Automatically infer table schemas from Kafka JSON messages and query topics without manual DDL statements.
What is a Kafka JSON catalog?
A Kafka JSON catalog eliminates manual schema definition by automatically inferring table structures from JSON-formatted Kafka messages. This allows you to query topics directly using SQL without writing DDL statements.
Key benefits:
Faster development: Query Kafka topics directly without declaring schemas
Fewer errors: Table names automatically match topic names
Schema evolution: Use with CTAS to sync data when schemas change
Example: Instead of writing this DDL statement:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id STRING,
product_name STRING,
quantity INT,
price DECIMAL(10,2)
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'orders',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '...',
'format' = 'json'
);You can directly query the topic:
SELECT * FROM kafka_catalog.kafka.orders;How it works
When you query a catalog table:
Flink samples up to 100 messages from the topic
Infers the schema from the JSON structure
Creates a table with:
Fields from your JSON message (key and value)
Metadata columns (partition, offset, timestamp)
A primary key (partition, offset)
This happens automatically—no DDL required.
For topics with mixed schemas, the catalog merges all fields into one schema. See Schema inference details.
This topic describes how to manage Kafka JSON catalogs:
Limitations
Only JSON-formatted messages are supported.
Requires VVR 6.0.2 or later.
Modifying a Kafka JSON catalog is not supported.
Catalog tables are read-only.
NoteIn CREATE DATABASE AS (CDAS) or CREATE TABLE AS (CTAS) scenarios that use a Kafka JSON catalog, topics can be created automatically.
Kafka JSON catalogs cannot read from or write to Kafka clusters that have SSL or SASL authentication enabled.
Tables provided by Kafka JSON catalogs can be used directly as source tables in Flink SQL jobs. They cannot be used as sink tables or lookup dimension tables.
ApsaraMQ for Kafka currently does not allow you to delete consumer groups using the same API operation as Apache Kafka. When you create a Kafka JSON catalog, you must configure the aliyun.kafka.instanceId, aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId, aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret, aliyun.kafka.endpoint, and aliyun.kafka.regionId parameters to automatically delete consumer groups. For more information, see Comparison between ApsaraMQ for Kafka and Apache Kafka.
Usage notes
Schema consistency: The catalog samples messages to infer schemas. If messages have different formats, the catalog merges all fields into one schema.
Impact of schema changes: If the message format changes, job restarts may fail because the execution plan uses the old schema.
Solution: Fix the schema with CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE. Example:
-- Define a fixed schema based on the catalog table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE orders (
value_order_id STRING,
value_product_name STRING,
value_quantity INT,
value_price DECIMAL(10,2)
) LIKE `kafka_catalog`.`kafka`.`orders`;This locks the schema, preventing restart failures.
Create a Kafka JSON catalog
In the SQL editor on Scripts, enter the statement to create a Kafka JSON catalog.
Self-managed Kafka cluster or EMR on ECS Kafka cluster
CREATE CATALOG <YourCatalogName> WITH( 'type'='kafka', -- Required 'properties.bootstrap.servers'='<brokers>', -- Required 'format'='json', -- Required 'default-database'='<dbName>', 'key.fields-prefix'='<keyPrefix>', 'value.fields-prefix'='<valuePrefix>', 'timestamp-format.standard'='<timestampFormat>', 'infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable'='<flattenNestedColumns>', 'infer-schema.primitive-as-string'='<primitiveAsString>', 'infer-schema.parse-key-error.field-name'='<parseKeyErrorFieldName>', 'infer-schema.compacted-topic-as-upsert-table'='true', 'max.fetch.records'='100' );CREATE CATALOG <YourCatalogName> WITH( 'type'='kafka', -- Required 'properties.bootstrap.servers'='<brokers>', -- Required 'format'='json', -- Required 'default-database'='<dbName>', 'key.fields-prefix'='<keyPrefix>', 'value.fields-prefix'='<valuePrefix>', 'timestamp-format.standard'='<timestampFormat>', 'infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable'='<flattenNestedColumns>', 'infer-schema.primitive-as-string'='<primitiveAsString>', 'infer-schema.parse-key-error.field-name'='<parseKeyErrorFieldName>', 'infer-schema.compacted-topic-as-upsert-table'='true', 'max.fetch.records'='100', 'aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId'='<aliyunAccessKeyId>', -- Required 'aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret'='<aliyunAccessKeySecret>', -- Required 'aliyun.kafka.instanceId'='<aliyunKafkaInstanceId>', -- Required 'aliyun.kafka.endpoint'='<aliyunKafkaEndpoint>', -- Required 'aliyun.kafka.regionId'='<aliyunKafkaRegionId>' -- Required );
Parameter
Type
Description
Required
Remarks
YourCatalogName
String
Catalog name.
Yes
Enter a custom name.
ImportantRemove the angle brackets (<>) after you replace the parameter placeholder with your catalog name.
type
String
The catalog type.
Yes
The value must be kafka.
properties.bootstrap.servers
String
Kafka broker addresses.
Yes
Format:
host1:port1,host2:port2,host3:port3.Separate multiple addresses with commas (,).
format
String
Kafka message format.
Yes
Set it to json.
default-database
String
Kafka cluster name.
No
Default: kafka. A catalog uses three-part names: catalog_name.db_name.table_name. This parameter sets db_name. Since Kafka has no databases, use any string to replace db_name.
key.fields-prefix
String
Prefix for message key fields. Avoids naming conflicts.
No
Default: key_. Example: Field a becomes key_a.
NoteThe value of the key.fields-prefix parameter cannot be a prefix of the value of the value.fields-prefix parameter. For example, if you set value.fields-prefix to test1_value_, you cannot set key.fields-prefix to test1_.
value.fields-prefix
String
Prefix for message value fields. Avoids naming conflicts.
No
Default: value_. Example: Field b becomes value_b.
NoteThe value of the value.fields-prefix parameter cannot be a prefix of the value of the key.fields-prefix parameter. For example, if you set key.fields-prefix to test2_value_, you cannot set value.fields-prefix to test2_.
timestamp-format.standard
String
Timestamp parsing format for JSON messages. Flink tries your configured format first, then other formats automatically.
No
Valid values:
SQL (default)
ISO-8601
infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable
Boolean
Recursively expand nested columns in message values.
No
Valid values:
true: Expand nested columns.
Expanded column names use the path as the name. Example: col in
{"nested": {"col": true}}becomes nested.col.NoteIf you set this parameter to true, use it with the CREATE TABLE AS (CTAS) statement. Other DML statements do not support automatic expansion of nested columns.
false (default): Treat nested types as String.
infer-schema.primitive-as-string
Boolean
Infer all primitive types as String.
No
Valid values:
true: Infer all primitive types as String.
false (default): Infer types based on basic rules.
infer-schema.parse-key-error.field-name
String
When parsing the JSON message key, if the key is not empty and parsing fails, a field of the VARBINARY type is added to the table schema to represent the message key data. The field name is a concatenation of the key.fields-prefix prefix and the value of this parameter.
No
The default value is col. For example, if the message value parses to a field named value_name, and the message key is not empty but fails to parse, the returned schema contains two fields: key_col and value_name.
infer-schema.compacted-topic-as-upsert-table
Boolean
Specifies whether to use the table as an Upsert Kafka table when the cleanup policy of the Kafka topic is compact and the message key is not empty.
No
The default value is true. Set this to true when using CTAS or CDAS syntax to synchronize data to ApsaraMQ for Kafka.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
max.fetch.records
Int
The maximum number of messages to consume when parsing JSON-formatted messages.
No
The default value is 100.
aliyun.kafka.accessKeyId
String
The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.
No
Required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka clusters.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
aliyun.kafka.accessKeySecret
String
The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.
No
Required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka clusters.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
aliyun.kafka.instanceId
String
The ID of the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. You can view the ID on the instance details page of the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console.
No
Required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka clusters.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
aliyun.kafka.endpoint
String
The API endpoint of ApsaraMQ for Kafka. For more information, see Endpoints.
No
Required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka clusters.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
aliyun.kafka.regionId
String
The region ID of the instance where the topic is located. For more information, see Endpoints.
No
Required for ApsaraMQ for Kafka clusters.
NoteOnly VVR 6.0.2 or later support this parameter.
Select the statement to create the catalog, and then click Run next to the line numbers on the left.

In the Catalogs area on the left, view the created catalog.
View a Kafka JSON catalog
In the SQL editor on Scripts, enter the following statement.
DESCRIBE `${catalog_name}`.`${db_name}`.`${topic_name}`;Parameter
Description
${catalog_name}
The catalog name.
${db_name}
The cluster name.
${topic_name}
The topic name.
Run the command to view the catalog.
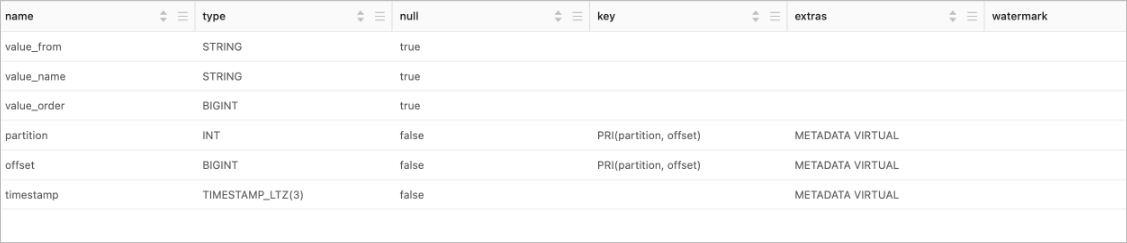
Use a Kafka JSON catalog
After you create a Kafka JSON catalog, reference its topics in Flink SQL jobs.
Use as a source table
Scenario: Extract Kafka data and write it to another system.
How to use: Query the catalog table directly:
-- Insert data from Kafka topic to target table
INSERT INTO ${other_sink_table}
SELECT order_id, product_name, quantity * price AS total_amount
FROM `${kafka_catalog}`.`${db_name}`.`${topic_name}`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset') */;Use SQL Hints to specify table options. For example, scan.startup.mode controls where to start reading. For more options, see Kafka source table parameters.
Use with CTAS to sync data
Scenario: Sync entire Kafka topics without writing DDL statements.
How it works: CREATE TABLE AS (CTAS) creates a target table with the same schema as the source. Useful for:
Syncing without manual schema definition
Auto-handling schema changes
Sync a single topic:
-- Create target table with inferred schema
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `${target_table_name}`
WITH (
'connector' = 'hologres',
'dbname' = 'my_database',
'tablename' = 'orders'
)
AS TABLE `${kafka_catalog}`.`${db_name}`.`${topic_name}`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset') */;Sync multiple topics in one job:
BEGIN STATEMENT SET;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `target_catalog`.`target_db`.`orders`
AS TABLE `kafka_catalog`.`kafka`.`orders`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset') */;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `target_catalog`.`target_db`.`products`
AS TABLE `kafka_catalog`.`kafka`.`products`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset') */;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `target_catalog`.`target_db`.`customers`
AS TABLE `kafka_catalog`.`kafka`.`customers`
/*+ OPTIONS('scan.startup.mode'='earliest-offset') */;
END;Requirements for syncing multiple topics:
When syncing multiple Kafka topics in the same job, ensure:
None of the tables use the topic-pattern parameter
All tables have identical Kafka configurations (same properties.bootstrap.servers, properties.group.id, etc.)
All tables use the same scan.startup.mode (group-offsets, latest-offset, or earliest-offset)
Example: The following image shows which configurations meet the requirements:
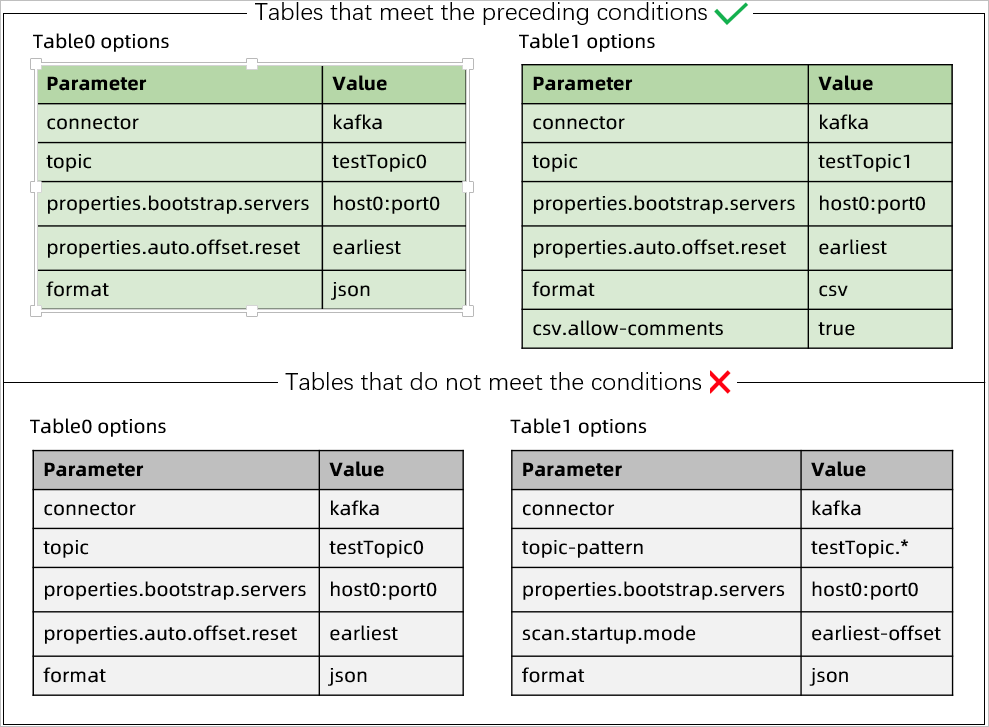
In this example, the top two tables meet all requirements, while the bottom two tables violate them.
For complete end-to-end examples, see Quick Start for real-time log warehousing.
Delete a Kafka JSON catalog
Deleting a catalog does not affect running jobs. However, deploying or restarting jobs that use the catalog will fail with "table not found" errors.
In the SQL editor on Scripts, enter the following statement.
DROP CATALOG ${catalog_name};Replace ${catalog_name} with the name of the Kafka JSON catalog that you want to delete.
Select the statement to delete the catalog, right-click, and select Run.
In the Catalogs area on the left, check whether the catalog is deleted.
Reference: Schema inference details
This section provides technical details about how Kafka JSON catalogs infer table schemas.
You can skip this section if you just want to use the catalog. Read this section when:
Troubleshooting schema-related issues
Understanding how the catalog handles inconsistent schemas
Optimizing schema inference performance
Schema inference process
When you query a Kafka topic, Flink samples messages (up to max.fetch.records, default 100) and merges their schemas.
Detailed process: Flink parses each message and then merges the schemas.
Schema inference creates a consumer group to consume topic data. The consumer group name includes a prefix indicating it was created by the catalog.
For ApsaraMQ for Kafka, use VVR 6.0.7 or later. Earlier versions don't auto-delete consumer groups, causing stacked message alerts.
The schema mainly includes the inferred physical columns and metadata columns with primary-key constraints:
Inferred physical columns
Flink infers physical columns from the message key and value, adding the configured prefixes to column names.
If the key is not empty but unparseable, Flink creates a VARBINARY column. The column name combines key.fields-prefix with the infer-schema.parse-key-error.field-name value.
Schema merging rules:
New fields are added to the final schema.
For fields with the same name:
Same types, different precision: Use higher precision.
Different types: Find the smallest parent node in the type tree (see figure). Decimal + Float merge to Double to preserve precision.
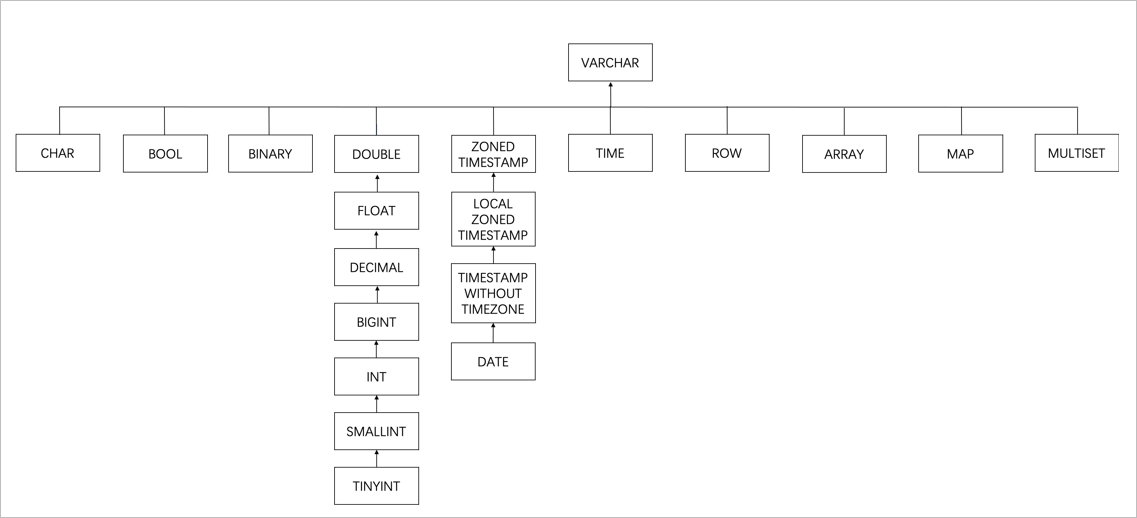
Example: For a topic with these three messages, the catalog produces this schema:
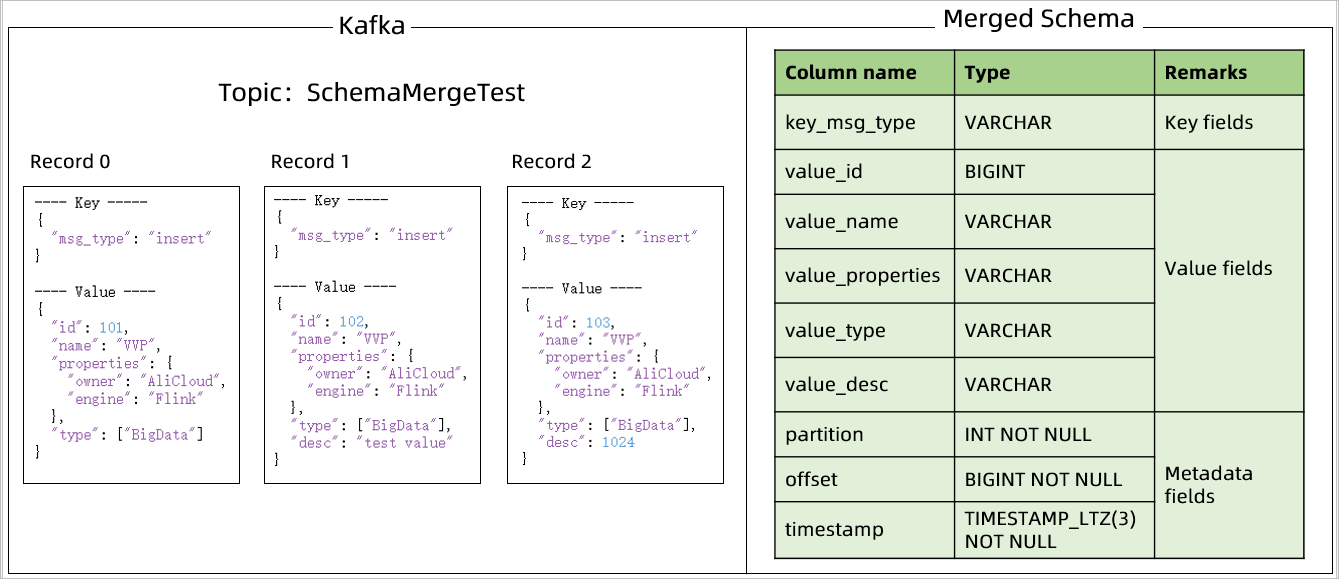
Default metadata columns
Flink adds three metadata columns by default: partition, offset, and timestamp.
Metadata name
Column name
Type
Description
partition
partition
INT NOT NULL
The partition value.
offset
offset
BIGINT NOT NULL
The offset.
timestamp
timestamp
TIMESTAMP_LTZ(3) NOT NULL
The message timestamp.
Default PRIMARY KEY constraint
During reading from Kafka,
partitionandoffsetserve as the primary key to ensure data uniqueness.
If the inferred schema doesn't meet your needs, use CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE ... LIKE to explicitly specify a custom schema. Example: If JSON contains a ts field in '2023-01-01 12:00:01' format, the catalog infers it as TIMESTAMP. To use it as STRING, declare the table as shown below. Note the value_ prefix for message value fields:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE tempTable (
value_name STRING,
value_ts STRING
) LIKE `kafkaJsonCatalog`.`kafka`.`testTopic`;Default table parameters
Parameter
Description
Remarks
connector
Connector type.
Value:
kafkaorupsert-kafka.topic
Corresponding topic name.
Same as table name.
properties.bootstrap.servers
Kafka broker addresses.
Corresponds to the value of the properties.bootstrap.servers parameter in the catalog configuration.
value.format
Format for Kafka connector to serialize/deserialize message values.
Fixed to JSON.
value.fields-prefix
Custom prefix for message value fields to avoid conflicts with key or metadata fields.
Corresponds to the value of the value.fields-prefix parameter in the catalog configuration.
value.json.infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable
Specifies whether to recursively expand nested columns in the JSON of the Kafka message value.
Corresponds to the value of the infer-schema.flatten-nested-columns.enable parameter in the catalog configuration.
value.json.infer-schema.primitive-as-string
Specifies whether to infer all primitive data types as the String type for the Kafka message value.
Corresponds to the value of the infer-schema.primitive-as-string parameter in the catalog configuration.
value.fields-include
Defines the policy for handling message key fields in the message value.
The value must be
EXCEPT_KEY. This indicates that the message value does not contain the message key fields.You must configure this parameter if the message key is not empty. Do not configure this parameter if the message key is empty.
key.format
The format used by the Flink Kafka connector to serialize or deserialize the Kafka message key.
The value must be json or raw.
You must configure this parameter if the message key is not empty. Do not configure this parameter if the message key is empty.
If the message key is not empty but cannot be parsed, set this parameter to raw. If parsing is successful, set this parameter to json.
key.fields-prefix
Specifies a custom prefix for all Kafka message key fields to avoid name conflicts with message value format fields.
Corresponds to the value of the key.fields-prefix parameter in the catalog configuration.
You must configure this parameter if the message key is not empty. Do not configure this parameter if the message key is empty.
key.fields
The fields where data parsed from the Kafka message key is stored.
The list of parsed key fields is automatically populated.
You must configure this parameter if the message key is not empty and the table is not an Upsert Kafka table. Otherwise, do not configure this parameter.