An elastic IP address (EIP) is a NAT IP address that resides on the Internet gateway Alibaba Cloud. An EIP is mapped to the associated resource by using the NAT method. Therefore, you cannot query the EIP on the network interface controller (NIC) of an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance. This topic describes how to expose an EIP on an NIC by adding a secondary CIDR block to a virtual private cloud (VPC). The EIP is specified as the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary elastic network interface (ENI).Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Background information
EIPs function as NAT IP addresses. In NAT mode, EIPs reside on gateways instead of the ENIs of ECS instances. Therefore, you can query only private IP addresses and cannot query EIPs on the operating system. Administrators must manually maintain the mappings between ENIs and EIPs or between servers and EIPs. In addition, EIPs that are associated with resources in NAT mode do not support protocols such as H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Domain Name System (DNS), or Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP).
Scenarios
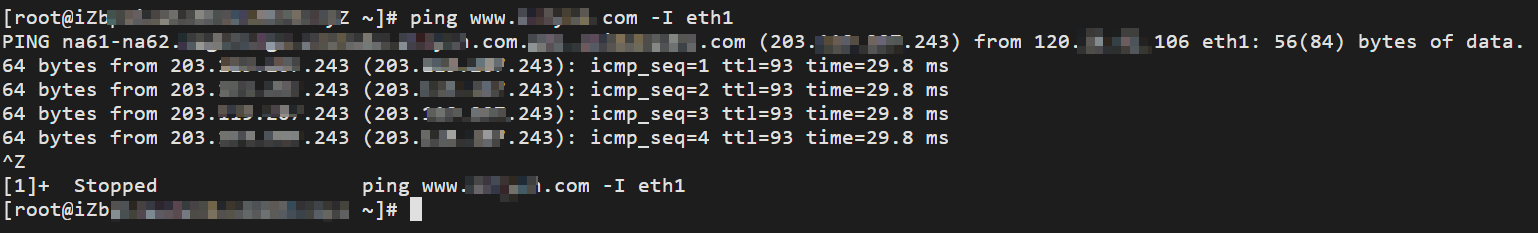
The following scenario is used as an example. A company created a VPC and a vSwitch (vSwitch 1) on Alibaba Cloud. An ECS instance is deployed in vSwitch 1. vSwitch 1 is deployed in Zone A. Due to business growth, the company wants the ECS instance to access the Internet and the IT engineers need to view the network configurations of the ECS instance.
To meet the preceding requirements, you must create the following resources:
A secondary IPv4 CIDR block for the VPC and vSwitch 2: Specify the CIDR block of an EIP as the secondary IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC. Then, create vSwitch 2 in the specified CIDR block. You must deploy vSwitch 2 in Zone A where vSwitch 1 resides.
A secondary ENI: Create a secondary ENI in vSwitch 2, and then specify the EIP as the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI.
After you create the secondary ENI, associate the secondary ENI with the EIP. Then, associate the secondary ENI with the ECS instance in Zone A. After you complete the preceding operations, the EIP is used as the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI. You can view the EIP on the NIC of the operating system.
The following table describes the networking details.
Parameter | CIDR block | |
EIP | 120.XX.XX.106 | |
Primary CIDR block of the VPC | Primary CIDR block | 10.0.0.0/8 |
vSwitch 1 | 10.0.0.0/24 | |
Private IPv4 address of the primary ENI | 10.0.0.202 | |
Secondary IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC | Secondary IPv4 CIDR block | 120.XX.XX.0/24 |
vSwitch 2 | 120.XX.XX.0/25 | |
Primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI | 120.XX.XX.106 | |
Limits
After you perform the operations described in this topic, ECS instances in the same VPC can communicate with each other through private IP addresses. However, these ECS instances cannot communicate with each other through public IP addresses.
The EIP must fall within the IP address range of the vSwitch to which the secondary IPv4 CIDR block belongs, and cannot be the system-reserved IP address. For example, a secondary CIDR block is added to a vSwitch whose CIDR block is 47.XX.XX.0/24. The IP address range of the vSwitch is 47.XX.XX.1 to 47.XX.XX.254. If the EIP is 47.XX.XX.255 (not within the IP address range) or 47.XX.XX.254 (the system-reserved IP address), the EIP cannot be assigned as the primary private IP address of the secondary ENI.
Preparations
A VPC and vSwitch 1 are created. vSwitch 1 is deployed in Zone A. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
An ECS instance is attached to vSwitch 1. For more information, see Create an instance by using the wizard.
Make sure that the security group rules of the ECS instance allow the ECS instance to access the Internet. For more information, see Overview.
An EIP is created for Internet access. For more information, see Apply for EIPs.
Procedure
Step 1: Add a secondary IPv4 CIDR block to the VPC
Specify the CIDR block of the EIP as the secondary IPv4 CIDR block of the VPC.
Log on to the VPC console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the VPC is created.
On the VPC page, find the VPC that you want to manage, and click the ID of the VPC.
On the VPC Details page, click the CIDR Block Management tab and click Add Secondary IPv4 CIDR Block.
In the Add Secondary CIDR Block dialog box, set the following parameters and click OK.
This topic describes only the key parameters. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
Parameter
Description
VPC
Displays the VPC to which you want to add the secondary IPv4 CIDR block.
Secondary CIDR Block
Select a method to configure the secondary IPv4 CIDR block:
Default CIDR Block
Custom CIDR Block
In this example, Custom CIDR Block is selected and the CIDR block 120.XX.XX.0/24 of the EIP is used.
Step 2: Create a vSwitch in the secondary IPv4 CIDR block
Create vSwitch 2 in the secondary IPv4 CIDR block.
Log on to the VPC console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click vSwitch.
Select the region of the VPC for which you want to create a vSwitch.
On the vSwitch page, click Create vSwitch.
On the Create vSwitch page, set the following parameters and click OK.
This topic describes only the key parameters. For more information, see Create a vSwitch.
Parameter
Description
VPC
Select the VPC in which you want to deploy vSwitch 2.
In this example, the VPC in which the ECS instance is deployed is selected.
IPv4 CIDR Block
Specify the CIDR block of vSwitch 2.
In this example, the IPv4 CIDR block created in Step 1: Add a secondary IPv4 CIDR block to the VPC is used.
Zone
Select the zone in which you want to deploy vSwitch 2. vSwitches that are deployed in different zones of the same VPC can communicate with each other.
In this example, Zone A where the ECS instance is deployed is selected.
IPv4 CIDR Block
Specify the IPv4 CIDR block of vSwitch 2.
In this example, 120.XX.XX.0/25 is specified. The CIDR block is a subset of the secondary IPv4 CIDR block.
Step 3: Create a secondary ENI
Create a secondary ENI in vSwitch 2, and then allocate the EIP to the secondary ENI so that the EIP can serve as the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI.
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click Create ENI. On the Create ENI page, set the following parameters and click Create ENI.
This topic describes only the key parameters. For more information, see Create and manage ENIs.
Parameter
Description
VPC
Select the VPC of the ECS instance that you want to associate with the secondary ENI. After an ENI is created, you cannot change the VPC of the ENI.
In this example, the VPC in which the ECS instance is deployed is selected.
vSwitch
Select the vSwitch of the ECS instance that you want to associate with the secondary ENI. After an ENI is created, you cannot change the vSwitch of the ENI.
In this example, vSwitch 2 created in Step 2: Create a vSwitch in the secondary IPv4 CIDR block is selected.
NoteAn ENI can be associated with only an ECS instance that is deployed in the same zone as the ENI. The ECS instance and the ENI can be attached to different vSwitches.
Security Group
Select security groups in the specified VPC. You can select one to five security groups.
In this example, the security group that applies to the ECS instance is selected.
NoteIf no security group is configured for the ECS instance, take note of the following items:
You cannot select basic security groups and advanced security groups at the same time.
You cannot select managed security groups that are used by other cloud services.
Make sure that the security group rules allow requests from the IP addresses of the ECS instance and the secondary ENI.
Make sure that the security group rules allow the secondary ENI to access the Internet.
For more information, see Overview.
Primary Private IP Address
Enter the primary private IPv4 address of the ENI. The IPv4 address must be an idle IP address within the CIDR block of the vSwitch. If you do not specify an IPv4 address, an idle private IPv4 address is automatically assigned to your ENI after the ENI is created.
In this example, the EIP 120.XX.XX.106 is used.
Step 4: Associate the EIP with the secondary ENI
Log on to the Elastic IP Address console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the EIP is created.
On the Elastic IP Addresses page, find the EIP that you created and click Associate with Resource in the Actions column.
In the Associate EIP with Resource dialog box, set the following parameters and click OK.Associate with Resource
This topic describes only the key parameters. For more information, see Associate a secondary ENI in NAT mode.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select Secondary ENI.
Mode
In this example, NAT Mode is selected.
Select an instance to associate
In this example, the secondary ENI created in Step 3: Create a secondary ENI is selected.
Step 5: Associate the secondary ENI with the ECS instance
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the ECS instance is deployed.
On the Instance page, find the ECS instance and choose in the Actions column.
In the Bind Secondary ENI dialog box, select the secondary ENI that you created in Step 3: Create a secondary ENI and click Confirm.
Configure the secondary ENI on the ECS instance.
After you associate the secondary ENI with the ECS instance, some images may fail to identify the IP address of the ENI or add routes. As a result, the secondary ENI cannot work as expected. In this case, you need to configure the secondary ENI on the ECS instance so that the IP address of the ENI can be identified.
For more information about how to check whether an ECS instance image supports the associated secondary ENI and how to configure an secondary ENI on an ECS instance, see Configure a secondary ENI.
Step 6: Test the network connectivity
Log on to the ECS instance.
For more information, see Connect to an ECS instance.
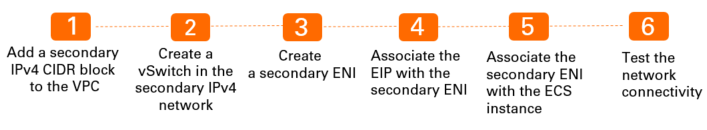
Run the following command to query the network configurations of the ECS instance.
ifconfigThe EIP is used as the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI and is exposed on the NIC in the operating system of the ECS instance.
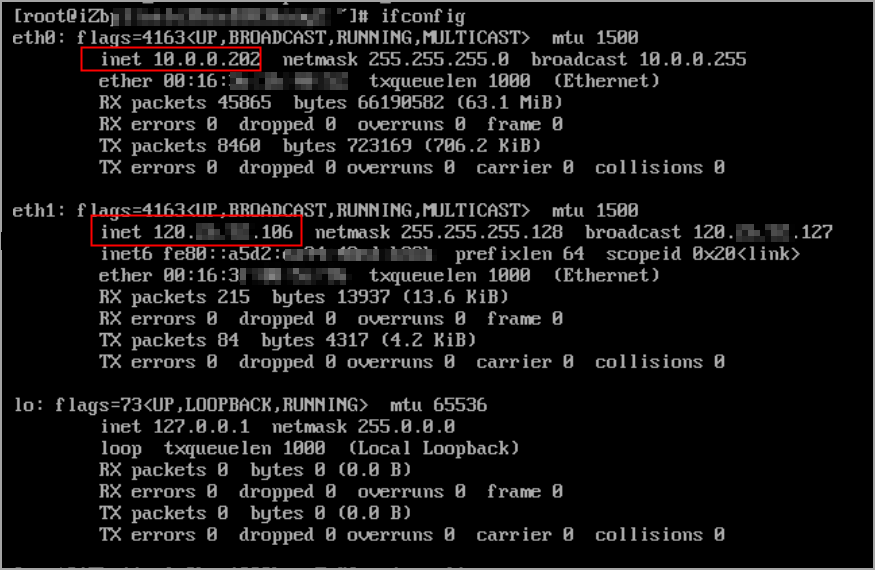
Run the following command to test the network connectivity between the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI and a network.
ping <Destination network> -I <Primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI>The result shows that the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI can reach the destination network. This indicates that the ECS instance can use the primary private IPv4 address of the secondary ENI to access the Internet.