After you purchase a resident resource pool, you can use the resource pool by setting the instance type to Resident Instance, attaching the resource pool to a function, and allocating a specific number of resident instances when you create a GPU function.
Limits
Only GPU functions that use Ada, Ada.2, Ada.3, Hopper, and Xpu.1 series cards support resident instances.
Resident instances and elastic instances cannot be used together. After a function is created, you cannot change its instance type.
Procedure
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click Create Function.
In the dialog box that appears, select GPU Function, and then click Create GPU Function.
On the Create GPU Function page, configure the following key parameters, and then click Create.
This topic describes only how to configure resident instances. For more information about advanced configurations, such as function code, instance prefetching, mounting storage, and configuring network access, logs, and roles, see Create a GPU function.
Configuration Item
Description
Example
Basic Configurations: Set basic information for the function.
Function Name
A unique name that identifies the function. The function name must be unique within the same account and region and must follow the naming conventions.
myFunction
Elastic Configurations: Select an instance type and configure an elasticity plan. Resident instances and elastic instances cannot be used together. After a function is created, its instance type cannot be changed.
Instance Type
Select Resident Instance. This allocates instances to the function from a purchased resident resource pool.
Use resident instances for scenarios that are sensitive to latency, require high resource utilization, and need fixed, predictable costs. This ensures business stability.
Resident Instance
Resident Resource Pool
A resident resource pool is a set of computing power resources that you purchase in advance. After purchase, you can allocate resident instances from the pool to a target function.
After you purchase a resident resource pool, the platform transforms the total specifications of the purchased resources into available capacity. This capacity can be flexibly allocated for use by functions. You can create resident instances based on this capacity.
Resident Resource Pool ID/Name: fc-pool-****
GPU Card Type: Ada series
Specification Plan
Set the Video Memory, vCPU, Memory, and Disk specifications for the function as needed.
Video Memory: 48 GB
vCPU: 8
Memory: 64 GB
Disk: 512 MB
Number Of Resident Instances
Allocate a number of resident instances to the target function based on the resources available in the resident resource pool.
1
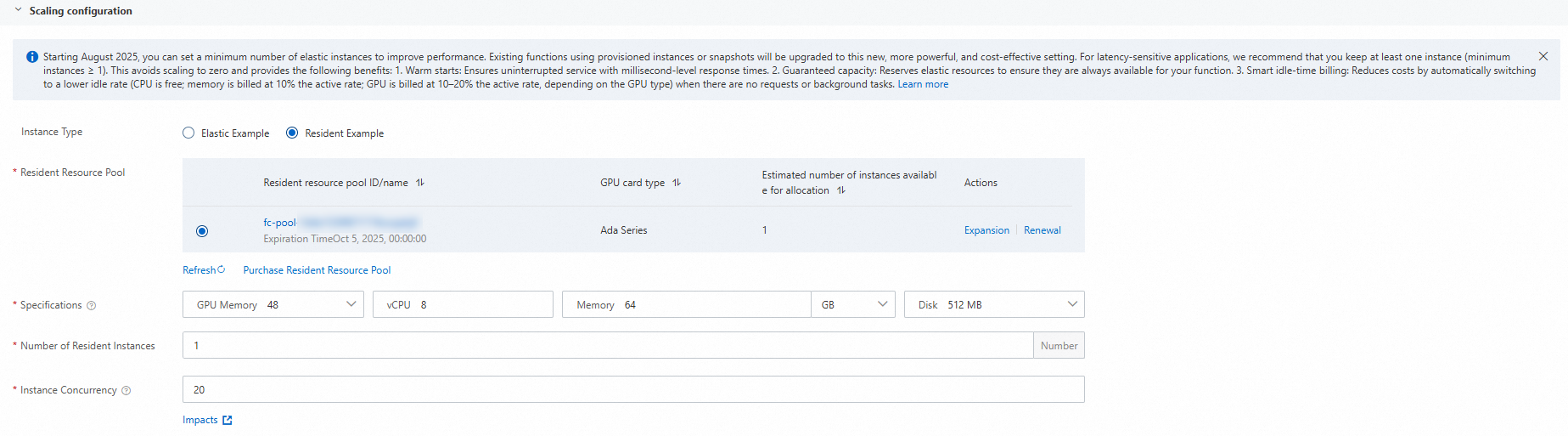
If your resident resource pool cannot be allocated to the objective function because the remaining quota is insufficient, click Scale-out in the Actions column and follow the on-screen instructions to scale out. For more information, see Scale out (upgrade) a resident resource pool.
References
Resident instances and elastic instances cannot be used simultaneously. For more information about their applicable scenarios, see Instance type selection.
For more information about how to purchase and manage resident resource pools, see Manage resident resource pools.