By default, functions created in Function Compute can access the Internet but cannot access resources in a virtual private cloud (VPC). To allow a function to access resources in a VPC or be invoked by a specified VPC, you must manually configure network settings and permissions for the function. This topic describes how to configure network settings for a function in the Function Compute console.
Notes
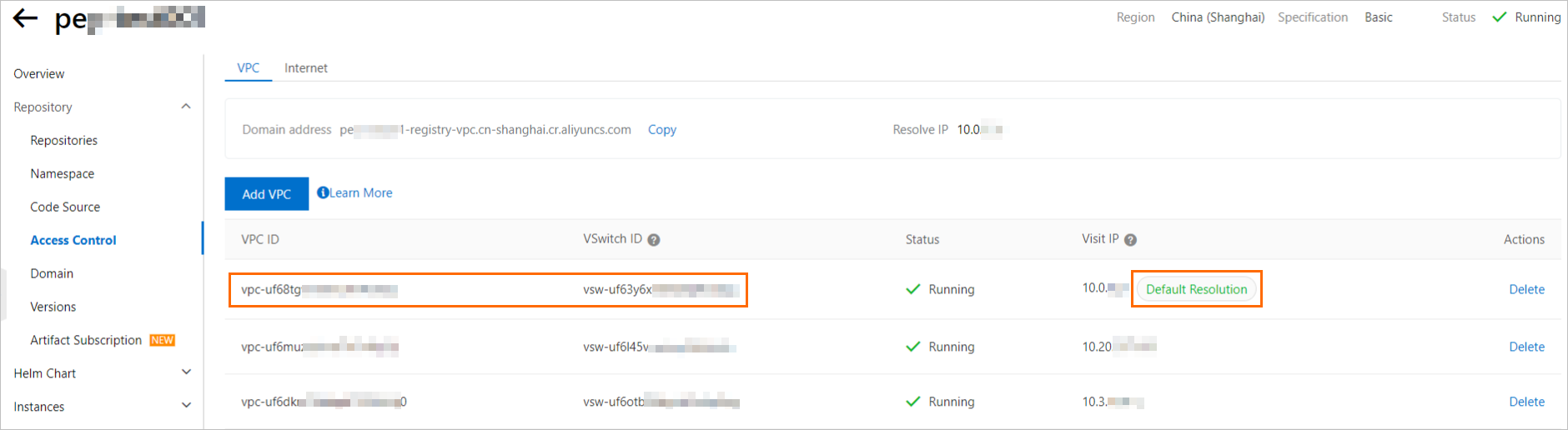
For GPU functions created from container images from an ACR Enterprise instance, you must select a VPC and vSwitch based on the following rules when you configure VPC access for the function.
If an Access IP on the Access Control page of an ACR Enterprise instance has the Default Resolution tag, you must set the function's VPC and vSwitch to the VPC and vSwitch associated with that IP address.
If an Access IP on the Access Control page of an ACR Enterprise instance does not have a Default Resolution tag, you can set the function's VPC and vSwitch to any VPC and vSwitch pair that is bound to the instance.
Network access capabilities
Using the VPC feature can reduce the cold start performance of Function Compute. Do not configure this feature unless necessary. We recommend that you first consider using RAM authorization to access resources. For more information, see Use a function role to grant a function permissions to access other Alibaba Cloud services.
Traffic is generated when a function is invoked or when it accesses a network address. Traffic is classified into the following types.
Internet traffic: traffic generated when accessing Internet addresses, such as the official Alibaba Cloud website, Taobao, and public endpoints of Alibaba Cloud services.
VPC traffic: traffic generated when accessing addresses within your VPC, such as the addresses of ApsaraDB RDS, NAS, and the internal IP addresses of ECS instances in the VPC.
Based on different network settings, a function has the following network access capabilities. Configure the settings as required.
Outbound traffic: Specifies whether to allow the function to send outbound traffic to the Internet or to resources in a VPC. The available settings are Allow Access To VPC and Allow Function To Access The Internet.
Table 1. Outbound traffic for a function
Network configuration
Description
Allow the function to access only the Internet
The function can access the Internet and internal networks through its own network. Access through your VPC is denied.
The required network settings are as follows:
Set Allow Access to VPC to No.
For Allow Function To Access The Internet, select Yes.
Allow the function to access only the VPC
The function can access the Internet and internal networks only through your VPC. This applies to scenarios such as PrivateZone, NAT Gateway, and function-VPC binding.
The required network settings are as follows:
Set Allow Access To VPC to Yes, and then configure the VPC access details.
Set Allow Function To Access The Internet to No.
Allow the function to access both the Internet and the VPC
Non-GPU functions
The function accesses the Internet through its own network.
The function accesses internal networks through your VPC. Private domain name parsing using PrivateZone is supported.
GPU functions:
The function accesses the Internet and internal networks in the 100.0.0.0/8 CIDR block through its own network.
The function accesses internal networks outside the 100.0.0.0/8 CIDR block through your VPC. Private domain name parsing using PrivateZone is not supported. To enable internal network parsing, you can submit a ticket.
The required network settings are as follows:
Set Allow Access To VPC to Yes, and then configure the VPC that the function can access.
Set Allow Function to Access the Internet to Yes.
Deny the function access to both the Internet and the VPC
The function can access internal networks through its own network. Access to the Internet and your VPC is denied. The required network settings are as follows:
Set Allow Access To VPC to No.
Set Allow Function To Access The Internet to No.
Inbound traffic: Specifies whether the function can be invoked from a public IP address or a VPC. This is configured by the Allow Only Specified VPCs To Invoke The Function setting.
Table 2. Inbound traffic for a function
Network configuration
Description
Allow the function to be accessed from both the Internet and a VPC
By default, a function can be invoked from the Internet and a VPC after it is created. The default network settings are as follows:
Set the Allow Only Specified VPCs To Invoke The Function option to No.
Allow the function to be accessed only from a VPC
The function can be invoked only from a specified VPC. Invocations from the Internet are denied. The required network settings are as follows:
Set Allow Only Specified VPCs To Invoke The Function to Yes, and then configure the VPCs that are allowed to invoke the function.
Zones supported by Function Compute
If your resource is in a zone that is not supported by Function Compute, you can create a vSwitch in a supported zone within your VPC environment and set this vSwitch ID in the VPC configuration of the Function Compute function. Because different vSwitches within the same VPC can communicate with each other over the private network, Function Compute can use this vSwitch to access resources in other zones within the VPC. For more information, see What do I do when I encounter the 'vSwitch is in unsupported zone' error?.
Prerequisites
(Optional) Create network resources
If you have not created the required resources, you can select Automatic Configuration. Alternatively, you can create the resources in advance as described in the following documents:
Configure network settings and roles
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click the target function.
On the function details page, click the Configuration tab. Then, click Edit to the right of Advanced Configuration.
In the Advanced Configuration panel, locate the Network section, modify the configuration items as needed, and click Deploy.
Allow access to VPC: Specifies whether the function can access resources in a VPC. Valid values:
Enable: Allows the function to access resources in a VPC. If you select Enable, you must also select a Configuration Method. Valid values:
(Recommended) Automatic Configuration: Function Compute automatically creates resources such as a VPC, a vSwitch, and a security group, so you do not need to create them manually. Existing resources in the current region are reused.
Custom Configuration: Manually select existing network resources. Ensure that you have created the required resources in advance.
VPC: Select the VPC to access from the list.
ImportantA maximum of 10 vSwitches can be created in the selected VPC.
VSwitch: Select at least one vSwitch.
This field specifies the subnets that Function Compute can access. We recommend that you specify two or more vSwitches so that if a zone fails or runs out of IP addresses, your function can run in other subnets.
Security Group: You can select a security group from the list.
This security group is used to associate an elastic network interface (ENI) with the function. It controls the function's behavior when it accesses resources in the VPC through the ENI. By default, the outbound rules of the security group allow all traffic. You can also configure outbound rules to implement fine-grained control over the function's access to resources in the VPC.
NoteThe outbound rules of the security group must allow the ICMP protocol. Function Compute uses the ICMP protocol to check VPC network connectivity.
Disable: Prevents the function from accessing resources in a VPC.
Static Public IP Address: Specifies whether to assign a static public IP address for outbound Internet access through a NAT Gateway and an Elastic IP Address. For more information, see Configure a static public IP address.
Allow Function To Access The Internet Using The Default ENI: Specifies whether to grant the function Internet access. Valid values:
Enable: Allows the function to access the Internet.
Disable: Prevents the function from accessing the Internet.
Allow Only Specified VPCs To Invoke The Function: Specifies whether only specified VPCs can invoke the function. Valid values:
Enable: If you select this option, only specified VPCs can invoke the function. Note the following:
A function can be bound to a maximum of 20 VPCs.
Function invocation by a trigger is not affected by this setting.
The VPC binding takes effect for all versions and aliases of the function.
After you configure this setting, invocation requests from the Internet and other VPCs are rejected. The
StatusCodeis 403, theErrorCodeisAccessDenied, and the error message isResource access is bound by VPC: VPC ID.You can bind a VPC only using a private HTTP endpoint. You cannot bind a VPC using a public endpoint or a private HTTPS endpoint.
Disable: The function can be invoked from the Internet and all VPCs.
FAQ
Why can't Function Compute connect to a VPC for debugging?
If you configured your function to access a VPC but the connection fails, the cause may be one of the following.
The subnet where the vSwitch resides is faulty, or the IP addresses in the subnet are exhausted. To improve fault tolerance, you can provide two or more vSwitch IDs when you configure the VPC. This allows your function to run in another zone if one zone fails.
The security group is configured incorrectly. Make sure that the security group is configured based on the following requirements.
The inbound rules of the VPC security group must allow access from the security group for Function Compute.
The outbound rules of the security group must allow the ICMP protocol. Function Compute uses the ICMP protocol to check VPC network connectivity.
For more information about how to configure a security group, see Add a security group rule.
What do I do if resources are insufficient when I add network resources?
When you create VPC network resources, the automatic configuration feature provides a network prefix of /24, which provides 252 available IP addresses. If you have many instances, this limit may be exceeded. In this case, you must manually adjust the CIDR block of the vSwitch and the corresponding security group.
Troubleshooting
Function Compute does not check permissions to access a VPC when you set the vpcConfig parameter. This check is performed when the function is executed. Therefore, new error types may occur when you invoke the function by calling the InvokeFunction API operation. The following table describes common errors that can occur when you connect to a VPC to help you quickly troubleshoot issues.
Error code | Status code | Cause | Solution |
InvalidArgument | 400 | The zone where the specified vSwitchId resides is not supported by Function Compute. | Reset the vSwitchId parameter. For more information, see Zones supported by Function Compute. |
The resource corresponding to vpcId, vSwitchIds, or securityGroupId in vpcConfig was not found. | Check the vpcConfig parameter settings. | ||
The specified vSwitch or security group is not in the corresponding VPC. | Check the vpcConfig parameter settings, and ensure that the resources that correspond to vSwitchId and securityGroupId are in the VPC that corresponds to vpcId. | ||
AccessDenied | 403 | Permissions to operate on the ENI are not granted. | Check the permissions of the function. For more information, see Use a function role to grant a function permissions to access other Alibaba Cloud services. |
ResourceExhausted | 429 | The number of available IP addresses in the CIDR block of the vSwitch is insufficient. Function Compute cannot create more ENIs. | Create a vSwitch with a larger CIDR block and update the vSwitchId parameter of vpcConfig. Note We recommend that you use a |
References
To access a database in a VPC, we recommend that you configure an IP address whitelist for the database. In the whitelist, specify the CIDR block of the vSwitch that you configured on this page. For more information, see Access a database.
To limit the outbound Internet traffic of a function, you must use a static IP address. For more information, see Configure a static public IP address.