In most cases, Linux software packages are stored in software repositories. After you add a software repository, you can use a package management tool provided by Linux to search for, install, or update software in the repository. This way, you can quickly perform system O&M or meet application development requirements. This topic describes how to install, manage, and use software repositories in different Linux distributions. In the following examples, Alibaba Cloud software repositories are used.
Background information
The speed of access to a software repository varies based on various factors, such as the region and distance. The Alibaba Cloud open source image website is built on the Alibaba Cloud infrastructure to provide high-speed all-in-one image services for Internet users free of charge, including the software repositories of mainstream Linux distributions such as CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, and openSUSE. All users can use the software repositories on the Alibaba Cloud open source image website free of charge, regardless of whether the users have Alibaba Cloud accounts. For more information, visit the Alibaba Cloud open source image website.
Important The public images provided by Alibaba Cloud automatically replace the software repository addresses of common Linux distributions with the private addresses of the Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service (ECS) software repositories of the Linux distributions. ECS users can use the ECS software repositories without the need to perform manual configuration. If you want to add or repair the software repository of a Linux distribution, perform the operations described in this topic.
In the following examples, the http://mirrors.aliyun.com public repository address is used, which is suitable for Linux servers that can access the Internet. If your servers are Alibaba Cloud ECS instances, we recommend that you use the http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com repository address, which is the private repository address of ECS, to accelerate the image download speed.
Add an Alibaba Cloud software repository to a Linux instance
Connect to a Linux instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance. In the following example, the ecs-user account is used to connect to a Linux instance. You can use another connection method.
Add an Alibaba Cloud software repository.
Note The following section describes how to add Alibaba Cloud software repositories to common Linux distributions. Perform operations based on the Linux distribution that you use. If you want to add Alibaba Cloud software repositories to other Linux distributions, go to the Alibaba Cloud open source image website and click the operating system distribution that you use to view the procedure.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 and 3
Back up the original software repository.
sudo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/AliYun.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/AliYun.repo.backup
Run one of the following commands to add the Alibaba Cloud software repository based on the operating system.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
sudo rpm -Uvh --reinstall https://mirrors.aliyun.com/alinux/3/updates/x86_64/Packages/alinux-repos-3.2104.10-2.al8.x86_64.rpm
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2
sudo rpm -Uvh --reinstall https://mirrors.aliyun.com/alinux/2/updates/x86_64/Packages/alinux-release-2.1903-11.al7.x86_64.rpm
Generate a local cache for fast searching and installation of software.
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum makecache
CentOS 6, 7, and 8
Back up the original software repository.
sudo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
Run one of the following commands to add the Alibaba Cloud software repository based on the operating system.
CentOS 8
url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-vault-8.5.2111.repo;if [ -f /usr/bin/curl ];then sudo curl -sSO $url;else sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/Centos-vault-8.5.2111.repo $url; fi
CentOS 7
url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo;if [ -f /usr/bin/curl ];then sudo curl -sSO $url;else sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/Centos-7.repo $url; fi
CentOS 6
url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-vault-6.10.repo;if [ -f /usr/bin/curl ];then sudo curl -sSO $url;else sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/Centos-vault-6.10.repo $url; fi
Generate a local cache for fast searching and installation of software.
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum makecache
Ubuntu
Back up the original software repository.
sudo mv /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.backup
Create and open a configuration file.
sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list
Press the I key to enter Insert mode and add the following information to the configuration file.
Ubuntu 24.04
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ noble-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Ubuntu 23.04
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ lunar-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Ubuntu 22.04
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Ubuntu 20.04
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Ubuntu 18.04
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
Update the software packages in the software repository.
sudo apt update
Debian
Back up the original software repository.
sudo mv /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.backup
Create and open a configuration file.
sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list
Press the I key to enter Insert mode and add the following information to the configuration file.
Debian 11.x
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian/ bullseye main non-free contrib
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian/ bullseye main non-free contrib
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-security/ bullseye-security main
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-security/ bullseye-security main
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian/ bullseye-updates main non-free contrib
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian/ bullseye-updates main non-free contrib
Debian 10.x
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ buster main non-free contrib
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian-security buster/updates main
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ buster main non-free contrib
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian-security buster/updates main
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ buster-updates main non-free contrib
Debian 9.x
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch main contrib non-free
#deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch-proposed-updates main non-free contrib
#deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch-backports main non-free contrib
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian-security stretch/updates main contrib non-free
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch main contrib non-free
#deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch-proposed-updates main contrib non-free
#deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian stretch-backports main contrib non-free
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian-security stretch/updates main contrib non-free
Debian 8.x
deb http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ jessie main non-free contrib
deb-src http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/debian-archive/debian/ jessie main non-free contrib
Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
Update the software packages in the software repository.
sudo apt update
Fedora
Back up the original software repositories.
sudo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora.repo.backup
sudo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-updates.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-updates.repo.backup
Add the Fedora software repository of Alibaba Cloud.
url=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/fedora.repo;if [ -f /usr/bin/curl ];then sudo curl -sSO $url;else sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora.repo $url; fi
Add the Fedora-updates software repository of Alibaba Cloud.
url=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/fedora-updates.repo;if [ -f /usr/bin/curl ];then sudo curl -sSO $url;else sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-updates.repo $url; fi
Generate a local cache.
sudo yum clean all && sudo yum makecache
openSUSE 15.6
Back up the original software repository.
sudo rename '.repo' '.repo.backup' /etc/zypp/repos.d/openSUSE*.repo
Add Alibaba Cloud software repositories.
sudo zypper addrepo -f http://mirrors.aliyun.com/opensuse/distribution/leap/15.6/repo/oss/ openSUSE-15.6-Oss
sudo zypper addrepo -f http://mirrors.aliyun.com/opensuse/distribution/leap/15.6/repo/non-oss/ openSUSE-15.6-Non-Oss
sudo zypper addrepo -f http://mirrors.aliyun.com/opensuse/update/leap/15.6/oss/ openSUSE-15.6-Update-Oss
sudo zypper addrepo -f http://mirrors.aliyun.com/opensuse/update/leap/15.6/non-oss/ openSUSE-15.6-Update-Non-Oss
Generate a local cache.
Use package management tools to manage software
In Linux operating systems, you can use package management tools to manage software in software repositories. Common package management tools include Yellowdog Updater Modified (YUM), Dandified YUM (DNF), Advanced Packaging Tool (APT), and Zypper. This section describes how to search for, install, update, and remove software by using package management tools in different operating system distributions. Replace the software package names in the following examples with the actual names based on your business requirements.
Note Software packages in Linux distributions are continuously updated to add new features, fix bugs, and provide security updates. You can update software packages to the latest versions based on your business requirements.
Alibaba Cloud Linux, CentOS, and Fedora
Search for a software package
Use the YUM package management tool to search for a software package.
sudo yum search <Search keyword>
For example, run the following command to search for software packages whose names contain the nginx keyword:
sudo yum search nginx
Install a software package
Use the YUM package management tool to install a software package.
sudo yum install <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to install the nginx software package:
sudo yum install nginx
Re-install a software package
Use the YUM package management tool to re-install a software package.
sudo yum reinstall <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to re-install the nginx software package:
sudo yum reinstall nginx
Update a software package
Use the YUM package management tool to update a software package.
sudo yum update <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to update the nginx software package:
sudo yum update nginx
Remove a software package
Use the YUM package management tool to remove a software package.
sudo yum remove <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to remove the nginx software package:
sudo yum remove nginx
Ubuntu and Debian
Search for a software package
Use the APT package management tool to search for a software package.
sudo apt search <Search keyword>
For example, run the following command to search for software packages whose names contain the nginx keyword:
sudo apt search nginx
Install a software package
Use the APT package management tool to install a software package.
sudo apt install <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to install the nginx software package:
sudo apt install nginx
Re-install a software package
Use the APT package management tool to re-install a software package.
sudo apt install --reinstall <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to re-install the nginx software package:
sudo apt install --reinstall nginx
Update a software package
Use the APT package management tool to update a software package.
sudo apt upgrade <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to update the nginx software package:
sudo apt upgrade nginx
Remove a software package
Use the APT package management tool to remove a software package.
sudo apt remove <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to remove the nginx software package:
sudo apt remove nginx
openSUSE
Search for a software package
Use the Zypper package management tool to search for a software package.
sudo zypper search <Search keyword>
For example, run the following command to search for software packages whose names contain the nginx keyword:
sudo zypper search nginx
Install a software package
Use the Zypper package management tool to install a software package.
sudo zypper install <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to install the nginx software package:
sudo zypper install nginx
Re-install a software package
Use the Zypper package management tool to re-install a software package.
sudo zypper install --force <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to re-install the nginx software package:
sudo zypper install --force nginx
Update a software package
Run the following command to use the Zypper package management tool to update a software package:
sudo zypper update <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to update the nginx software package:
sudo zypper update nginx
Remove a software package
Use the Zypper package management tool to remove a software package.
sudo zypper remove <Software package name>
For example, run the following command to remove the nginx software package:
sudo zypper remove nginx
FAQ
What do I do if the "Failed to fetch" error occurs when I install OpenJDK on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu 14.04?
Problem description
When you run the following command to install the openjdk-7-jre-headless package on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu 14.04, the Failed to fetch error occurs.
apt-get install openjdk-7-jre-headless
The following figure shows a sample command output.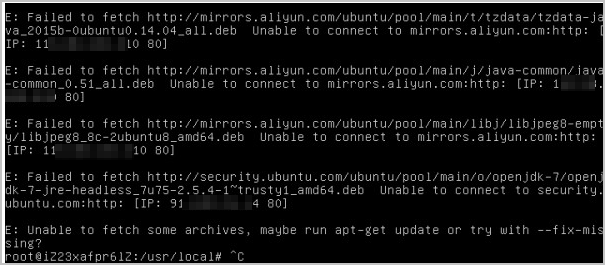
Cause
The ECS instance that runs Ubuntu 14.04 is connected to an external software repository. As a result, you cannot install Open Java Development Kit (OpenJDK) on the instance.
Solution
Connect to the Linux ECS instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Run the following command to re-install OpenJDK:
apt-get install openjdk-7-jre-headless --fix-missing
What do I do if I cannot use the YUM package management tool to install MySQL on an ECS instance that runs CentOS 7.0 and the "File contains no section headers." error message appears?
Problem description
When you run a yum command to install MySQL on an ECS instance that runs CentOS 7.0, the following error message appears:
File contains no section headers.
Cause
The software repository does not provide the relevant software package.
Solution
To switch to the official CentOS software repository, perform the following steps:
Connect to the Linux ECS instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Modify the /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo configuration file.
Open the /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo configuration file.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
Press the I key to enter Insert mode and replace the content of the configuration file with the following content:
[epel-source]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Source
#baseurl=http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/SRPMS
mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-source-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
gpgcheck=1
[epel]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch #baseurl=http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/$basearch mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
[epel-debuginfo]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Debug #baseurl=http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/$basearch/debug mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-debug-7&arch=$basearch failovermethod=priority
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
gpgcheck=1
Press the Esc key to exit Insert mode. Then, enter :wq and press the Enter key to save and close the file.
Run the following commands in sequence to make the new software repository take effect:
yum makecache
yum repolist
Re-install MySQL. If the issue is resolved, the preceding error message no longer appears.
How do I configure the RPMForge software repository on an ECS instance that runs CentOS 6?
Procedure
RPMForge is a third-party software repository recommended by the CentOS official community. To configure the RPMForge software repository on an ECS instance that runs CentOS 6, perform the following steps:
Connect to the Linux ECS instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Check the system architecture.
uname -i
The following command output shows that the x86_64 architecture is used.
x86_64
Run a command, such as the wget command, to download the required RPM package based on the actual system architecture.
http://repository.it4i.cz/mirrors/repoforge/redhat/el6/en/i386/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.i686.rpm
http://repository.it4i.cz/mirrors/repoforge/redhat/el6/en/x86_64/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
Import the GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) key of the Dag repository.
rpm --import http://apt.sw.be/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt
Install the downloaded RPM package.
rpm -i rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.*.rpm
Go to the following directory and check whether the repository configuration files whose names contain the rpmforge keyword exist in the directory:
/etc/yum.repos.d/
The following command output indicates that the RPMForge software repository is installed. 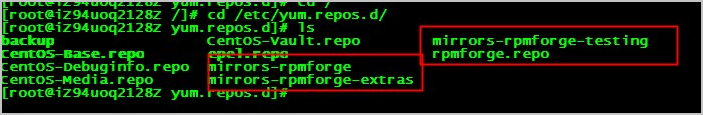
What do I do if the "error processing package install-info (--configure)" error message appears when I run the apt-get command to install software?
Problem description
When you run the apt-get command to install software on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu, the error processing package install-info (--configure) error message appears.
Cause
The preceding issue may occur because the Ubuntu software package is corrupted, which results in a software installation failure.
Solution
To update and synchronize the APT software repository and re-install the software, perform the following steps:
Connect to the Ubuntu instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Rename the info folder.
mv /var/lib/dpkg/info/ /var/lib/dpkg/info.bak.old/
Create a new info folder.
mkdir /var/lib/dpkg/info/
Update and synchronize the APT software repository.
apt-get update
Re-install the software. Replace <xxxxx> with the name of the software package that you want to re-install. If the issue is resolved, the preceding error message no longer appears.
apt-get install <xxxxx>
What do I do if the "Segmentation faultsts" error occurs when I run the apt-get command to install or update software?
Problem description
When you run the apt-get command to install or update software on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu, the Segmentation faultsts" error occurs.
Cause
The preceding issue may occur because of a conflict in the APT cache, which results in a software installation or update failure.
Solution
Perform the following steps to update and synchronize the APT software repository:
Connect to the Ubuntu instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Back up files in the /var/cache/apt/ directory.
Delete all .bin files from the /var/cache/apt/ directory.
rm /var/cache/apt/*.bin
Update and synchronize the APT software repository.
apt-get update
Check whether you can run the apt-get command to install or update software as expected.
Note If the Segmentation faults error occurs on an ECS instance that has a low memory specification, such as a memory size of only 512 MB, you can also run the top command to check the memory usage, temporarily stop specific non-essential processes, and then rerun the apt-get command.
What do I do if the "Reading package lists... Error!" error message appears when I run the apt-get command to install software?
Problem description
When you run the apt-get command to install software on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu, the following error message appears:
Reading package lists... Error! E: Encountered a section with no Package: header E: Problem with MergeList /var/lib/apt/lists/AZ.archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_natty_main_i18n _Translation-en E: The package lists or status file could not be parsed or opened.
Cause
The software package list is corrupted, which causes a software installation error.
Solution
To clear the corrupted software package list and regenerate the latest software package list, perform the following steps:
Clear the corrupted software package list from the software package list directory.
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
Regenerate the latest software package list.
apt-get update
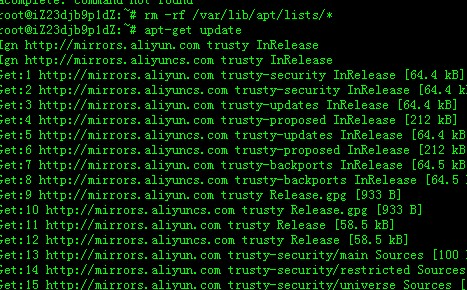
Re-install the software. If the issue is resolved, the preceding error message no longer appears.
What do I do if the "Error http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main unzip amd64 6.0-9ubuntu1.1 404 Not Found [IP: 112.124.XXX.XXX 80]" error message appears when I run the apt-get install unzip or aptitude install unzip command?
Problem description
When you run the apt-get install unzip or aptitude install unzip command on an ECS instance that runs Ubuntu, the following error message appears:
Error http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main unzip amd64 6.0-9ubuntu1.1 404 Not Found [IP: 112.124.XXX.XXX 80]
Error http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main unzip amd64 6.0-9ubuntu1.1 404 Not Found [IP: 112.124.XXX.XXX 80]
Error http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main unzip amd64 6.0-9ubuntu1.1 404 Not Found [IP: 112.124.XXX.XXX 80]
Cause
In most cases, the preceding issue occurs because the software version requested by the command does not exist in the APT software repository.
Solution
To update and synchronize the APT software repository, perform the following steps:
Connect to the Ubuntu instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Update and synchronize the APT software repository.
apt-get update
After the APT software repository is updated and synchronized, run the apt-get install command to install the required software.
What do I do if the "The following signatures were invalid: KEYEXPIRED 1544811256" error message appears when I run the apt-get update command?
Problem description
When you run the apt-get update command on an Ubuntu instance, the following error message appears:
The following signatures were invalid: KEYEXPIRED 1544811256
Cause
An update error occurred because the signatures of the used software repository expired.
Solution
Perform the following steps to update the expired key:
Connect to the Ubuntu instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Obtain the expired key.
sudo apt-key list | grep -A 1 expired

Update the expired key.
apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys [$Key]
Note Replace [$Key] with the expired key that you obtained in the previous step.
Update and synchronize the APT software repository.
apt-get update
What do I do if I cannot install Docker by using third-party YUM repositories on an Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 instance?
Problem description
When you use third-party YUM repositories, such as Docker Community Edition (Docker-CE) and Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repositories, that are compatible with CentOS 7 and run the yum install docker-ce command to install Docker on an Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 instance that meets the following conditions, Docker cannot be installed and the following error message is returned.
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks, update-motd
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* epel: mirror.sjtu.edu.cn
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/2.1903/x86_64/stable/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] HTTPS Error 404 - Not Found
Trying other mirror.
Downloading packages:
docker-ce-20.10.6-3.el7.x86_64 FAILED
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/2.1903/x86_64/stable/Packages/docker-ce-20.10.6-3.el7.x86_64.rpm: [Errno 14] HTTPS Error 404 - Not Found
Trying other mirror.
docker-ce-rootless-extras-20.1 FAILED
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/2.1903/x86_64/stable/Packages/docker-ce-rootless-extras-20.10.6-3.el7.x86_64.rpm: [Errno 14] HTTPS Error 404 - Not Found
Trying other mirror.
Error downloading packages:
3:docker-ce-20.10.6-3.el7.x86_64: [Errno 256] No more mirrors to try.
docker-ce-rootless-extras-20.10.6-3.el7.x86_64: [Errno 256] No more mirrors to try.
Cause
Third-party YUM repositories are compatible only with CentOS 7. The $releasever value of Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 is different from that of CentOS 7. As a result, the Docker package cannot be downloaded because the resolved YUM repository addresses are invalid.
Note When YUM installs Docker-CE, YUM obtains the version number ($releasever value) from the system and replaces the $releasever value in the baseurl of the corresponding YUM repository with the obtained version number to obtain required data. The $releasever value of CentOS 7 is 7, and the $releasever value of Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 is 2.1903. As a result, the baseurl is resolved to a non-expected address for Alibaba Cloud Linux 2, and YUM cannot obtain the required data from the address.
Solutions
Use one of the following methods to resolve the issue:
Change the value of $releasever.
Install the yum-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in, and then use the plug-in to change the value of $releasever.
Note In the examples, the Docker-CE repository is used. You can perform the same operations for other YUM repositories.
Solution 1: Change the $releasever value
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Modify the /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo configuration file.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
Press the I key to enter Insert mode. In the docker-ce.repo file, find all repositories for which enabled=1 is displayed, and change the $releasever value in the baseurls of the repositories to 7, as shown in the following figure. 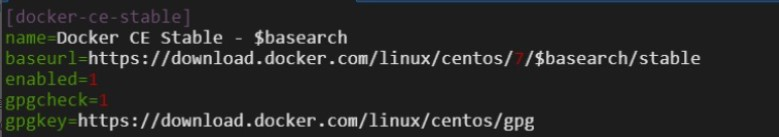
Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file. Then, re-install Docker.
Solution 2: Use a plug-in to change the $releasever value
Install the yum-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in to automatically change the $releasever value from 2.1903 to 7.
Check whether the instance supports the yum-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in.
The following table describes the current versions of the yum-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in and the third-party repositories that are supported by default.
Plug-in version | Third-party repository supported by default | Limits on the plug-in |
1.0-1.3 | Docker-CE and EPEL | To use the plug-in, make sure that the following requirements are met: The operating system is Alibaba Cloud Linux 2. Run the following command to check whether the plus repository exists: cat /etc/yum.repos.d/AliYun.repo |grep -A3 plus
The following command output indicates that the plus repository exists. 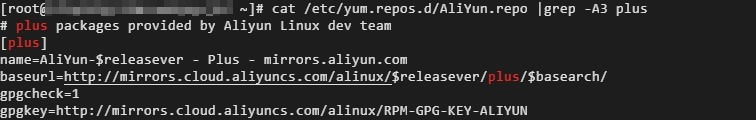
|
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Install the yum-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in. The plug-in changes the $releasever values of the Docker-CE and EPEL repositories.
yum install yum-plugin-releasever-adapter --disablerepo=* --enablerepo=plus
If you do not need to change the value of $releasever for other YUM repositories, install Docker after the plug-in is installed. If you need to change the value of $releasever for other YUM repositories, perform the following operations:
Go to the specified directory.
cd /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/
Modify the releasever-adapter.conf configuration file. If you want to add other YUM repositories, append the .repo file names of the YUM repositories to the includes field. Separate the file names with commas (,).
vim releasever-adapter.conf
The following sample command output is displayed:
[main]
enabled=1
hostfilepath=timedhosts.txt
[releasevermapping]
release_dict={'2.1903':'7', '3':'8'}
[reposlist]
includes=docker-ce.repo, epel.repo
Note The following parameters are used in the configuration file:
[main]: the main control part of the plug-in that is used to enable or disable the plug-in. If enabled is set to 1, the plug-in is enabled. If enabled is set to 0, the plug-in is disabled.
[releasevermapping]: the mappings between the $releasever values that you want to change. 2.1903 is mapped to 7, and 3 is mapped to 8.
[repolist]: the list of repositories that you want to modify. If you want to add other YUM repositories, append the .repo file names of the repositories to the includes field. Separate the file names with commas (,).
A .repo file contains multiple repositories, and each repository name is unique within the system. For example, the docker-ce-stable and docker-ce-stable-debuginfo repositories exist at the same time in the docker-ce.repo file.
Make sure that each .repo file name added to the releasever-adapter.conf configuration file is the prefix of the names of the repositories that are contained in the .repo file. For example, the docker-ce.repo file contains the docker-ce-stable-debuginfo and docker-ce-stable repositories that share the docker-ce prefix.
Save the configuration file and run the following command to install Docker by using the Docker-CE and EPEL repositories.
yum install docker-ce
What do I do if I cannot install Docker by using third-party DNF repositories on an Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 instance?
Problem description
You cannot install Docker by running the dnf install docker-ce command on an Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 instance that meets the following conditions, and an error message is returned.
Sample error message:
Docker CE Stable - x86_64
Failed to download metadata for repo 'docker-ce-stable'
Error: Failed to download metadata for repo 'docker-ce-stable'
Cause
Third-party DNF repositories are compatible only with CentOS 8. The $releasever value of Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 is different from that of CentOS 8. As a result, the Docker package cannot be downloaded because the resolved DNF repository addresses are invalid.
Note When DNF installs Docker-CE, DNF obtains the version number ($releasever value) from the system and replaces the $releasever value in the baseurl of the corresponding DNF repository with the obtained version number to obtain required data. The $releasever value of CentOS 8 is 8, and the $releasever value of Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 is 3. As a result, the baseurl is resolved to a non-expected address for Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, and DNF cannot obtain the required data from the address.
Solutions
Use one of the following methods to resolve the issue:
Change the value of $releasever.
Install the dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in, and then use the plug-in to change the value of $releasever.
Note In the examples, the Docker-CE repository is used. You can perform the same operations for other DNF repositories.
Solution 1: Change the $releasever value
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Open the /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo configuration file.
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
Press the I key to enter Insert mode. In the docker-ce.repo file, find all repositories for which enabled=1 is displayed, and change the $releasever value in the baseurls of the repositories to 8, as shown in the following figure.
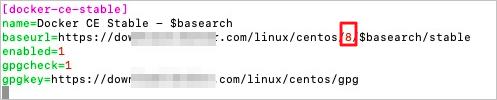
Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file. Then, re-install Docker.
Solution 2: Use a plug-in to change the $releasever value
Install the dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in to automatically change the $releasever value from 3 to 8.
Check whether the instance supports the dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in.
The following table describes the current versions of the dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in and the third-party repositories that are supported by default.
Plug-in version | Third-party repository supported by default | Limits on the plug-in |
New version: 1.0-2 Old version: 1.0-1.3
Note The new and old versions of the plug-in are not compatible with each other. The configuration file of the new version is named releasever_adapter.conf, and the configuration file of the old version is named releasever-adapter.conf. When the plug-in is upgraded to the new version, the configuration file of the old version is deleted. After the plug-in is upgraded, if you want the plug-in to support third-party repositories other than Docker-CE and EPEL, modify the include field of the configuration file and keep the other settings unchanged. | Docker-CE and EPEL | To use the plug-in, make sure that the following requirements are met: The operating system is Alibaba Cloud Linux 3. Run the following command to check whether the alinux3-plus repository exists: cat /etc/yum.repos.d/AliYun.repo |grep -A3 alinux3-plus
The command output shown in the following figure indicates that the alinux3-plus repository exists. 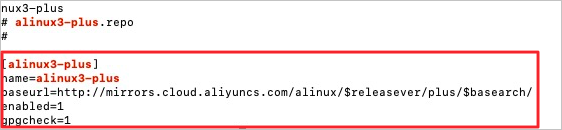
|
Connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Install the dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter plug-in.
Note The plug-in changes the $releasever values of the Docker-CE and EPEL repositories.
dnf install dnf-plugin-releasever-adapter --repo alinux3-plus
If you do not need to change the value of $releasever for other DNF repositories, install Docker after the plug-in is installed. If you need to change the value of $releasever for other DNF repositories, perform the following operations:
Go to the /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/ directory.
cd /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/
Modify the releasever_adapter.conf configuration file.
vim releasever_adapter.conf
Press the I key to enter Insert mode. If you want to add other DNF repositories, append the .repo file names of the DNF repositories to the include field. Separate the file names with commas (,).
Note In most cases, the .repo files of DNF repositories reside in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory.
Sample command output:
[main]
enabled=1
[releasevermapping]
2.1903 = 7
3 = 8
[reposlist]
include=docker-ce.repo, epel.repo
Note The following parameters are used in the configuration file:
[main]: the main control part of the plug-in that is used to enable or disable the plug-in. If enabled is set to 1, the plug-in is enabled. If enabled is set to 0, the plug-in is disabled.
[releasevermapping]: the mappings between the $releasever values that you want to change. 2.1903 is mapped to 7, and 3 is mapped to 8.
[repolist]: the list of repositories that you want to modify. If you want to add other DNF repositories, append the .repo file names of the repositories to the include field. Separate the file names with commas (,).
In most cases, a .repo file contains multiple repositories, and each repository name is unique within the system. For example, the docker-ce-stable and docker-ce-stable-debuginfo repositories exist at the same time in the docker-ce.repo file.
Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
Run the following command to install Docker-CE by using the Docker-CE and EPEL repositories and the other repositories that you added:
dnf install docker-ce
What do I do if the "-bash: /usr/bin/yum: /usr/bin/python: bad interpreter: No such file or directory" error message appears when I run a yum command on a CentOS 7 ECS instance?
Problem description
When you run a yum command on an ECS instance that runs CentOS 7, the following error message appears:
-bash: /usr/bin/yum: /usr/bin/python: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
Cause
The preceding issue may be caused by a Python exception, such as when Python is uninstalled, a file is
renamed, or a file path is moved.
Note YUM is a shell frontend package manager for Fedora, Red Hat, and SUSE.
Solution
To check whether a Python exception occurs and repair the exception, perform the following steps:
Connect to the Linux ECS instance.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
Query the YUM file path.
which yum
The following command output indicates that the YUM file path is /usr/bin/yum.
/usr/bin/yum
View the YUM content.
cat /usr/bin/yum
The following command output indicates that the path of the Python version is used.
#!/usr/bin/python
Note In the following example, the /usr/bin/python path is used. Replace the path with the actual path.
Check the preceding path.
ls -al /usr/bin/python
If the following command output is displayed, Python may be uninstalled, the names of Python-related files may be changed, or the paths of Python-related files may be moved.
ls: cannot access /usr/bin/python: No such file or directory
Check whether Python-related files exist.
rpm -qa | grep python
If Python-related files exist, the following command output is displayed:
python-decorator-3.4.0-3.el7.noarch
libselinux-python-2.5-14.1.el7.x86_64
python-backports-1.0-8.el7.x86_64
python-pyudev-0.15-9.el7.noarch
rpm-python-4.11.3-35.el7.x86_64
python-2.7.5-76.el7.x86_64
.....
If Python-related files exist, this indicates that the names of the files were changed or the paths of the files were moved.
View Python-related files.
ls -al /usr/bin/python*
The following command output is displayed, in which /usr/bin/python.bak -> python2 indicates that the name of Python was changed.
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 14 Feb 15 2019 /usr/bin/python-config -> python2-config
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Feb 15 2019 /usr/bin/python.bak -> python2
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 Feb 15 2019 /usr/bin/python2 -> python2.7
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Feb 15 2019 /usr/bin/python2-config -> python2.7-config
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7216 Oct 31 2018 /usr/bin/python2.7
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1835 Oct 31 2018 /usr/bin/python2.7-config
Change /usr/bin/python.bak to /usr/bin/python.
mv python.bak python
Rerun the yum command. If the issue is resolved, the preceding error message no longer appears.
If Python-related files do not exist, this indicates that Python was uninstalled.
Run the following commands in sequence to install Python:
mkdir /python/
yum install python --downloadonly --downloaddir=/python/
Rerun the yum command. If the issue is resolved, the preceding error message no longer appears.







