Google released Gemma, its first open-source model family, on February 21, 2024. The model weights are available in two sizes: Gemma 2B and Gemma 7B. You can use GPU-accelerated instances and the idle mode of Function Compute to quickly deploy a Gemma model service at a low cost.
Prerequisites
Function Compute is activated. For more information, see Quickly create a function.
A namespace and an image repository are created. For more information, see Create a namespace and Create an image repository.
Procedure
You are charged for the resources that you use to deploy the service, such as GPU resources, vCPU resources, memory resources, disk resources, outbound Internet traffic, and function invocations. For more information, see Billing overview.
Create an application
Follow these steps to obtain the domain name and address of the ACR repository.
Log on to the Container Registry console, select the region where your function resides, and click Manage on the target Enterprise instance card.
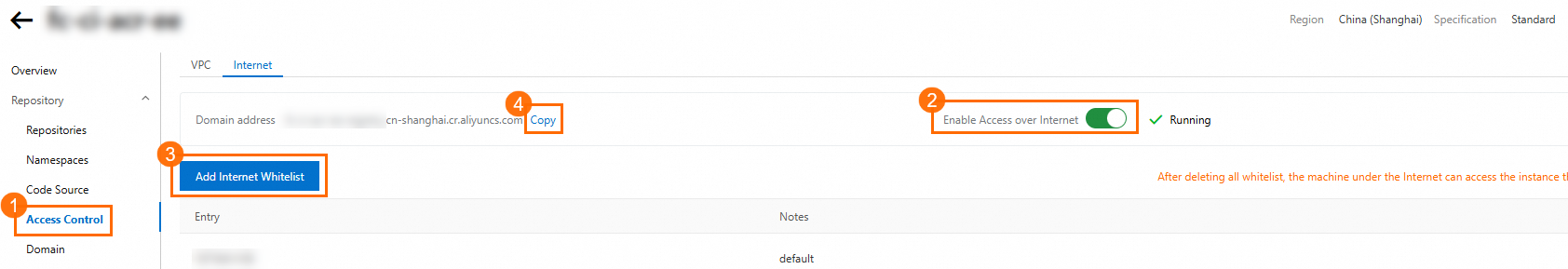
In the navigation pane on the left, click Access Control and select the Internet tab. If Internet access is disabled, enable it. To allow any machine on the Internet to log on to your repository, delete all Internet whitelists. Otherwise, configure an Internet whitelist. After you complete the configuration, copy the Domain Name of the ACR instance.
In the left navigation pane, click Image Repositories. Then, click the Repository Name of the target repository to open its details page.
You can save the Internet Address of the repository.

Download a Gemma model. You can download the model from Hugging Face or ModelScope. This topic uses a Gemma-2b-it model downloaded from ModelScope as an example. For more information, see Gemma-2b-it.
ImportantIf you use Git to download the model, you must install the Git LFS extension, run the
git lfs installcommand to initialize Git LFS, and then run thegit clonecommand to download the model. Otherwise, the downloaded model may be incomplete because of its large size, and the Gemma service may fail to work.Create a Dockerfile and a model service code file named
app.py.Dockerfile
FROM registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/modelscope-repo/modelscope:fc-deploy-common-v17 WORKDIR /usr/src/app COPY . . RUN pip install -U transformers RUN pip install -U accelerate CMD [ "python3", "-u", "/usr/src/app/app.py" ] EXPOSE 9000app.py
from flask import Flask, request from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM model_dir = '/usr/src/app/gemma-2b-it' app = Flask(__name__) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_dir) model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_dir, device_map="auto") @app.route('/invoke', methods=['POST']) def invoke(): request_id = request.headers.get("x-fc-request-id", "") print("FC Invoke Start RequestId: " + request_id) text = request.get_data().decode("utf-8") print(text) input_ids = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda") outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=1000) response = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]) print("FC Invoke End RequestId: " + request_id) return str(response) + "\n" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=False, host='0.0.0.0', port=9000)For more information about all HTTP headers that Function Compute supports, see Common request headers in Function Compute.
After you complete these steps, the code directory has the following structure:
. |-- app.py |-- Dockerfile `-- gemma-2b-it |-- config.json |-- generation_config.json |-- model-00001-of-00002.safetensors |-- model-00002-of-00002.safetensors |-- model.safetensors.index.json |-- README.md |-- special_tokens_map.json |-- tokenizer_config.json |-- tokenizer.json `-- tokenizer.model 1 directory, 12 filesRun the following commands in sequence to build and push the image. In the commands,
{REPO_ENDPOINT}is the Internet address of the destination image repository from Step 1, and{REGISTRY}is the domain name of the ACR instance.IMAGE_NAME={REPO_ENDPOINT}:gemma-2b-it docker login --username=mu****@test.aliyunid.com {REGISTRY} docker build -f Dockerfile -t $IMAGE_NAME . && docker push $IMAGE_NAMEReplace {NAMESPACE} and {REPO} in the preceding commands with the names of the namespace and image repository that you created.
Create a function.
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click Create Function.
On the Create Function page, select the GPU Function type, set the following parameters, and then click Create.
The following table describes the key parameters. You can use the default values for other parameters.
Parameter
Description
GPU Type
Select Tesla Series.
Specifications
Set GPU Memory to 16 GB.
Set VCPU to 2 vCPUs.
Set Memory to 16 GB.
Image Configuration
Container Image
Click Select ACR Image. In the Select Container Image panel, select the image that you pushed to your ACR image repository in Step 4.
Listener Port
Set this parameter to 9000.
When the status of your function changes to Activated, you can set the minimum number of instances to a value greater than 0 to mitigate cold starts.
On the function details page, select the Elasticity Configuration tab. In the Elasticity Policy section, click Configure for the target policy.
In the Configure Elasticity Policy panel, set Minimum Instances to 1 or greater, and then click OK.
Use the Google Gemma service
On the function details page, click the Triggers tab. In the Configuration Information column for the target HTTP trigger, obtain its URL.
Run the following command to invoke the function.
curl -X POST -d "who are you" https://func-i****-****.cn-shanghai.fcapp.run/invokeThe following example shows the expected output:
<bos>who are you? I am a large language model, trained by Google. I am a conversational AI that can understand and generate human language, and I am able to communicate and provide information in a comprehensive and informative way. What can I do for you today?<eos>On the function details page, select the tab to view the metrics.
You can see that the GPU memory usage of the instance drops to zero when no function invocation occurs. When a new function invocation request arrives, Function Compute promptly restores and allocates the required GPU memory resources. This helps reduce costs.
NoteTo view instance metrics, you must first enable the logging feature. For more information, see Configure the logging feature.
Delete resources
If you no longer need to use this function, you can delete its resources to avoid incurring further charges. If you want to use this application for a long time, you can skip this step.
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the function list, find the target function and click Delete in the Actions column. In the dialog box that appears, verify that the resources to be deleted are correct, and then confirm the deletion.
References
For more information about Gemma, the open model family released by Google, see gemma-open-models.