When you analyze text in social media, forums, or online communications, you may encounter obscure, illogical, or garbled content, which lowers the accuracy of data analysis and further affects the quality of data-driven decision making. This topic describes how to use a natural language processing (NLP) model to identify and filter out garbled text in an Elasticsearch cluster.
Preparations
Upload a model
In this example, the text classification model madhurjindal/autonlp-Gibberish-Detector-492513457 in a library of Hugging Face is used.
Access to Hugging Face over a network in the Chinese mainland is slow. In this example, the model is uploaded to Elasticsearch in offline mode.
Download the model by clicking madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector-492513457.tar.gz.
Upload the model to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Create a folder in the root directory of an ECS instance and upload the model to the folder. Do not upload the model to the /root/ directory of the ECS instance. In this example, a folder named model is created.
The size of the model file is large. We recommend that you use WinSCP to upload the model file. For more information, see Use WinSCP to upload or download a file (on-premises host running the Windows operating system).
Run the following commands in the ECS instance to decompress the model in the model folder:
cd /model/ tar -xzvf madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector-492513457.tar.gz cdRun the following command in the ECS instance to upload the model to the Elasticsearch cluster:
eland_import_hub_model --url 'http://es-cn-lbj3l7erv0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200' \ --hub-model-id '/model/root/.cache/huggingface/hub/models--madhurjindal--autonlp-Gibberish-Detector-492513457/snapshots/c068f552cdee957e45d8773db9f7158d43902244' --task-type text_classification --es-username elastic --es-password **** --es-model-id models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector \
Deploy the model
Log on to the Kibana console of the Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the Kibana console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Analytics > Machine Learning.
icon in the upper-left corner of the Kibana console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Analytics > Machine Learning. In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose Model Management > Trained Models.
Optional. In the upper part of the Trained Models page, click Synchronize your jobs and trained models. In the panel that appears, click Synchronize.
On the Trained Models page, find the uploaded model and click the
 icon in the Actions column to start the model.
icon in the Actions column to start the model. 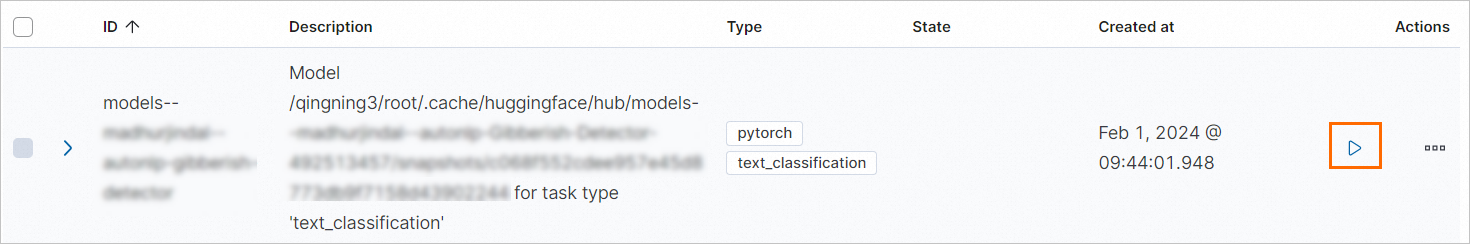
In the dialog box that appears, configure the model and click Start.
If a message indicating that the model is started is displayed in the lower-right corner of the page, the model is deployed.
NoteIf the model cannot be started, the memory of the Elasticsearch cluster may be insufficient. You can start the model again after you upgrade the configuration of the Elasticsearch cluster. In the dialog box that prompts you about the failure, you can click View complete error message to view the failure cause.
Test the model
On the Trained Models page, find the deployed model, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and then click Test model.
icon in the Actions column, and then click Test model. 
In the Test trained model panel, test the model and check whether the output result meets your expectations.
Output description:
word salad: garbled text or terminologies that are disordered or cannot be understood. This metric is used to detect garbled text. A higher metric score indicates a higher probability of garbled text.
In the following sample test, the word salad metric obtains the highest score, which indicates that the test text is very likely to be garbled.
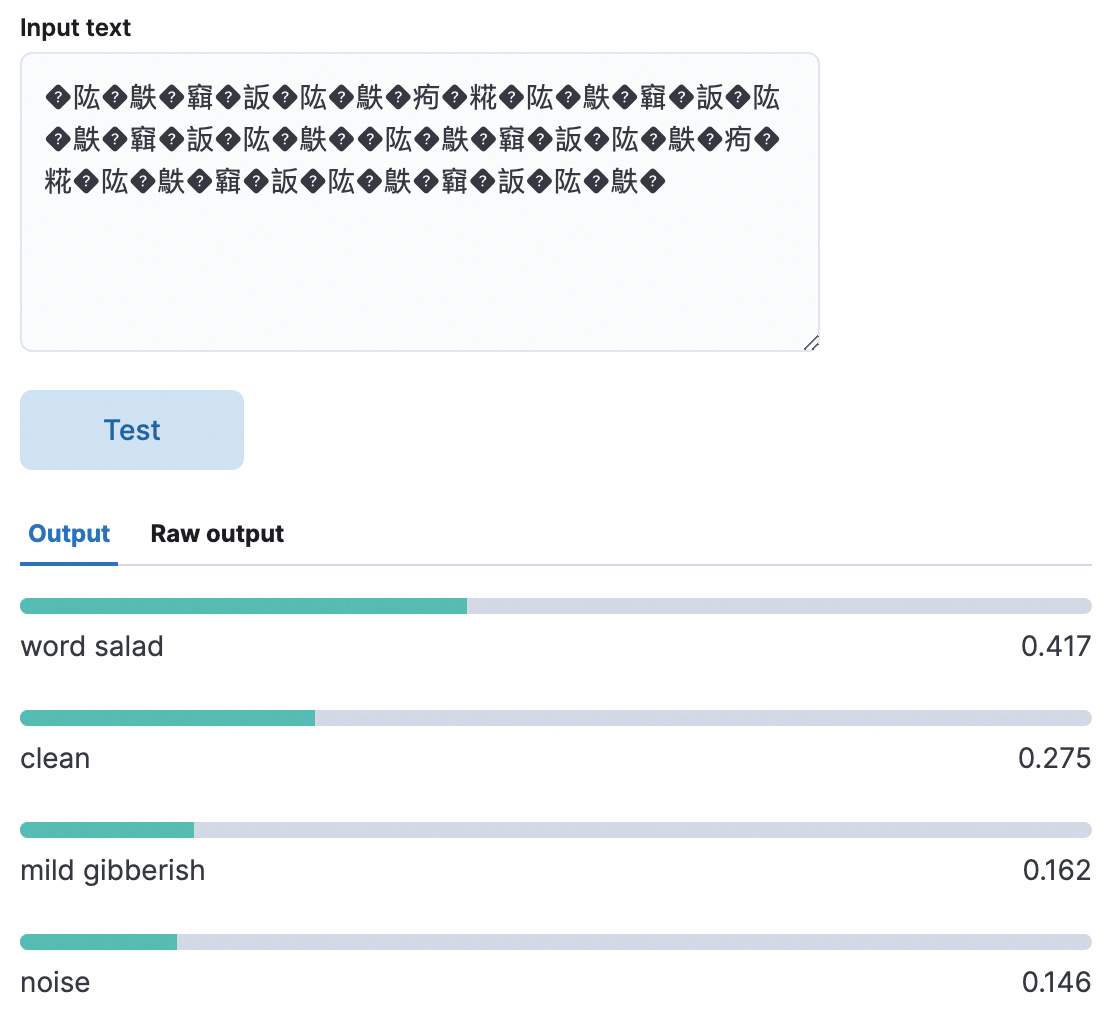
clean: normal text
mild gibberish: possibly gibberish
noise: gibberish
In the following test, the noise metric obtains the highest score, which indicates that the input text is very likely to be gibberish.
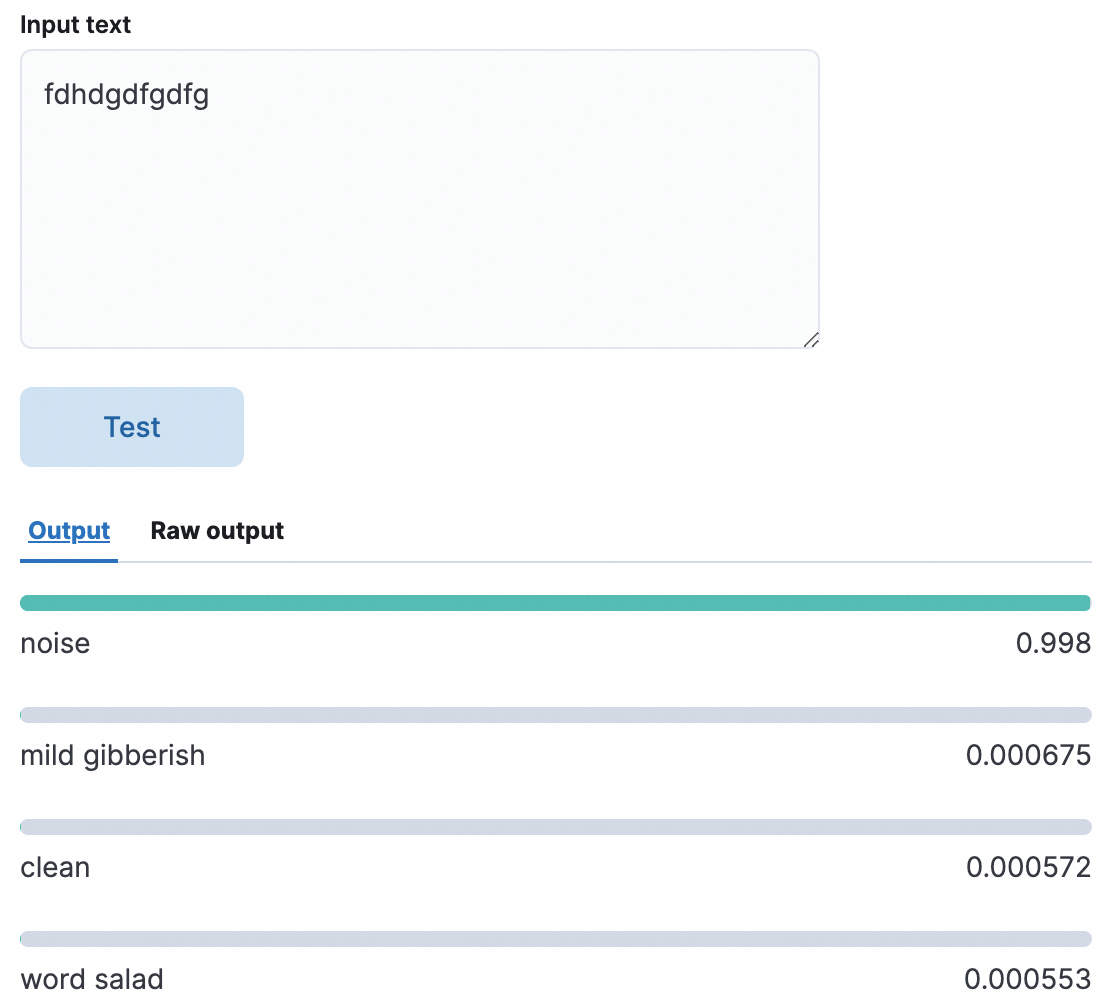
Identify garbled text on the Dev Tools page of the Kibana console
In the upper-left corner of the Kibana console, click the
 icon. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Management > Dev Tools.
icon. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Management > Dev Tools. On the Console tab of the Dev Tools page, run the following code:
1. Create an index. PUT /gibberish_index { "mappings": { "properties": { "text_field": { "type": "text" } } } } 2. Add data. POST /gibberish_index/_doc/1 { "text_field": "how are you" } POST /gibberish_index/_doc/2 { "text_field": "sdfgsdfg wertwert" } POST /gibberish_index/_doc/3 { "text_field": "I am not sure this makes sense" } POST /gibberish_index/_doc/4 { "text_field": "�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�" } POST /gibberish_index/_doc/5 { "text_field": "The test fields." } POST /gibberish_index/_doc/6 { "text_field": "䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�" } 3. Create an ingestion pipeline. Inference processor fields: model_id: the ID of the machine learning model that is used for inference. target_field: the field that is used to store the inference result. field_map.text_field: the field that is used to map the input fields in documents to the fields expected by the model. PUT /_ingest/pipeline/gibberish_detection_pipeline { "description": "A pipeline to detect gibberish text", "processors": [ { "inference": { "model_id": "models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector", "target_field": "inference_results", "field_map": { "text_field": "text_field" } } } ] } 4. Use the pipeline to update documents in the index. POST /gibberish_index/_update_by_query?pipeline=gibberish_detection_pipeline 5. Search for the documents that contain the inference result. GET /gibberish_index/_search { "query": { "exists": { "field": "inference_results" } } } 6. Perform an exact match. inference_results.predicted_value.keyword The value of a field matches "word salad". inference_results.prediction_probability The value of a field is greater than or equal to 0.1. GET /gibberish_index/_search { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "inference_results.predicted_value.keyword": "word salad" } }, { "range": { "inference_results.prediction_probability": { "gte": 0.1 } } } ] } } }The following two data records are returned after you perform an exact match. The word salad metric for the two data records obtains the highest score, which indicates that the two data records are very likely to be garbled.
{ "took": 6, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": { "value": 2, "relation": "eq" }, "max_score": 2.0296195, "hits": [ { "_index": "gibberish_index", "_id": "4", "_score": 2.0296195, "_source": { "text_field": "�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�", "inference_results": { "predicted_value": "word salad", "prediction_probability": 0.37115721979929084, "model_id": "models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector" } } }, { "_index": "gibberish_index", "_id": "6", "_score": 2.0296195, "_source": { "text_field": "䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�", "inference_results": { "predicted_value": "word salad", "prediction_probability": 0.3489011155424212, "model_id": "models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector" } } } ] } }
Use a Python script to identify garbled text
You can also use a Python script to identify garbled text. Run the Python3 command in the ECS instance to load the Python environment. Then, run the following command:
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
es_username = 'elastic'
es_password = '****'
# Use the basic_auth parameter to create an Elasticsearch client instance.
es = Elasticsearch(
"http://es-cn-lbj3l7erv0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200",
basic_auth=(es_username, es_password)
)
# Create an index and configure mappings for the index.
create_index_body = {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"text_field": { "type": "text" }
}
}
}
es.indices.create(index='gibberish_index2', body=create_index_body)
# Insert documents.
docs = [
{"text_field": "how are you"},
{"text_field": "sdfgsdfg wertwert"},
{"text_field": "I am not sure this makes sense"},
{"text_field": "�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�"},
{"text_field": "The test fields."},
{"text_field": "䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�"}
]
for i, doc in enumerate(docs):
es.index(index='gibberish_index2', id=i+1, body=doc)
# Create a processor and a pipeline.
pipeline_body = {
"description": "A pipeline to detect gibberish text",
"processors": [
{
"inference": {
"model_id": "models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector",
"target_field": "inference_results",
"field_map": {
"text_field": "text_field"
}
}
}
]
}
es.ingest.put_pipeline(id='gibberish_detection_pipeline2', body=pipeline_body)
# Use the pipeline to update existing documents.
es.update_by_query(index='gibberish_index2', body={}, pipeline='gibberish_detection_pipeline2')
# Search for the documents that contain the inference result.
search_body = {
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "inference_results"
}
}
}
response = es.search(index='gibberish_index2', body=search_body)
print(response)
# Perform an exact match.
# 1.inference_results.predicted_value.keyword The value of a field matches "word salad".
# 2.inference_results.prediction_probability The value of a field is greater than or equal to 0.1.
search_query = {
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"inference_results.predicted_value.keyword": "word salad"
}
},
{
"range": {
"inference_results.prediction_probability": {
"gte": 0.1
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
response = es.search(index='gibberish_index2', body=search_query)
print(response)The following two data records are returned after you perform an exact match. The word salad metric for the two data records obtains the highest score, which indicates that the two data records are very likely to be garbled.
{
'took': 3,
'timed_out': False,
'_shards': {
'total': 1,
'successful': 1,
'skipped': 0,
'failed': 0
},
'hits': {
'total': {
'value': 2,
'relation': 'eq'
},
'max_score': 2.0296195,
'hits': [{
'_index': 'gibberish_index2',
'_id': '4',
'_score': 2.0296195,
'_source': {
'text_field': '�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�',
'inference_results': {
'predicted_value': 'word salad',
'prediction_probability': 0.37115721979929084,
'model_id': 'models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector'
}
}
}, {
'_index': 'gibberish_index2',
'_id': '6',
'_score': 2.0296195,
'_source': {
'text_field': '䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�痀�糀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�䳀�䇀�䛀�䧀�',
'inference_results': {
'predicted_value': 'word salad',
'prediction_probability': 0.3489011155424212,
'model_id': 'models--madhurjindal--autonlp-gibberish-detector'
}
}
}]
}
}References
Use a client to access an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster