When a vCPU is idle, the processor enters progressively deeper power-saving states called C-states. Deeper C-states save more power but take longer to wake from, adding latency when the vCPU needs to handle work again. For workloads that demand consistent, low-latency CPU response, such as real-time applications, in-memory databases, or high-frequency network packet processing, limit the C-state to C1 so that idle vCPUs resume execution almost instantly.
Background
C-states range from C0 to C6. C0 is the active state where the CPU runs instructions normally. C6 is the deepest power-saving state. The higher the C-state number, the more power the CPU saves while idle, but the longer it takes to wake up and begin running instructions again.
In a virtualized environment, keeping the vCPU at a low-level C-state reduces hypervisor-induced overheads of instructions such as HLT and MWAIT, and reduces the wake-up latency of the vCPU. When the operating system sets the vCPU to a high-level C-state, a specific period of time is required to wake up the vCPU, for example, when an interrupt occurs on the network interface controller (NIC). The exact wake-up time varies based on the CPU chip architecture.
To reduce vCPU response latency, configure the operating system to disable high-level C-states. Two kernel boot parameters control this behavior:
intel_idle.max_cstate: Controls the maximum C-state for theintel_idledriver (Intel processors).processor.max_cstate: Controls the maximum C-state for theacpi_idledriver (AMD processors and fallback).
Setting both parameters to 1 keeps idle vCPUs in C1, regardless of the processor type. You can safely add both parameters to the configuration.
Limiting C-states reduces wake-up latency but increases power consumption. Idle cores remain in C1 and do not enter deep sleep, which may also reduce the thermal headroom available for Turbo Boost on other cores.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that you have:
An Elastic Compute Service (ECS) Linux instance (this procedure uses ecs.g8i.large with Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 as an example; command output may vary based on the instance type and image)
Root or sudo access to the instance
The
cpupowerutility installed (provided by thekernel-toolspackage on Alibaba Cloud Linux)
Procedure
Step 1: Connect to the instance
Log on to the ECS instance. For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
Step 2: Check the current C-state configuration
Run the following command to view the CPUidle driver and supported C-states:
cpupower idle-infoIf this command does not display the corresponding CPUidle driver, you may need to update the image.
The output shows the number of supported C-states and lists each available idle state. For example:
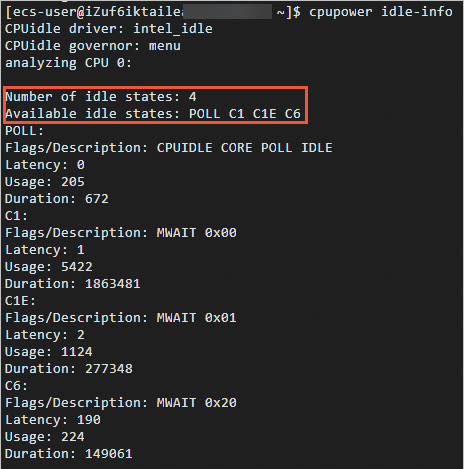
The Number of idle states field indicates how many C-states the system supports, and Available idle states lists them by name.
Step 3: Set the maximum C-state to C1
Open the GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) configuration file:
sudo vim /etc/default/grubPress the
ikey to enter Insert mode.Find the
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=line and append the following parameters at the end (inside the closing quotation mark): This limits the idle vCPU to C1.
intel_idle.max_cstate=1 processor.max_cstate=1Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press theEnterkey to save and close the file.Regenerate the GRUB configuration file:
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Step 4: Restart the instance
Restart the instance for the new configuration to take effect:
sudo rebootStep 5: Verify the change
After the instance restarts, log back in and run the following command:
cpupower idle-infoThe output should show that the system supports only two C-states: POLL and C1.
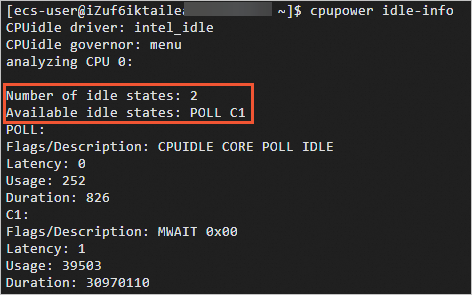
If the output lists only POLL and C1, the configuration is successful. The vCPU no longer enters deep C-states, and wake-up latency is minimized.