Elastic Compute Service (ECS) Network Connectivity Diagnostics is a feature that allows you to diagnose the network connectivity between diagnostic objects in the cloud and identify the causes of related issues.
Prerequisites
If you want to use instances or elastic network interfaces (ENIs) as diagnostic objects, the instances or ENIs are in the Running state.
If you want to use secondary ENIs as diagnostic objects, the ENIs are bound to instances. For more information, see Bind a secondary ENI.
If you want to diagnose an instance and check its operating system configurations, the instance's operating system meets the requirements described in the following table.
Operating system architecture
Operating system version
Operating system configuration
x86_64-bit
Windows Server 2008 or later
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or 3
AlmaLinux 8.x
Anolis OS 7.x/8.2
CentOS 7.x/8.x
CentOS Stream 8
Debian 8.x/9.x/10.x
Fedora 33/34
OpenSUSE 15.x/42.x
Rocky Linux 8.x
SUSE Linux 12.x/15.x
Ubuntu 20.04
Python 2.7 or a Python version ranging from 3.6 to 3.9 is installed.
The Cloud Assistant Agent is installed on the instance. For more information, see Install Cloud Assistant Agent.
Limits
The following table describes the quotas on paths and diagnostic tasks.
Item | Limit | Method to raise limits |
The maximum number of paths per region | 100 | N/A |
The maximum number of diagnostic tasks per region | 1,000 | N/A |
The maximum number of concurrent diagnostic tasks per region | 5 | N/A |
Procedure
Specify a path.
Each path includes all information required to execute a diagnostic task, such as a virtual private cloud (VPC) and diagnostic objects (instances, ENIs, or public IP addresses). You can create a path and clone a path.
NoteWhen you create a path and initiate a diagnostic task, the system checks whether the AliyunServiceRoleForECSNetworkInsights service-linked role exists. If the role does not exist, the system creates the role. For more information, see Manage the service-linked role for ECS Network Connectivity Diagnostics.
Initiate a diagnostic task.
A diagnostic task is performed to check the real-time network connectivity between the source and destination diagnostic objects configured in a path. After a path is created or cloned, the system immediately initiates a diagnostic task for the path. You can also manually initiate a diagnostic task for an existing path. For more information, see Diagnose a path.
View diagnostic results.
In the diagnostic task list, you can view the results and details of diagnostic tasks. For more information, see Manage diagnostic tasks.
NoteThe ECS Network Connectivity Diagnostics feature is used as an auxiliary tool to provide insight into critical network connectivity configurations. However, its diagnostic results cannot indicate whether communication over networks is allowed or denied.
Create a path
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click the Network Connectivity Diagnostics tab and then click Create Path.
Configure the parameters described in the following table and click Create.
Parameter
Description
Path Name
Enter a name for the path. The name must be 2 to 128 characters in length and can contain letters, digits, periods (
.), underscores (_), hyphens (-), and colons (:). It cannot start with a special character, a digit,http://, orhttps://.VPC
Select a VPC. At least one of the diagnostic objects must be an ECS instance or ENI in a VPC.
Source and Destination
Select a diagnostic object type and then specify the source and destination diagnostic objects. Valid values for the diagnostic object type:
ECS Instance: existing ECS instances. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be the same instance.
NIC: existing ENIs. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be the same ENI or the ENIs bound to the same instance.
Public IP Address: public IP addresses. You can manually enter public IP addresses as diagnostic objects. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be public IP addresses at the same time.
Destination Port and Protocol
Specify the destination port and protocol. The supported destination port is determined by the selected protocol.
If you set Protocol to Custom TCP or Custom UDP, select a port from the drop-down list or enter a port number for Destination Port.
SSH (22), Telnet (23), HTTP (80), HTTPS (443), MS SQL (1433), Oracle (1521), MySQL (3306), RDP (3389), PostgreSQL (5432), and Redis (6379) are displayed on the drop-down list.
If you set Protocol to All ICMP(IPv4) or All GRE, Destination Port is automatically set to -1.
After a path is created, the system initiates a diagnostic task to diagnose the network connectivity over the specified protocol from the source diagnostic object to the specified port of the destination diagnostic object.
NoteDiagnostic tasks take a few minutes to complete. You can view the status and result of a diagnostic task in the path list or by visiting the details page of the path. For more information, see Manage diagnostic tasks.
Clone a path
You can clone an existing path and modify some settings, such as the source or destination diagnostic object, to quickly create a path.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click the Network Connectivity Diagnostics tab and then click Clone in the Actions column corresponding to a path.
Configure the parameters described in the following table and click Create.
Parameter
Description
Path Name
Enter a name for the path. The name must be 2 to 128 characters in length and can contain letters, digits, periods (
.), underscores (_), hyphens (-), and colons (:). It cannot start with a special character, a digit,http://, orhttps://.VPC
Select a VPC. At least one of the diagnostic objects must be an ECS instance or ENI in a VPC.
Source and Destination
Select a diagnostic object type and then specify the source and destination diagnostic objects. Valid values for the diagnostic object type:
ECS Instance: existing ECS instances. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be the same instance.
NIC: existing ENIs. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be the same ENI or the ENIs bound to the same instance.
Public IP Address: public IP addresses. You can manually enter public IP addresses as diagnostic objects. The source and destination diagnostic objects cannot be public IP addresses at the same time.
Destination Port and Protocol
Specify the destination port and protocol. The supported destination port is determined by the selected protocol.
If you set Protocol to Custom TCP or Custom UDP, select a port from the drop-down list or enter a port number for Destination Port.
SSH (22), Telnet (23), HTTP (80), HTTPS (443), MS SQL (1433), Oracle (1521), MySQL (3306), RDP (3389), PostgreSQL (5432), and Redis (6379) are displayed on the drop-down list.
If you set Protocol to All ICMP(IPv4) or All GRE, Destination Port is automatically set to -1.
After a path is cloned, the system initiates a diagnostic task to diagnose the network connectivity over the specified protocol from the source diagnostic object to the specified port of the destination diagnostic object.
NoteDiagnostic tasks take a few minutes to complete. You can view the status and result of a diagnostic task in the path list or by visiting the details page of the path. For more information, see Manage diagnostic tasks.
Diagnose a path
You can manually initiate a diagnostic task for an existing path. Each path can have only one ongoing diagnostic task.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click the Network Connectivity Diagnostics tab, click Diagnose in the Actions column corresponding to a path, and then click Continue.
Manage diagnostic tasks
The latest diagnostic results for paths are displayed in the path list. Sometimes you may want to view diagnostic task details or historical diagnostic tasks. For example, when Unconnectable is displayed as the diagnostic result for a path, you may want to view the task details to identify the cause of the issue. This section describes how to manage diagnostic tasks.
The number of diagnostic task records that can be retained for each path is limited. We recommend regularly deleting diagnostic tasks that you no longer need.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click the Network Connectivity Diagnostics tab and find the path you want to manage.
Perform the following operations on the path based on your business requirements:
To initiate a diagnostic task, click Diagnose and then click Continue.
To delete a diagnostic task, click the path ID, find the task in the Diagnosis List section, click Delete in the Actions column, and then click Continue.
To view the details of a diagnostic task, click the path ID, find the task in the Diagnosis List section, and then click the
 icon. Note
icon. NoteFor information about diagnostic items, see Diagnostic items of ECS Network Connectivity Diagnostics.
Figure 1. Details of a sample diagnostic task whose result is Normal
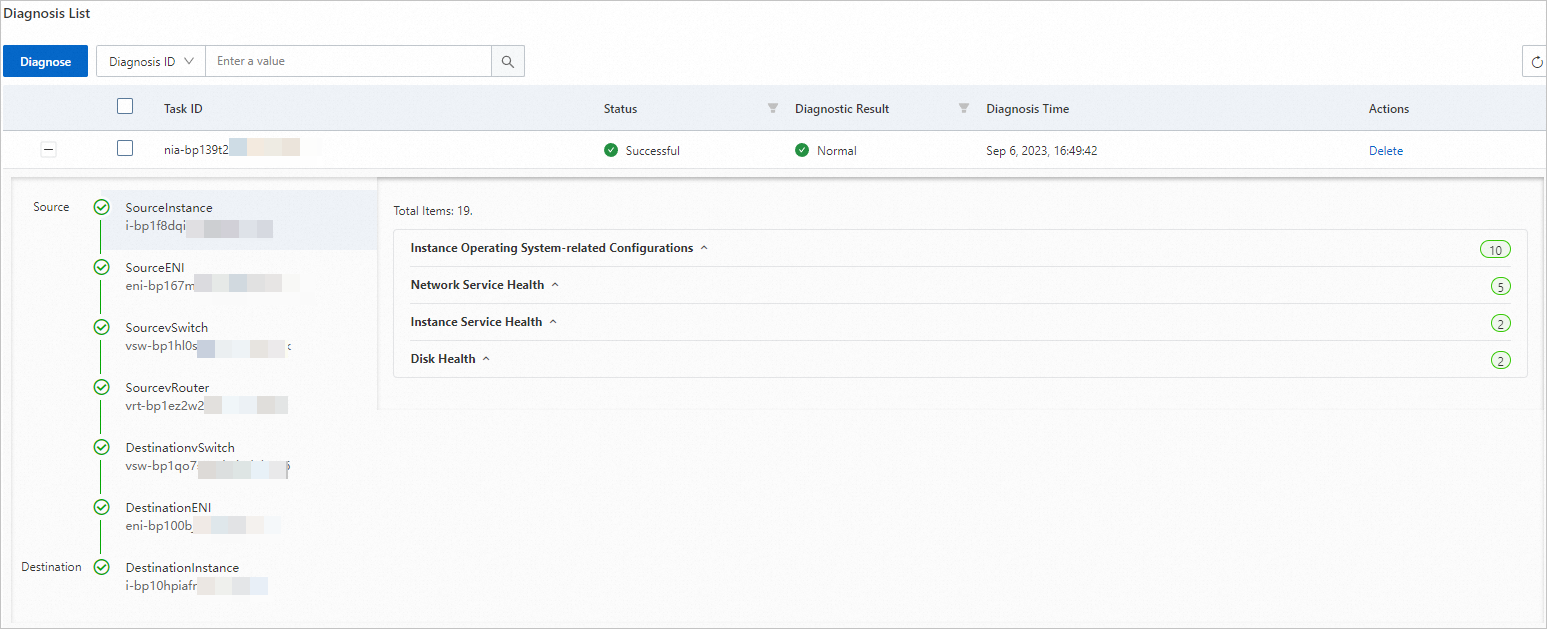
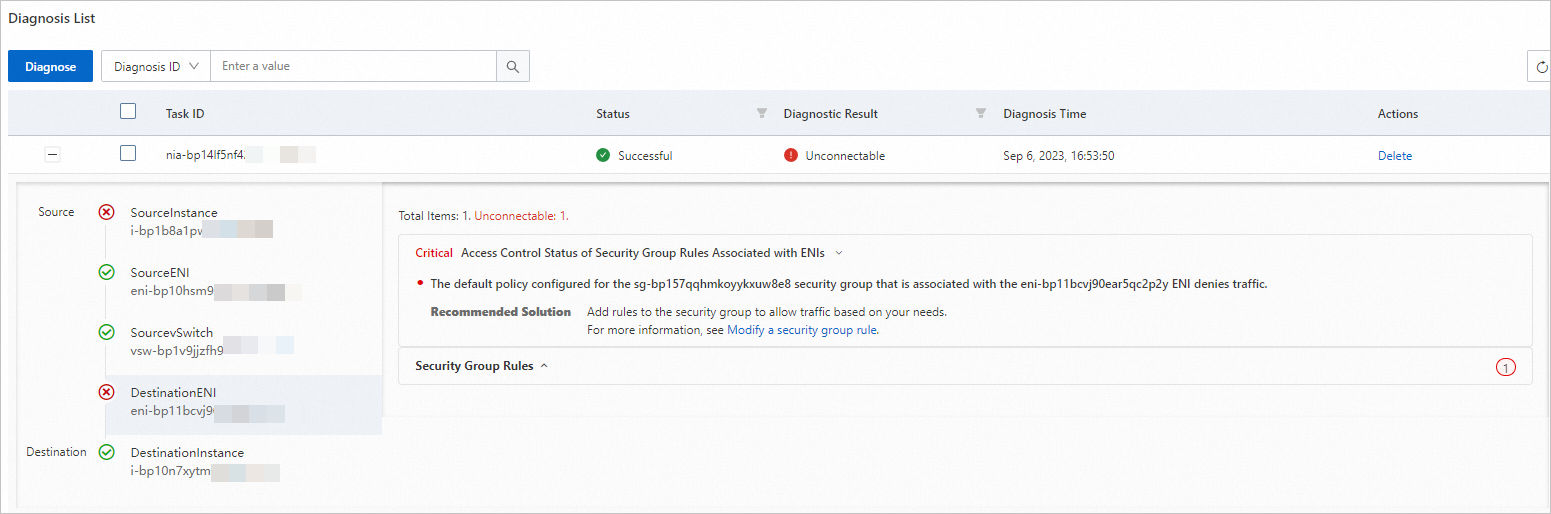
Figure 2. Details of a sample diagnostic task whose result is Unconnectable
Delete a path
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Click the Network Connectivity Diagnostics tab, click Delete in the Actions column corresponding to a path, and then click Continue.