variable "region_id" {
type = string
default = "cn-shenzhen"
}
# main.tf
provider "alicloud" {
region = var.region_id
}
resource "local_file" "python_script" {
content = <<EOF
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
sys.path.append('/opt/python')
import json
import logging
import jmespath # Use jmespath instead of jsonpath.
from alibabacloud_tea_openapi import models as open_api_models
from alibabacloud_tea_openapi.client import Client as OpenApiClient
from alibabacloud_openapi_util.client import Client as OpenApiUtilClient
from alibabacloud_tea_util import models as util_models
logger = logging.getLogger()
def handler(event, context):
logger.info(f"This is event: {str(event, encoding='utf-8')}")
get_resources_non_compliant(event, context)
def get_resources_non_compliant(event, context):
# Get information about non-compliant resources.
resources = parse_json(event)
# Traverse the non-compliant resources and perform remediation.
for resource in resources:
remediation(resource, context)
def parse_json(content):
"""
Parse string to json object
:param content: json string content
:return: Json object
"""
try:
return json.loads(content)
except Exception as e:
logger.error('Parse content:{} to json error:{}.'.format(content, e))
return None
def remediation(resource, context):
logger.info(f"Information about the resource to be remediated: {resource}")
region_id = resource['regionId']
account_id = resource['accountId']
resource_id = resource['resourceId']
resource_type = resource['resourceType']
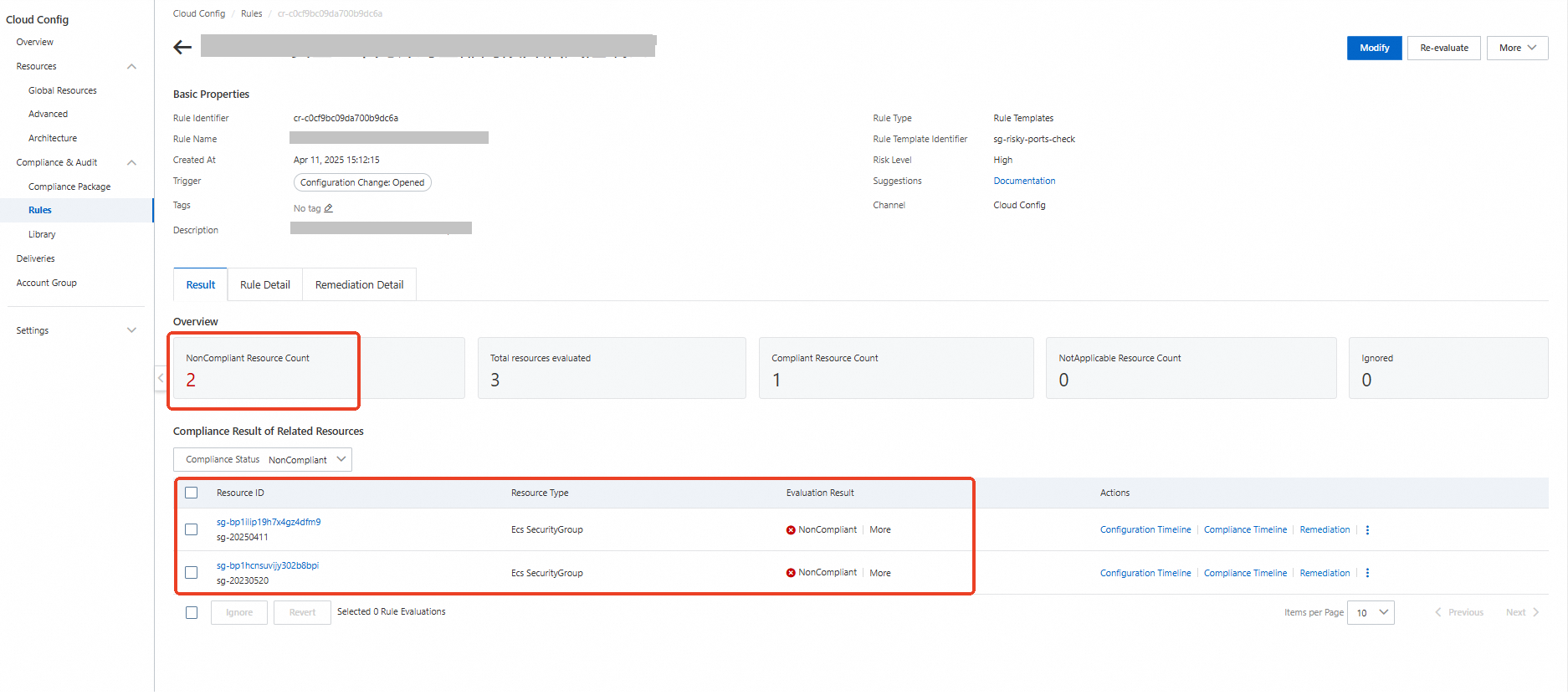
if resource_type == 'ACS::ECS::SecurityGroup':
# Get the configuration of the non-compliant security group and re-verify it to ensure the accuracy of the assessment.
resource_result = get_discovered_resource(context, resource_id, resource_type, region_id)
configuration = json.loads(resource_result["body"]["DiscoveredResourceDetail"]["Configuration"])
# Check whether the security group is a managed security group.
is_managed_security_group = configuration.get('ServiceManaged')
# Use jmespath to get the IDs of security group rules that have an inbound direction and grant access to 0.0.0.0/0.
delete_security_group_rule_ids = jmespath.search(
"Permissions.Permission[?SourceCidrIp=='0.0.0.0/0'].SecurityGroupRuleId",
configuration
)
# If the security group is not a managed security group and has an inbound rule that grants access to 0.0.0.0/0, delete the rule.
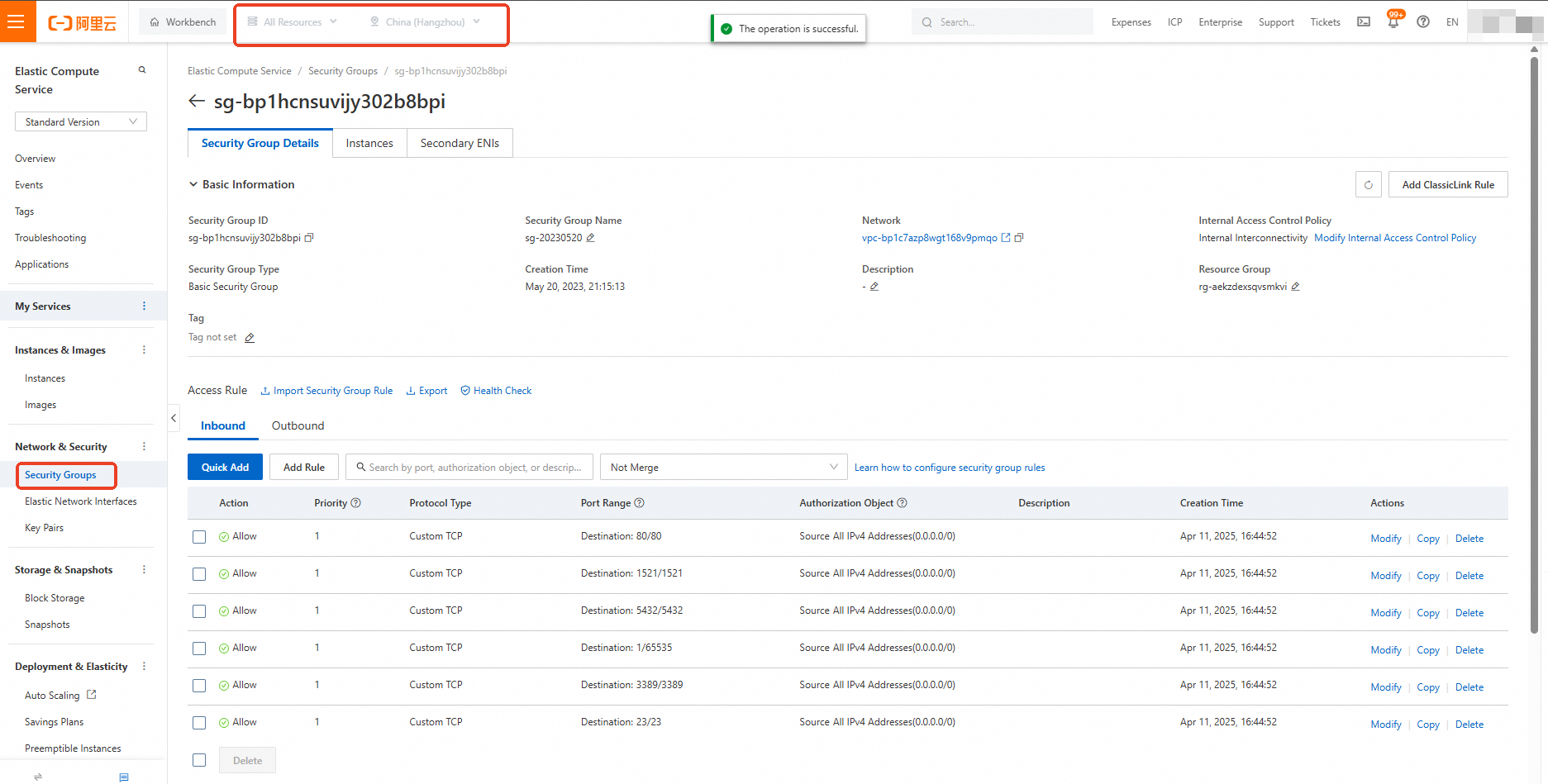
if is_managed_security_group is False and delete_security_group_rule_ids:
logger.info(f"Note: Deleting security group rule {region_id}:{resource_id}:{delete_security_group_rule_ids}")
revoke_security_group(context, region_id, resource_id, delete_security_group_rule_ids)
def revoke_security_group(context, region_id, resource_id, security_group_rule_ids):
creds = context.credentials
config = open_api_models.Config(
access_key_id=creds.access_key_id,
access_key_secret=creds.access_key_secret,
security_token=creds.security_token,
endpoint=f'ecs.{region_id}.aliyuncs.com'
)
client = OpenApiClient(config)
params = open_api_models.Params(
style='RPC', # API style
version='2014-05-26', # API version number
action='RevokeSecurityGroup', # API name
method='POST', # Request method
pathname='/', # The API path. The default path for an RPC API is "/".
protocol='HTTPS', # The API protocol.
auth_type='AK',
req_body_type='json', # The format of the request body.
body_type='json' # The format of the response body.
)
query = {'RegionId': region_id, 'SecurityGroupId': resource_id, 'SecurityGroupRuleId': security_group_rule_ids}
# Create an API request object.
request = open_api_models.OpenApiRequest(
query=OpenApiUtilClient.query(query),
)
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
response = client.call_api(params, request, runtime)
logger.info(f"Deletion result: {response}")
# Get resource details.
def get_discovered_resource(context, resource_id, resource_type, region_id):
"""
Call an API operation to get the configuration details of a resource.
:param context: The Function Compute context.
:param resource_id: The resource ID.
:param resource_type: The resource type.
:param region_id: The ID of the region where the resource resides.
:return: The resource details.
"""
# The service role for Function Compute (FC) must have the AliyunConfigFullAccess permission.
creds = context.credentials
config = open_api_models.Config(
access_key_id=creds.access_key_id,
access_key_secret=creds.access_key_secret,
security_token=creds.security_token,
endpoint='config.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com'
)
client = OpenApiClient(config)
params = open_api_models.Params(
style='RPC', # API style
version='2020-09-07', # API version number
action='GetDiscoveredResource', # API name
method='POST', # Request method
pathname='/', # The API path. The default path for an RPC API is "/".
protocol='HTTPS', # The API protocol.
auth_type='AK',
req_body_type='json', # The format of the request body.
body_type='json' # The format of the response body.
)
query = {'ResourceId': resource_id, 'ResourceType': resource_type, 'Region': region_id}
# Create an API request object.
request = open_api_models.OpenApiRequest(
query=OpenApiUtilClient.query(query),
)
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
try:
response = client.call_api(params, request, runtime)
return response
except Exception as e:
logger.error('GetDiscoveredResource error: %s' % e)
EOF
filename = "${path.module}/python/index.py"
}
resource "local_file" "requirements_txt" {
content = <<EOF
alibabacloud-tea-openapi
jmespath>= 0.10.0
EOF
filename = "${path.module}/python/requests/requirements.txt"
}
locals {
code_dir = "${path.module}/python/"
archive_output = "${path.module}/code.zip"
base64_output = "${path.module}/code_base64.txt"
}
data "archive_file" "code_package" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = local.code_dir
output_path = local.archive_output
depends_on = [
local_file.python_script,
local_file.requirements_txt,
]
}
resource "null_resource" "upload_code" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = <<EOT
base64 -w 0 ${local.archive_output} > ${local.base64_output}
EOT
interpreter = ["sh", "-c"]
}
depends_on = [data.archive_file.code_package]
}
data "local_file" "base64_encoded_code" {
filename = local.base64_output
depends_on = [null_resource.upload_code]
}
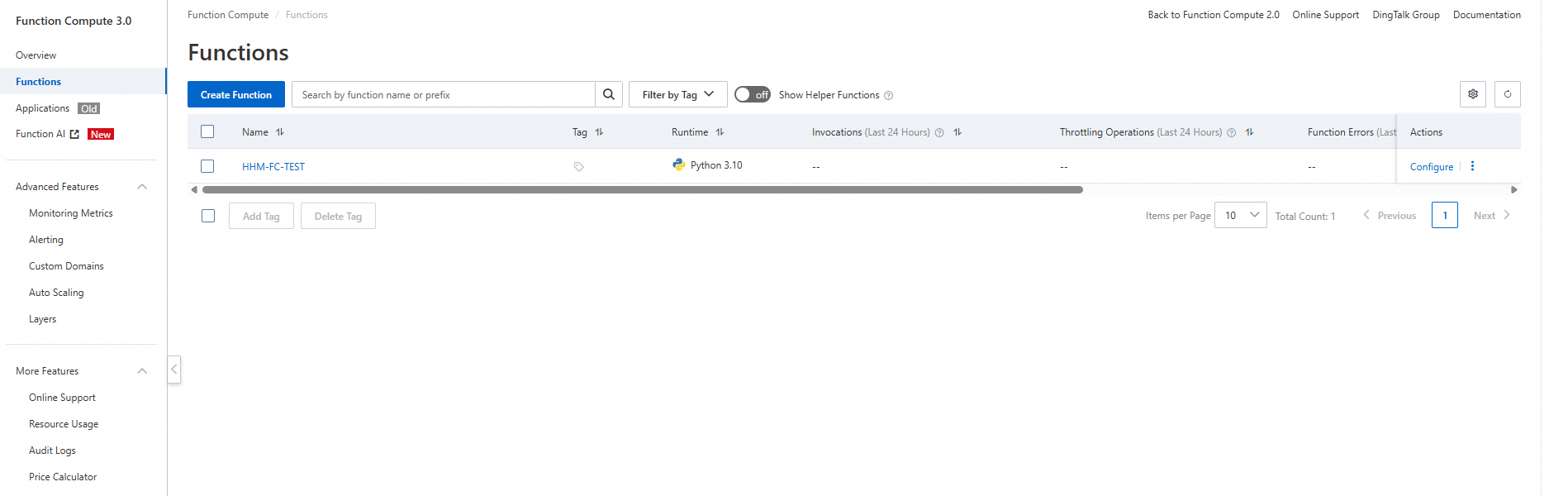
resource "alicloud_fcv3_function" "fc_function" {
runtime = "python3.10"
handler = "index.handler"
function_name = "HHM-FC-TEST"
role = alicloud_ram_role.role.arn
code {
zip_file = data.local_file.base64_encoded_code.content
}
lifecycle {
ignore_changes = [
code
]
}
# Explicitly set log_config to empty.
log_config {}
depends_on = [data.local_file.base64_encoded_code]
}
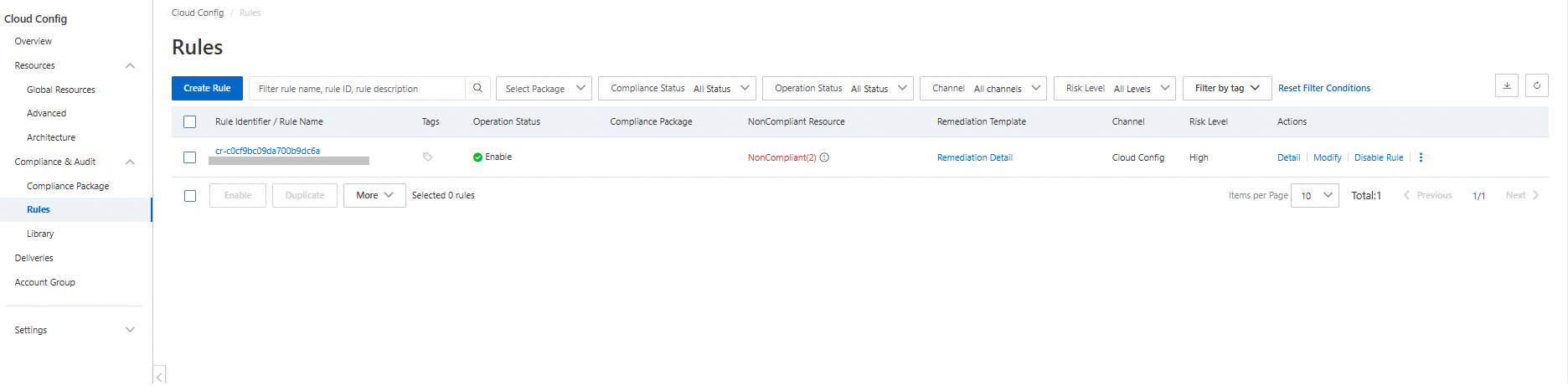
resource "alicloud_config_rule" "default" {
rule_name = "SPM0014-sg-disallow-risky-ports-for-all-ips"
description = "Prohibits security groups from opening vulnerable ports 22 and 3389 to all IP ranges."
source_owner = "ALIYUN"
# (Required, ForceNew) Specifies whether you or Alibaba Cloud owns and manages the rule. Valid values: CUSTOM_FC: The rule is a custom rule that you own. ● ALIYUN: The rule is a managed rule that Alibaba Cloud owns.
source_identifier = "sg-risky-ports-check"
# The identifier of the rule. For a managed rule, the value is the name of the managed rule. For a custom rule, the value is the Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of the custom rule. (Required, ForceNew)
resource_types_scope = ["ACS::ECS::SecurityGroup"]
# The IDs of resources that are excluded from the monitoring scope. Separate multiple IDs with commas (,). This parameter applies only to rules created based on managed rules. For custom rules, this parameter is empty.
config_rule_trigger_types = "ConfigurationItemChangeNotification" # The rule is triggered when a configuration changes.
# Valid values: One_Hour, Three_Hours, Six_Hours, Twelve_Hours, and TwentyFour_Hours.
risk_level = 1 # ● 1: Critical ● 2: Warning ● 3: Informational
input_parameters = {
"ports" : "22,3389"
}
}
resource "alicloud_config_remediation" "default" {
config_rule_id = alicloud_config_rule.default.id
remediation_template_id = alicloud_fcv3_function.fc_function.function_arn
remediation_source_type = "CUSTOM"
invoke_type = "AUTO_EXECUTION"
params = "{}"
remediation_type = "FC"
}
resource "random_integer" "default" {
min = 10000
max = 99999
}
resource "alicloud_ram_role" "role" {
name = "tf-example-role-${random_integer.default.result}"
document = <<EOF
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"fc.aliyuncs.com"
]
}
}
],
"Version": "1"
}
EOF
description = "Ecs ram role."
force = true
}
resource "alicloud_ram_policy" "policy" {
policy_name = "tf-example-ram-policy-${random_integer.default.result}"
policy_document = <<EOF
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"config:GetDiscoveredResource",
"ecs:RevokeSecurityGroup"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": ["*"]
}
],
"Version": "1"
}
EOF
description = "This is a policy test."
force = true
}
resource "alicloud_ram_role_policy_attachment" "attach" {
policy_name = alicloud_ram_policy.policy.policy_name
policy_type = "Custom"
role_name = alicloud_ram_role.role.name
}