You can use Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch Kernel-enhanced Edition clusters with Indexing Service enabled based on the read and write requirements of your business. You can use the cloud-based write hosting capability of Indexing Service to experience a low-cost and high-performance Elasticsearch service that is suitable for time-series logging scenarios. This service supports the pay-as-you-go billing method and on-demand purchase. This topic describes the scenarios, architecture, benefits, and performance test results of Indexing Service.
Based on a read/write splitting architecture, Elasticsearch Kernel-enhanced Edition clusters with Indexing Service enabled not only offload write operations to Indexing Service, but also provide comprehensive optimizations in terms of hardware selection, cluster architecture, and kernel performance. Indexing Service allows you to evaluate your business requirements from the read and write perspectives and pay for the actual write operations while improving the write performance of a cluster. You are charged based on the actual amount of data written, which eliminates the need to reserve resources based on the peak write throughput of the cluster. This greatly reduces resource costs and O&M costs when you use Elasticsearch in the cloud.
Indexing Service is available in the China (Hong Kong) region. Stay tuned for its availability in other regions.
Scenarios
Indexing Service is suitable for time series data analysis scenarios that have high write transactions per second (TPS), significant fluctuations in write traffic, and low queries per second (QPS), such as log retrieval and analysis, metric monitoring and analysis, and intelligent IoT hardware data collection, monitoring, and analysis.
Data synchronization between a Kernel-enhanced Edition cluster with Indexing Service enabled and a user cluster depends on the apack/cube/metadata/sync task. You can run the GET _cat/tasks?v command to obtain the task information. We recommend that you do not manually clear the task. If the task is cleared, run the POST /_cube/meta/sync command to restore the task at the earliest opportunity. Otherwise, data writes are affected.
Architecture
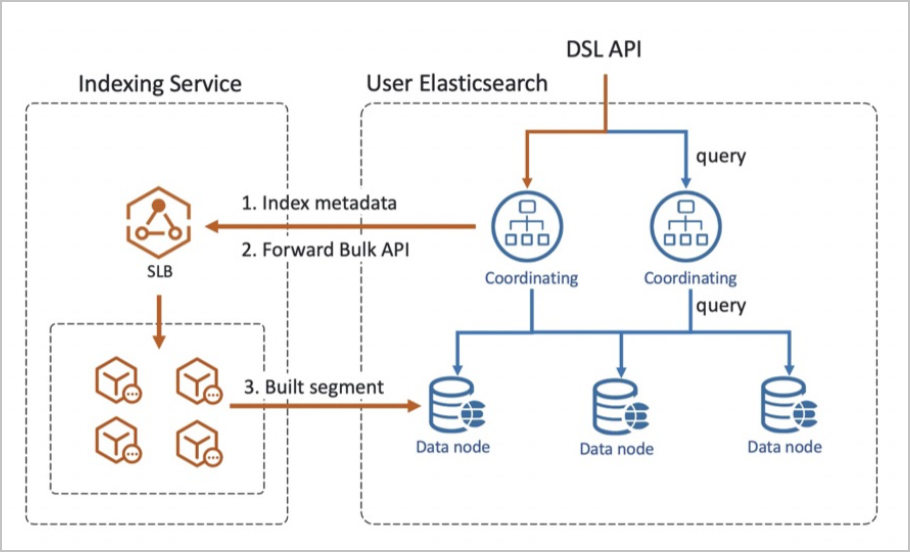
This architecture provides the following benefits:
High performance: Indexing Service provides professional-grade write optimization for index building. By leveraging the features developed by Alibaba Cloud, such as physical replication of indexes, separation of compute and storage, and faster-bulk, Indexing Service significantly enhances write performance. You can experience professional-grade write performance without the need to perform configuration changes.
Low latency: Indexing Service supports real-time cross-cluster physical replication at the segment level to ensure that even under saturated write traffic conditions, the data latency between the user cluster and the write hosting cluster remains in the range of hundreds of milliseconds.
High stability: For geo-disaster recovery, Indexing Service supports multi-cluster backup across different regions. If an exception occurs in a cluster, you can transfer the index of the cluster to another functioning cluster for hosting. This further improves write availability.
Billing
Indexing Service charges fees for write hosting, which includes fees for write traffic and storage space for hosting.
You are charged write hosting fees for an Elasticsearch cluster based on the amount of written data and the amount of storage space used for hosting, regardless of whether the billing method of the cluster is subscription or pay-as-you-go. For more information, see Elasticsearch billing.
You are charged write hosting fees when you use Indexing Service. Indexing Service reduces the costs associated with the resources used to handle write operations in a cluster.
Benefits
Low cost: The cost of computing resources for write operations is reduced by an average of 60%.
Elastic scaling: Write resources are provisioned and managed by Indexing Service in the background to handle fluctuations in write traffic. This allows for elastic scaling of write capabilities in Elasticsearch clusters without the need for data migration, which allows you to easily handle peak loads in logging scenarios.
No O&M required: You do not need to manage the write resources or write load on Elasticsearch clusters. Indexing Service handles all write operations in the cloud, which greatly reduces cluster O&M costs.
Limits
The cloud-based hosting feature provides serverless write service for the Elasticsearch clusters that you create. However, specific limits are imposed on data write and index configuration when you use the feature. The following table describes the limits.
Category | Item | Limits | Remarks |
Cluster | Write traffic | The maximum write throughput is limited to 200 MB/s. | If the limit is exceeded, HTTP status code 429 is returned and the "Inflow Quota Exceed" error message appears. If you require more than 200 MB/s of write throughput, submit a ticket . |
Number of written documents | The maximum number of written documents is limited to 200,000. | If the limit is exceeded, HTTP status code 429 is returned and the "Write QPS Exceed" error message appears. If you need to process more than 200,000 documents per second, submit a ticket . | |
Number of Put Mapping requests | The Put Mapping operation has a rate limit of 50 TPS. | If the limit is exceeded, HTTP status code 429 is returned and the Note Frequent Put Mapping requests consume a large amount of computing resources and greatly affect the stability of the hosting service. We recommend that you define an index template in advance before you write data to reduce the number of Put Mapping operations. | |
Shard | Write traffic | The maximum write traffic without primary keys is 10 MB/s. The maximum write traffic with primary keys is 5 MB/s. | If the limit is exceeded, HTTP status code 429 is returned and the |
Number of written documents | The maximum number of documents that can be written per second is 5,000. | This limit is not strictly imposed. If the limit is reached, the system continues to provide services, but the service quality cannot be guaranteed. | |
Number of shards | Maximum number of shards that can be created for a single index | You can create up to 300 shards for a single index. | None. |
Configuration | index.refresh_interval | In cloud-based hosting clusters, this parameter is automatically configured, and client-side configurations for this parameter do not take effect. | None. |
index.translog.durability | By default, the index.translog.durability parameter is set to async in a cloud-based hosting cluster to enable asynchronous write to translogs. Client-side configurations for this parameter do not take effect. | None. | |
Write parameters such as refresh and merge | By default, write parameters such as refresh and merge are configured for cloud-based hosting clusters. Client-side configurations for the parameters do not take effect. | Default configuration: | |
Index | Lifecycle configuration | You cannot modify the freeze parameter within the index lifecycle. | None. |
Shrink operation | In the context of Indexing Service, a hosted index is incompatible with the shrink operation specified in the Index Lifecycle Management (ILM) action. We recommend that you perform the shrink operation only if the index is not hosted. For more information, see Shrink. | None. | |
Duration after which hosting is canceled | Hosting is automatically disabled for an index three days after the index is hosted. | You can change the duration after which hosting is canceled within the lifecycle of your business data. | |
Ingest Node |
| ||
Performance testing
Test environments
Dataset: nyc_taxis provided by Rally in open source Elasticsearch.
Cluster specifications: three data nodes with 2 cores and 8 GB of memory, three data nodes with 4 cores and 16 GB of memory, and three data nodes with 8 cores and 32 GB of memory.
Index configuration: 15 shards and 1 replica. Asynchronous write to translogs and physical replication are enabled. The refresh_interval parameter is set to 5 seconds.
Test results
Specifications
Cluster edition
Write TPS
Write visibility delay
2 cores, 8 GB memory (for three data nodes)
Standard Edition
24,883
5 seconds
Kernel-enhanced Edition with Indexing Service enabled
226,649
6 seconds
4 cores, 16 GB memory (for three data nodes)
Standard Edition
52,372
5 seconds
Kernel-enhanced Edition with Indexing Service enabled
419,574
6 seconds
8 cores, 32 GB memory (for three data nodes)
Standard Edition
110,277
5 seconds
Kernel-enhanced Edition with Indexing Service enabled
804,010
6 seconds
Test conclusion
Performance comparison results of Kernel-enhanced Edition with Indexing Service enabled and Standard Edition:
For the three nodes with 2 cores and 8 GB of memory, the performance is improved by 910%.
For the three nodes with 4 cores and 16 GB of memory, the performance is improved by 801%.
For the three nodes with 8 cores and 32 GB of memory, the performance is improved by 729%.