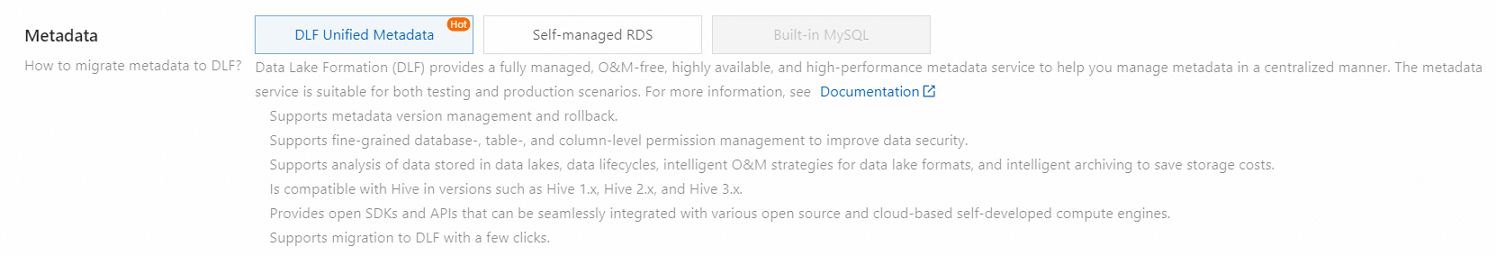
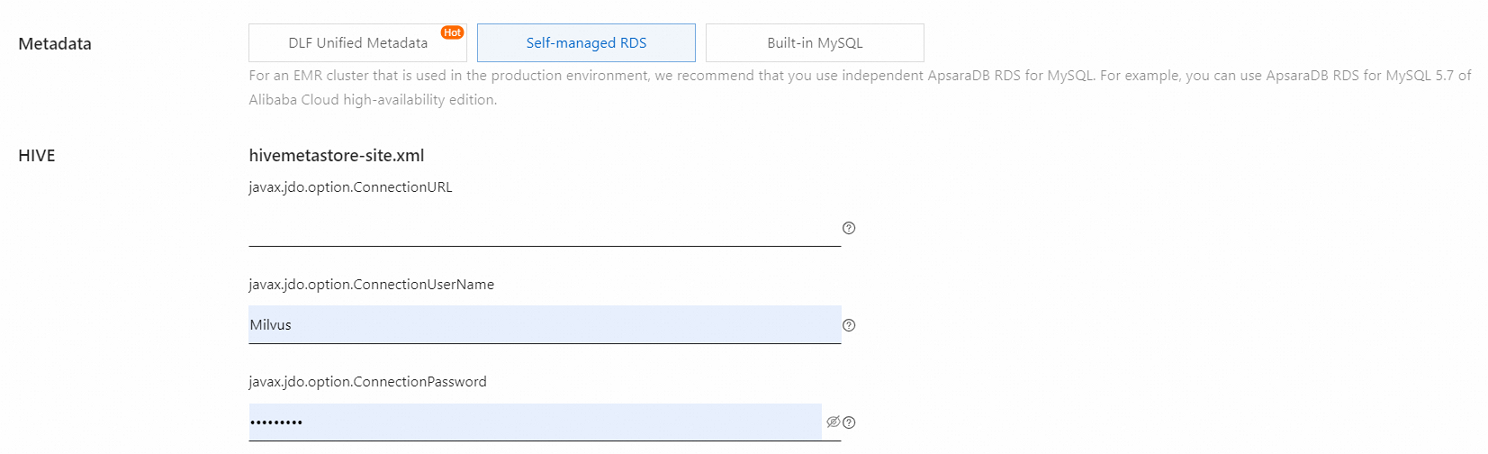
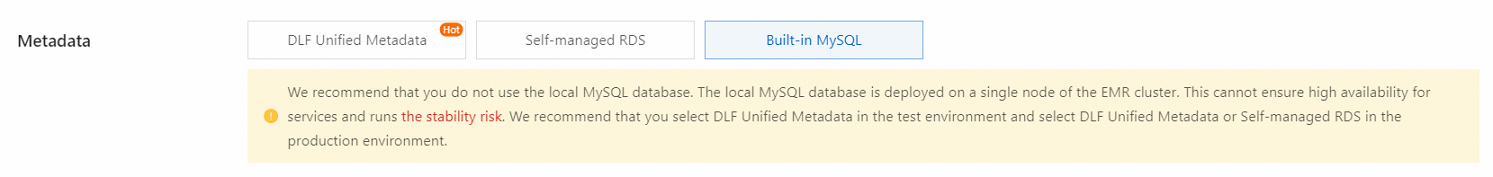
You can call the CreateCluster operation to create an E-MapReduce (EMR) cluster. You must configure a large number of parameters when you call the CreateCluster operation to create a cluster. The most complex and important parameters are Applications and ApplicationConfigs. This topic describes how to configure the core parameters when you call the CreateCluster operation to create an EMR cluster.
RegionId
The region ID. The following tables describe the regions supported by EMR.
Regions in China
Region name
Region ID
China (Hangzhou)
cn-hangzhou
China (Shanghai)
cn-shanghai
China (Qingdao)
cn-qingdao
China (Beijing)
cn-beijing
China (Zhangjiakou)
cn-zhangjiakou
China (Hohhot)
cn-huhehaote
China (Ulanqab)
cn-wulanchabu
China (Shenzhen)
cn-shenzhen
China (Chengdu)
cn-chengdu
China (Hong Kong)
cn-hongkong
China North 2 Ali Gov 1
cn-north-2-gov-1
Regions outside China
Region name
Region ID
Japan (Tokyo)
ap-northeast-1
Singapore
ap-southeast-1
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
ap-southeast-3
Indonesia (Jakarta)
ap-southeast-5
Germany (Frankfurt)
eu-central-1
UK (London)
eu-west-1
US (Silicon Valley)
us-west-1
US (Virginia)
us-east-1
UAE (Dubai)
me-east-1
SAU (Riyadh)
me-central-1
Example: cn-hangzhou.
ResourceGroupId
Optional. The resource group ID. Example: rg-acfmzabjyop****.
PaymentType
The billing method of the cluster. Valid values:
PayAsYouGo
Subscription
The following figure shows the corresponding configuration in the EMR console.
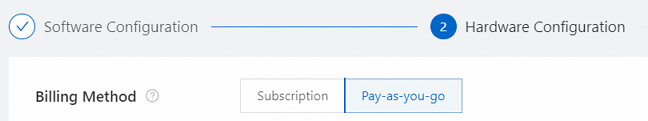
Example: PayAsYouGo.
SubscriptionConfig
This parameter takes effect only if you set the PaymentType parameter to Subscription. For more information, see SubscriptionConfig.
The following figure shows the corresponding configuration in the EMR console.

ClusterType
The cluster type. Valid values:
DATALAKE: DataLake cluster.
OLAP: online analytical processing (OLAP) cluster.
DATAFLOW: Dataflow cluster.
DATASERVING: DataServing cluster.
CUSTOM: custom cluster.
HADOOP: Hadoop cluster in the original data lake scenario. We recommend that you set this parameter to DATALAKE rather than HADOOP.
The following figure shows the corresponding configuration in the EMR console.
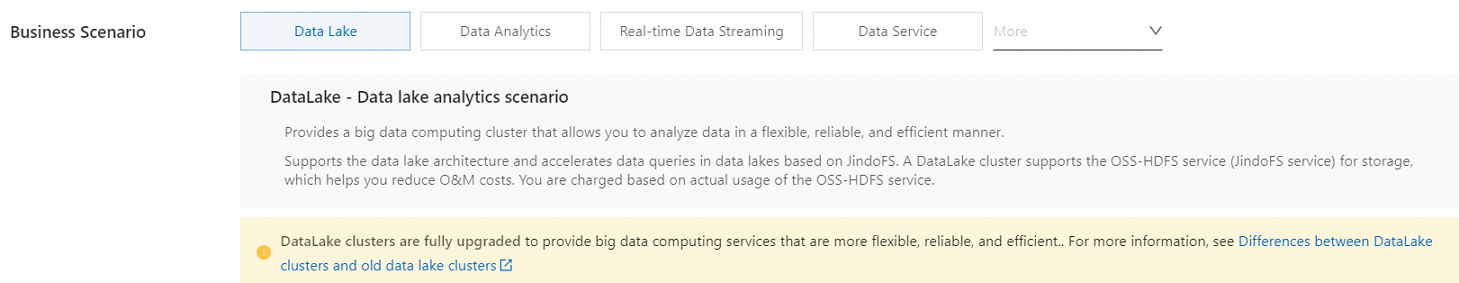
Example: DATALAKE.
ReleaseVersion
The EMR version. You can query available EMR versions in the EMR console or by calling the ListReleaseVersions operation.
The following figure shows the corresponding configuration in the EMR console.
Example: EMR-5.16.0.
ClusterName
The cluster name. The name must be 1 to 128 characters in length. The name must start with a letter but cannot start with http:// or https://. The name can contain letters, digits, colons (:), underscores (_), periods (.), and hyphens (-).
Example: emrtest.
DeployMode
The deployment mode of master nodes in the cluster. Valid values:
NORMAL: regular mode. A cluster that contains only one master node is created.
HA: high availability (HA) mode. A cluster that contains three master nodes is created.
The following figure shows the configuration of enabling the HA mode in the EMR console.
Example: NORMAL.
SecurityMode
The security mode of the cluster. Valid values:
NORMAL: disables Kerberos authentication for the cluster.
KERBEROS: enables Kerberos authentication for the cluster.
The following figure shows the configuration of enabling Kerberos authentication in the EMR console.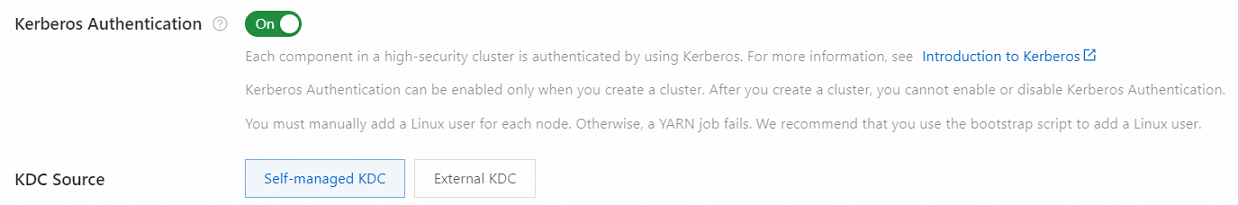
Example: NORMAL.
Applications
The following figure shows the services that can be deployed in a DataLake cluster.

In EMR, some services are mutually dependent or mutually exclusive.
Service dependency: Service A depends on Service B. In this case, if you want to deploy Service A in your cluster, you must also deploy Service B. For example, Hive depends on YARN. If you want to deploy Hive, you must also deploy YARN.
Service exclusion: Service A and Service B are mutually exclusive. If you want to deploy Service A, you cannot deploy Service B. For example, Spark 2 and Spark 3 are mutually exclusive. If you want to deploy Spark 2, you cannot deploy Spark 3.
Service deployment of HA clusters
Service to deploy | Dependency | Exclusive service |
HDFS | Hadoop-Common and ZooKeeper | OSS-HDFS |
OSS-HDFS | Hadoop-Common | HDFS |
Hive | Hadoop-Common, YARN, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Spark 2 | Hadoop-Common, YARN, Hive, and ZooKeeper | Spark 3 |
Spark 3 | Hadoop-Common, YARN, Hive, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | Spark 2 |
Tez | Hadoop-Common, YARN, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Trino | Hadoop-Common | None |
Flume | Hadoop-Common | None |
Kyuubi | Hadoop-Common, YARN, Hive, Spark 3, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
YARN | Hadoop-Common, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Impala | Hadoop-Common, YARN, Hive, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Ranger | Hadoop-Common and Ranger-plugin | None |
Presto | Hadoop-Common | None |
Sqoop | Hadoop-Common, YARN, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Knox | OpenLDAP | None |
StarRocks 2 | None | StarRocks 3 |
StarRocks 3 | None | StarRocks 2 |
ClickHouse | ZooKeeper | None |
Flink | Hadoop-Common, YARN, OpenLDAP, ZooKeeper, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
HBase | Hadoop-Common, HDFS or OSS-HDFS, and ZooKeeper | None |
Phoenix | Hadoop-Common, HDFS or OSS-HDFS, ZooKeeper, and HBase | None |
Service deployment of non-HA clusters
If you set the DeployMode parameter to NORMAL, the cluster is a non-HA cluster. The following table describes the dependencies and exclusions between services.
Service to deploy | Dependency | Exclusive service |
HDFS | Hadoop-Common | OSS-HDFS |
OSS-HDFS | Hadoop-Common | HDFS |
Hive | Hadoop-Common and YARN | None |
Spark 2 | Hadoop-Common, YARN, and Hive | Spark 3 |
Spark 3 | Hadoop-Common, YARN, and Hive | Spark 2 |
Tez | Hadoop-Common, YARN, and HDFS or OSS-HDFS | None |
Trino | Hadoop-Common | None |
Flume | Hadoop-Common | None |
Kyuubi | Hadoop-Common, YARN, Hive, Spark 3, and ZooKeeper | None |
YARN | Hadoop-Common | None |
Impala | Hadoop-Common, YARN, and Hive | None |
Ranger | Hadoop-Common and Ranger-plugin | None |
Presto | Hadoop-Common | None |
Sqoop | Hadoop-Common and YARN | None |
Knox | OpenLDAP | None |
StarRocks 2 | None | StarRocks 3 |
StarRocks 3 | None | StarRocks 2 |
ClickHouse | ZooKeeper | None |
Flink | Hadoop-Common, YARN, and OpenLDAP | None |
HBase | Hadoop-Common, HDFS or OSS-HDFS, and ZooKeeper | None |
Phoenix | Hadoop-Common, HDFS or OSS-HDFS, ZooKeeper, and HBase | None |
ApplicationConfigs
The following tables describe the required configurations of the ApplicationConfigs parameter for different types of clusters.
Replace ${Parameter name} with the actual value based on your business requirements.
DataLake cluster
Scenario | Required configuration | Description |
OSS-HDFS is deployed. | |
|
DLF is used to store metadata. | In EMR V3.43.0 and later V3.X.X versions and EMR V5.9.0 and later V5.X.X versionsIn EMR V3.42.0 and earlier V3.X.X versions and EMR V5.8.0 and earlier V5.X.X versions |
|
ApsaraDB RDS is used to store metadata. | |
|
Built-in MySQL is used to store metadata. | | hive.metastore.type: the metadata storage type. The value of this parameter is LOCAL, which corresponds to Built-in MySQL of the Metadata parameter in the EMR console.
|
OLAP cluster
Scenario | Required configuration | Description |
ClickHouse is deployed. | | The following figure shows the corresponding configuration in the EMR console.
Important Make sure that the following condition is met: |
StarRocks 2 is deployed and is connected to Data Lake Formation (DLF). | |
|
StarRocks 3 is deployed and is connected to DLF. | |
|
Dataflow cluster
Scenario | Required configuration | Description |
OSS-HDFS is deployed. | |
|
Flink is deployed and is connected to DLF. | |
|
DataServing cluster
Scenario | Required configuration | Description |
OSS-HDFS is deployed. | |
|
OSS-HDFS and HBase are deployed, and HBase is used to store logs. | | The value of the hbase.wal.mode parameter is HDFS, which corresponds to the selection of the Use HDFS as HBase HLog Storage check box in the EMR console.
|
Custom cluster
The required configurations of the ApplicationConfigs parameter for custom clusters are the same as those for other types of clusters.
NodeAttributes
Required. Configure parameters related to Elastic Compute Service (ECS). For more information, see NodeAttributes.
Parameter | Description |
VpcId | The virtual private cloud (VPC) ID of the cluster. Example: vpc-bp1tgey2p0ytxmdo5****. |
ZoneId | The zone ID. Example: ch-hangzhou-h. |
SecurityGroupId | The security group ID. Only basic security groups are supported. Example: sg-hp3abbae8lb6lmb1****. |
RamRole | The RAM role that you want to assign to EMR to access other Alibaba Cloud resources from ECS. Default value: AliyunECSInstanceForEMRRole. |
KeyPairName | The name of the key pair that is used to log on to the ECS instance in SSH mode. |
MasterRootPassword | The initial password of the root user on the master node. This password is used only when the ECS instance is created. You can use the password the first time you configure and verify the identity of the root user. |
NodeGroups
Required. The node groups of the cluster. For more information, see NodeGroupConfig.
BootstrapScripts
Optional. The bootstrap actions of the cluster. For more information, see Script.
Tags
Optional. The tags that you want to add to the cluster. For more information, see Tag.
ClientToken
Optional. The client token that is used to ensure the idempotence of the request. You can configure this parameter to prevent repeated calls to create clusters. The same ClientToken value for multiple calls to the CreateCluster operation results in identical responses. Only one cluster can be created by using the same ClientToken value.
References
For more information about the CreateCluster operation, see CreateCluster.