To test the connectivity and performance of the network between an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance and its gateway, you must obtain the gateway IP address in the internal network. This topic describes how to obtain the IP address of the internal gateway connected to an ECS instance.
Background information
An Alibaba Cloud virtual private cloud (VPC) is a logically isolated network that is segmented into subnets by vSwitches. By default, subnets in the same VPC can communicate with each other, which allows the internal gateway to forward traffic between the subnets in the VPC. When you create an ECS instance, you must select a VPC and a vSwitch for it. The instance can communicate with other subnets in the VPC via the designated internal gateway IP address.
Prerequisites
Before you perform the following operations on an ECS instance, make sure that the instance meets the following requirements:
It is in the Running state.
It resides in a
VPC.
Procedure
The internal gateway
IPaddress is automatically designated based on thevSwitchCIDR block. To prevent issues such as network disconnections and routing abnormalities, do not change the internal gateway IP address or any related routing configurations.In this example, an ECS instance that has two elastic network interfaces (ENIs) is used. If your instance has special network configurations, such as IPv6 dual-stack, the gateway information may exist in a different route table. To view the full network topology, log on to the VPC console.
Linux instance
Run the ip command
Run the following command to view the route table information:
sudo ip route showIf the instance resides in a dual-stack IPv6 environment and needs the IPv6 route table displayed, run the
ip -6 route showcommand.If the instance runs
openSUSE, we recommend that you run theipcommand to view the route table information instead of therouteornetstatcommand.
The following command output is returned:
default via 172.16.0.253 dev eth0 proto dhcp src 172.16.0.71 metric 100
172.16.0.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 172.16.0.71 metric 100 In the command output, the default via parameter indicates the default route. In this example, 172.16.0.253 is the internal gateway IP address for the eth0 ENI.
Run the route command
Run the following command to view the route table information in the kernel:
sudo route -nThe following command output is returned:
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 172.16.0.253 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0In the command output, find the row where Destination is 0.0.0.0 (default route), and then obtain the corresponding Gateway value, which is the internal gateway IP address for the eth0 ENI.
Run the netstat command
Run the following command to view the route table information:
sudo netstat -r -nThe following command output is returned:
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
0.0.0.0 172.16.0.253 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0In the command output, find the row where Destination is 0.0.0.0 (default route), and then obtain the corresponding Gateway value, which is the internal gateway IP address for the eth0 ENI.
Windows instance
Run the ipconfig command
Connect to the Windows instance. For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Windows instance over RDP.
Click the Start icon, enter PowerShell, and then press Enter to open Windows PowerShell.
Run the following command to view the network configuration:
ipconfigThe following command output is returned, from which you can obtain the gateway
IPaddress for the relevant ENI.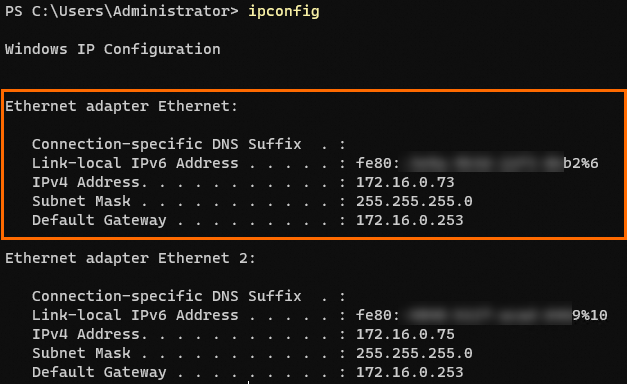
Run the route command
Connect to the Windows instance. For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Windows instance over RDP.
Click the Start icon, enter PowerShell, and then press Enter to open Windows PowerShell.
Run the following command to view the network configuration:
route printNoteIf the instance resides in an IPv6 dual-stack environment and needs the IPv6 route table displayed, run the
route print -6command.The following figure shows the command output.

In the command output, find the row where Network Destination is 0.0.0.0, and then obtain the corresponding Gateway value, which is the default gateway
IPaddress for the current ENI.
If you want to test the network connectivity after you obtain the internal gateway IP address for the ECS instance, run the ping or traceroute command to diagnose and analyze network connectivity.