, the session becomes idle. If the configured Session Idle Timeout is exceeded, the server automatically destroys the session and no longer guarantees affinity.
1800 seconds
Cookie affinity
Configuration item
Description
Example
Session Affinity
Select Cookie Affinity. Session affinity is implemented based on the attribute value in the HTTP cookie.
Cookie Affinity
Cookie Processing Method
Currently, only the cookie insertion method is supported. When a client accesses the service for the first time, Function Compute automatically inserts a cookie into the response. Specifically,
Set-Cookie:x-fc-cookie-session-id={CookieID}is inserted into the HTTP/HTTPS response message. When the client subsequently accesses the service withCookie:x-fc-cookie-session-id={CookieID}, Function Compute forwards the request to the function instance where the first request was processed.Insert cookie
Number of Concurrent Sessions per Instance
After you enable session isolation, the number of concurrent sessions per instance is automatically set to 1 and cannot be changed.
1
Session Lifecycle
The entire process from session creation and use to final destruction. If the Session Lifecycle is exceeded, the server automatically destroys the session and no longer guarantees affinity.
21600 seconds
Session Idle Timeout
If a user performs no operations for a period of time, the session becomes idle. If the configured Session Idle Timeout is exceeded, the server automatically destroys the session and no longer guarantees affinity.
1800 seconds
Verify the results
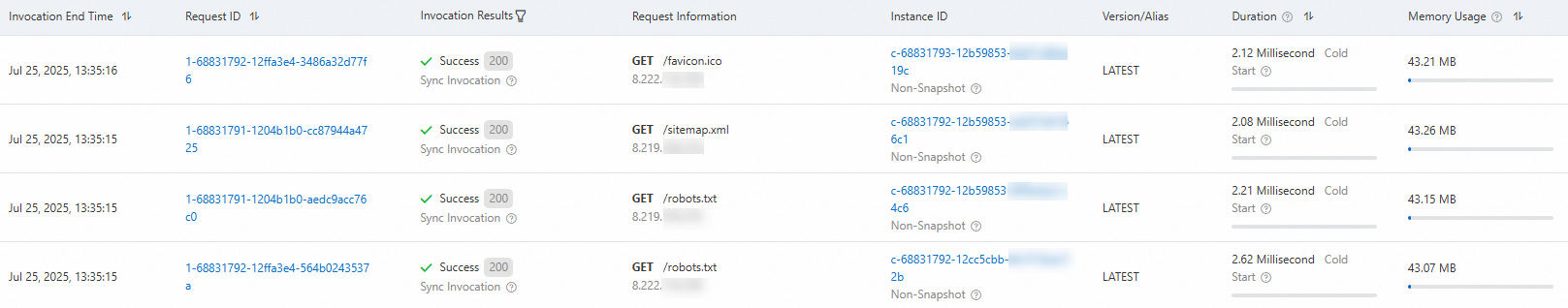
Request isolation
For example, use the curl command to call the function multiple times. In the following command, replace example and regionID with your function URL. You can retrieve the function URL from the Configuration Information column of the HTTP trigger on the Triggers tab of the function details page.
curl https://example.{regionID}.fcapp.runOn the function details page, click the Logs tab. The logs show that each request is scheduled to a different function instance.
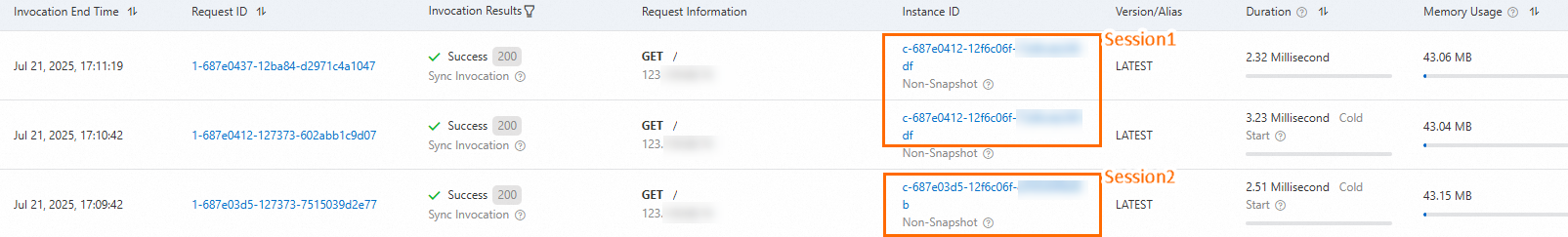
Session isolation
This example uses HeaderField affinity. To test the configuration, call the function and specify different values for the HTTP request header. Session1:
curl -H "x-custom-affinity-header:Session1" https://example.{regionID}.fcapp.runSession2:
curl -H "x-custom-affinity-header:Session2" https://example.{regionID}.fcapp.runOn the function details page, click the Logs tab. The logs show that requests with the same SessionId are scheduled to the same function instance, while requests with different SessionIds are scheduled to different function instances.