This topic describes how to use the Enclave CLI to create an enclave in an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance. After you create the enclave, you can start or stop the enclave based on your business requirements.
Procedure
Create an ECS instance that supports Enclave and pre-allocate resources for the enclave.
For more information, see Build a confidential computing environment by using Enclave.
Create an enclave image file.
After you install the Enclave CLI, you can find a sample Dockerfile in the
/usr/share/ali-enclaves/examples/hellodirectory. You can use the Dockerfile to create the enclave image file.Run the following command to create a Docker image that is named
helloand tagged withlatest:sudo docker build /usr/share/ali-enclaves/examples/hello -t helloRun the following command to check whether the Docker image is created:
sudo docker images hello:latestIf the command output contains information about the
helloDocker image that is tagged withlatest, the Docker image is created.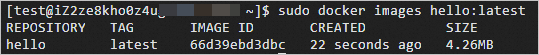
Run the following command to use the Enclave CLI to create the
hello.eifenclave image file:sudo enclave-cli build-enclave --docker-uri hello:latest --output-file hello.eifIf no errors are returned, the
hello.eifenclave image file is created. The platform configuration registers (PCRs) that are returned by the Enclave CLI indicate the hashes that are specific to the enclave. You can use the hashes for remote attestation. Sample command output:Start building the Enclave Image... Enclave Image successfully created. { "Measurements": { "HashAlgorithm": "Sha256 { ... }", "PCR11": "dc5dcd841f87e2b6c0e65a11b46b25ebe2999a8a5f0318e10c0175b60000****", "PCR8": "2c6944f47864f1f8ab276000a9f057fcdf9f56a015c0bc5e2339f24b0000****", "PCR9": "8ef5fe53a7709cc1c1a0aa7b5149a55bcd524cccc9f43e7a3baf44ca0000****" } }
Run the following command to run the enclave.
You can use the created
hello.eifimage file to start an enclave. The following command starts an enclave in debug mode based on the enclave image file. The enclave has 2 vCPUs and 1024 MiB of memory. For information about more parameters, see the "run-enclave" section in Subcommands of the Enclave CLI.sudo enclave-cli run-enclave --cpu-count 2 --memory 1024 --eif-path hello.eif --debug-modeA command output similar to the following one indicates that the enclave is run. In the following sample output, the ID of the enclave is
4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1. You must specify this ID when you use the Enclave CLI to manage the enclave.NoteThe context identifier (CID) of the enclave is 4. The CID is automatically assigned to define the vsock address of the enclave. You can only use the vsock address to establish connections between the enclave that is in non-debug mode and the instance in which the enclave is created.
Start allocating memory... Started enclave with enclave-cid: 4, memory: 1024 MiB, cpu-ids: [2, 3] { "EnclaveID": "4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1", "ProcessID": 1234, "EnclaveCID": 4, "NumberOfCPUs": 2, "CPUIDs": [ 2, 3 ], "MemoryMiB": 1024 }Run the following command to check the state of the enclave:
enclave-cli describe-enclavesThe command returns information such as the enclave ID, number of vCPUs, memory size, and enclave state. If the enclave works as expected, the returned state is
RUNNING.[ { "EnclaveID": "4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1", "ProcessID": 1234, "EnclaveCID": 4, "NumberOfCPUs": 2, "CPUIDs": [ 2, 3 ], "MemoryMiB": 1024, "State": "RUNNING", "Flags": "DEBUG_MODE" } ]You can also run the following command to view the debugging output of the enclave that runs in debug mode:
enclave-cli console --enclave-id 4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1If the enclave works as expected, a command output similar to the following one is returned:
[ 1] Hello from the enclave side! [ 2] Hello from the enclave side! [ 3] Hello from the enclave side! ...NoteIn this sample command output, the
[ N] Hello from the enclave side!message is returned for the enclave every five seconds. N indicates the number of times the message is returned.Run the following command to stop the enclave:
sudo enclave-cli terminate-enclave --enclave-id 4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1A command output similar to the following one indicates that the enclave is stopped:
Successfully terminated enclave 4f39d839-0f7a-4bee-a09d-93b8b1d6****-enc1. { "EnclaveID": "12345678-1234-5678-1234-12345678****-enc1", "Terminated": true }