Alibaba Cloud Bastionhost provides a unified operations and maintenance (O&M) entry point, fine-grained permission control, and end-to-end operation audits. This helps you secure your Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances and meet the core Multi-Level Protection Scheme (MLPS) 2.0 Level 3 requirements for identity authentication, access control, and audit trails.
Security risks
Traditional O&M methods, such as allowing O&M engineers to directly access servers from the Internet or an office network using the Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), present several risks that are difficult to control:
Unknown identities and permission abuse: When local server accounts, such as root or Administrator, or shared accounts are used for O&M, it is impossible to accurately identify the operator. If credentials for a high-privilege account are leaked, an attacker can obtain direct access and abuse permissions to perform malicious operations. This makes it difficult to determine who is responsible.
Operation black hole: Operations performed locally on a server are often not fully recorded unless complex audit tools are configured. After a security incident, the lack of detailed evidence, such as operation logs and screen recordings, makes it impossible to trace the incident to the responsible person. This also makes it difficult to analyze the attack path and determine the extent of the loss.
Chaotic credential management and leakage risks: When O&M engineers manage hundreds or thousands of servers, they must manage numerous passwords and keys. This often leads to insecure practices, such as using weak passwords, reusing passwords, or storing credentials in insecure locations. These practices greatly increase the risk of credential leakage.
Breeding ground for lateral movement: If an attacker gains access to a server through a compromised jump server or an O&M engineer's PC, they can use that server as a foothold. From there, they can launch lateral movement attacks across the internal network and compromise more core systems.
Sensitive data leakage: Uncontrolled O&M channels allow O&M engineers or attackers to easily download sensitive core data to local machines using file transfers or database exports, which can lead to a data breach.
Best practices
You can use Bastionhost to centrally manage your ECS instance assets, configure security groups to restrict access, manage O&M engineer accounts and permissions, and audit all user operations. This ensures that users can log on to systems only through Bastionhost.
Plan and deploy Bastionhost
Go to the Bastionhost purchase page to purchase an instance and select specifications based on your business needs. Then, enable the instance in the Bastionhost console. For more information, see Purchase and log on to a Bastionhost instance.
Design a deny by default network access policy
You can enforce a network-layer rule that requires all traffic to pass through Bastionhost.
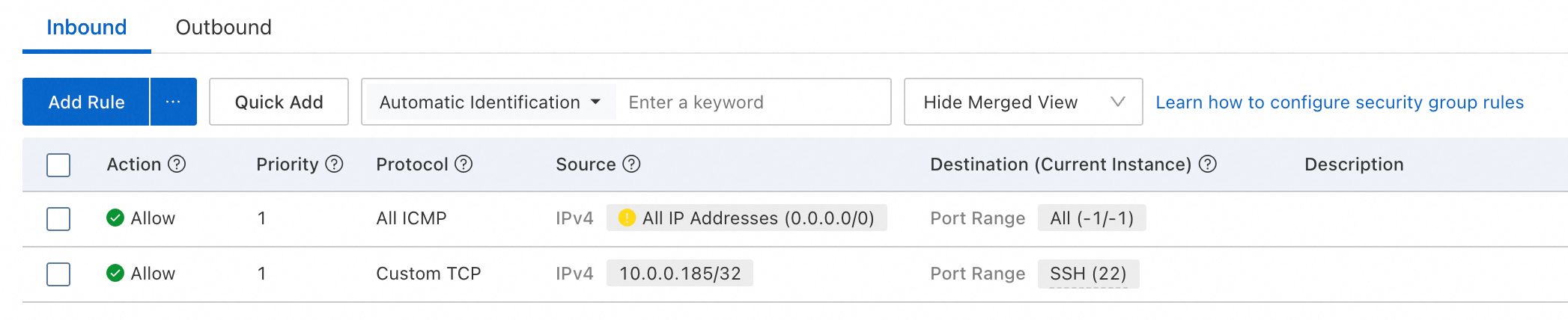
Create a dedicated security group: Create or use a dedicated security group for your ECS instances. Configure its inbound rules to deny all external access by default, especially to the SSH (port 22) and RDP (port 3389) ports.
Configure exception rules to allow access: In the security group, add an inbound rule that allows traffic only from the Bastionhost egress IP address to access the O&M ports of the destination ECS instances, such as port 22 and port 3389.
Example rule:
Action: Allow
Priority: 1 (highest)
Protocol: TCP
Source: Enter the Bastionhost egress IP address that you obtained. For example, 47.100.XX.XX/32.
Destination: 22/22 (SSH) or 3389/3389 (RDP)
As shown in the following figure, the security group allows only 10.0.0.185 (the Bastionhost IP address) to access port 22 of the servers in the group.
Centrally manage assets and identities
Import assets: In the Bastionhost console, you can centrally import and manage assets that require O&M, such as ECS instances, databases, and applications.
For more information, see Create a host.
Integrate identity sources:
You can create Bastionhost users. The users can then log on to Bastionhost to perform O&M on assets. For more information, see Manage users.
If your enterprise has a mature identity authentication system, you can integrate Bastionhost with your existing identity sources, such as Resource Access Management (RAM) users, Active Directory (AD)/Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), or services such as DingTalk and WeCom using IDaaS. This allows for unified identity management. For more information, see Identity authentication best practices.
Configure access control policies
Grant permissions to users for assets: Follow the principle of least privilege. Grant each Bastionhost user permissions for only the minimum set of assets required for their work. For example, developers can access only servers in the development environment, and database administrators can access only database servers. For more information, see Grant permissions on assets and asset accounts to a user.
Configure fine-grained control policies: You can use the control policy feature of Bastionhost for more fine-grained control. For example, you can restrict specific users from running important commands, such as `rm -rf`, set limits on the type and size of file transfers, and enable dual-person review and approval for sensitive operations. For more information, see Configure a control policy.