You can scale in a Core or Task node group to save resources if your cluster load is low for an extended period and a large amount of cluster resources are idle. You can scale in pay-as-you-go Task node groups in the console. For other types of node groups, such as pay-as-you-go Core node groups, subscription Task node groups, and subscription Core node groups, follow the procedures in this topic.
Limitations
To avoid data loss, if the number of Core nodes in your cluster equals the number of replicas in Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), do not scale in the core node group.
If your cluster is an old version high availability (HA) Hadoop cluster with 2 master nodes, do not scale in the emr-worker-1 node (in old version high availability clusters, Zookeeper is deployed on worker-1).
Precautions
The operations in this topic cannot be rolled back. The components of a service cannot be recovered after you unpublish the components.
This topic describes the best practices for scale-in operations. We recommend that you evaluate the impacts on your business before you scale in a node group and proceed with caution. This can help prevent job scheduling failures and data security risks.
How to select nodes for removal
Scaling in a node group is primarily achieved by removing nodes from the node group. Select the node that you want to remove from your cluster based on the service load of the cluster. You can use one of the following methods to view the resource usage of a cluster and select the node that you want to remove:
Method 1: EMR console Monitoring and Diagnostics
On the Metric Monitoring page, view the AvailableVCores metric on the YARN-Queues dashboard. A consistently high AvailableVCores metric indicates that many cores are available in the queue, and you can consider scaling in the Core or Task node groups.
On the Metric Monitoring page, view the AvailableGB metric in the YARN-NodeManagers dashboard. If the AvailableGB metric for a node remains at a high level for an extended period, this indicates that the node has a large amount of available memory, and you can consider releasing the node.
You can evaluate other metrics in the context of your business requirements.
Method 2: Use the web UI of YARN
View the queue resource usage of a cluster. If the queue resources are often underutilized, consider scaling in the Core or Task node group.

On the Nodes page, sort the nodes by Nodes Address and identify the node that has largest amount of available memory resources. Then, remove the node.

If your cluster is an old version Hadoop cluster, take note of the following items:
If your cluster is a non-high-availability cluster, you cannot remove the emr-worker-1 or emr-worker-2 node from the cluster.
If your cluster is a high availability cluster but the number of master nodes in the cluster is 2, you cannot remove the emr-worker-1 node from the cluster.
Step 1: View the components on the node
When you scale in a Core or Task node group by removing nodes, you must first unpublish the components on those nodes before you can release the corresponding node resources. You can view which components are deployed on each node on the Nodes page in the console.

Step 2: Unpublish the components deployed on nodes
If the following components are deployed on the node that you want to remove, you must unpublish the components before you remove the nodes. If you remove the node on which following components are deployed without unpublishing the components, jobs that run on the node may fail and data security risks may occur.
Unpublish the NodeManager component of the YARN service
Go to the Status tab of the YARN service page.
Log on to the EMR console. In the left-side navigation pane, click EMR on ECS.
In the top navigation bar, select a region and a resource group as needed.
On the EMR on ECS page, find the target cluster and click Services in the Actions column.
On the Cluster Services page, click Status in the YARN service area.
Unpublish the NodeManager component that is deployed on a desired node.
In the Components list, click in the Actions column for NodeManager.
In the dialog box that appears, select , enter Execution Reason, and click OK.
In the pop-up dialog box, click OK.
Click Operation History in the upper-right corner to view the operation progress.
Unpublish the DataNode component of the HDFS service
Log on to the master node of the cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Switch to the hdfs user and view the number of NameNodes.
sudo su - hdfs hdfs haadmin -getAllServiceStateLog on to the nodes on which NameNode is deployed in SSH mode and add the nodes whose DataNode component you want to unpublish to the dfs.exclude file. We recommend that you add only one node at a time.
Hadoop clusters
touch /etc/ecm/hadoop-conf/dfs.exclude vim /etc/ecm/hadoop-conf/dfs.excludeIn vim, press
oto start a new line and enter the hostname of the DataNode that you want to unpublish.emr-worker-3.cluster-xxxxx emr-worker-4.cluster-xxxxxNon-legacy Hadoop clusters
touch /etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/dfs.exclude vim /etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/dfs.excludeEnter
oto insert a new line and enter the hostname of the DataNode that you want to unpublish.core-1-3.c-0894dxxxxxxxxx core-1-4.c-0894dxxxxxxxxx
Switch to the hdfs user on a node on which NameNode is deployed and run the following commands. Then, HDFS automatically starts to unpublish the DataNode component.
sudo su - hdfs hdfs dfsadmin -refreshNodesConfirm the result.
Run the following command to determine whether the offline process is complete.
hadoop dfsadmin -reportIf the status is Decommissioned, the data of the DataNode component is migrated to other nodes and the DataNode component is unpublished.
Unpublish the Backend component of the StarRocks service
Log on to the cluster and use a client to access it. For more information, see Quick Start.
Run the following command to unpublish the BE node using the
DECOMMISSIONmethod.ALTER SYSTEM DECOMMISSION backend "be_ip:be_heartbeat_service_port";Replace the following parameters as needed:
be_ip: The internal IP address of the BE node that you want to scale in. You can find the IP address on the Nodes page.be_heartbeat_service_port: The default value is 9050. You can run theshow backendscommand to view the port.
If Decommission is slow, you can use the
DROPmethod to unpublish the BE by force.ImportantIf you use the
DROPmethod to unpublish the BE node, ensure that the system has three complete replicas.ALTER SYSTEM DROP backend "be_ip:be_heartbeat_service_port";Run the following command to check the status of the BE node:
show backends;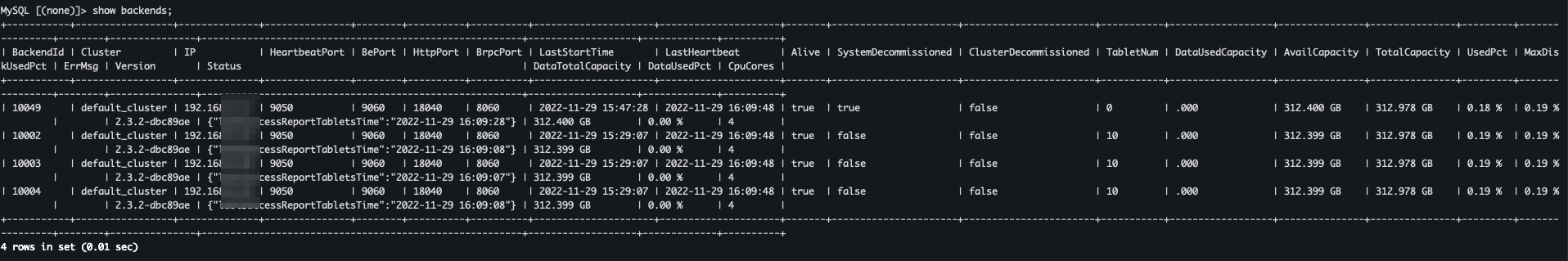
If the value in the SystemDecommissioned column is true, the BE nodes are being removed. If the value in the TabletNum column is 0, the system cleans up the metadata.
If the BE nodes are not displayed in the preceding figure, the nodes are successfully removed.
Unpublish the HRegionServer component of the HBase service
Go to the Status tab of the HBase service page.
Log on to the EMR console. In the left-side navigation pane, click EMR on ECS.
In the top menu bar, select a region and a resource group as needed.
On the EMR on ECS page, find the desired cluster and click Services in the Actions column.
On the Cluster Services page, click Status in the HBase service area.
Unpublish the HRegionServer component that is deployed on the desired node.
In the Components section, click Stop in the Actions column of HRegionServer.
In the dialog box, select , enter the Execution Reason, and click OK.
In the dialog box, click OK.
Click Operation History in the upper-right corner to view the operation progress.
Unpublish the DataNode component of the HBase-HDFS service
Log on to the master node of the cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Run the following commands to switch to the hdfs user and set the environment variable:
sudo su - hdfs export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/namenodeRun the following command to view information about the NameNode:
hdfs dfsadmin -reportLog on to the nodes on which NameNode is deployed in SSH mode and add the nodes on which you want to unpublish the DataNode component to the dfs.exclude file. We recommend that you add only one node at a time.
touch /etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/dfs.exclude vim /etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/dfs.excludeIn vim, press
oto start a new line and enter the hostname of the DataNode that you want to unpublish.core-1-3.c-0894dxxxxxxxxx core-1-4.c-0894dxxxxxxxxxSwitch to the hdfs user on a node on which NameNode is deployed and run the following commands. Then, HDFS automatically starts to unpublish the DataNode component.
sudo su - hdfs export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/etc/taihao-apps/hdfs-conf/namenode hdfs dfsadmin -refreshNodesConfirm the result.
Run the following command to check whether the DataNode component is unpublished:
hadoop dfsadmin -reportIf the status is Decommissioned, the data of the DataNode component is migrated to other nodes and the DataNode component is unpublished.
Unpublish the JindoStorageService component of the SmartData service (Hadoop clusters)
Go to the Status tab of the SmartData service page.
Log on to the EMR console. In the left-side navigation pane, click EMR on ECS.
In the top menu bar, select a region and a resource group as needed.
On the EMR on ECS page, click Services in the Actions column of the target cluster.
On the Cluster Services page, click Status in the SmartData service area.
Unpublish the JindoStorageService component that is deployed on a desired node.
In the Components List, click in the Actions column of JindoStorageService.
In the dialog box that appears, select , enter the Execution Reason, and click OK.
In the pop-up dialog box, click OK.
Click Operation History in the upper-right corner to view the operation progress.
Step 3: Release the node
To remove nodes in a node group of your EMR cluster, you must go to the ECS console to release the ECS instance that corresponds to the nodes. If you want to perform this operation as a RAM user, you must have the required ECS permissions. We recommend that you attach the AliyunECSFullAccess policy to the RAM user.
Go to the Nodes tab.
Log on to the EMR console. In the left-side navigation pane, click EMR on ECS.
In the top navigation bar, select a region and a resource group as needed.
On the EMR on ECS page, find the desired cluster and click Nodes in the Actions column.
On the Nodes page, click the ECS ID of the node that you want to release.
You are navigated to the Elasitc Compute Service (ECS) console.
Release the instance in the ECS console. For more information, see Release an instance.
References
For information about how to scale in a Task node group that contains pay-as-you-go or preemptible instances, see Scale in a cluster.
If your cluster has insufficient computing resources, you can scale out the Core and Task node groups. For more information, see Scale out a cluster.
If you want to automatically adjust cluster computing resources as needed, you can set managed auto scaling or custom auto scaling rules for your node groups. For more information, see Auto Scaling.