This topic describes the following issue, the causes of the issue, and solutions to the issue: You cannot access a website from a Windows instance and find that the IP addresses to which the domain name of the website is resolved are different on the instance and an on-premises machine.
Problem description
You cannot use a browser on a Windows instance to access a website, but can access the website from other devices. When you troubleshoot the issue, you find that the domain name of the website is resolved to different IP addresses on the instance and the other devices.
You cannot access the website from a Windows instance, and an error is reported, as shown in the following figure. However, you can access the website from your computer.

You log on to the Windows instance and run the
ping <Domain name of the website>andnslookup <Domain name of the website>commands in Command Prompt on the instance. In the command outputs, the IP addresses to which the domain name of the website is resolved are different on the instance and your computer, as shown in the following figure.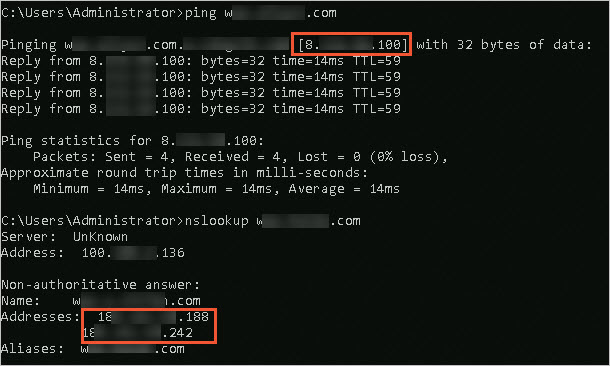
Causes
The domain name of the website may be resolved to different IP addresses on the Windows instance and on your computer because of the following reasons:
DNS resolution results are cached in the DNS cache of the Windows operating system. In this case, flush the DNS cache and then re-access the website. For more information, see the Flush the DNS cache section of the topic.
In the hosts file of the Windows operating system, the domain name of the website is mapped to specific IP addresses. In this case, delete the domain name-to-IP address mappings of the website from the hosts file and then access the website again. For more information, see the Delete the mappings of the website from the hosts file section of this topic.
A private DNS (PrivateZone) record is configured for the domain name of the website on the Windows instance that resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC). In this case, modify the private DNS (PrivateZone) record and then re-access the website from the instance. For more information, see the Modify the private DNS (PrivateZone) record for the website section of this topic.
Solutions
This section describes how to resolve the issue based on the cause of the issue. In the examples, an instance that runs Windows Server 2019 Datacenter 64-bit is used. For instances that run other Windows operating system versions, the operations that you must perform may vary.
Flush the DNS cache
Connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see Connection method overview.
Flush the DNS cache of the Windows operating system.
Enter
cmdin the search box and then click Command Prompt.
At the command prompt, run the
ipconfig /flushdnscommand to flush the DNS cache.
At the command prompt, run the
ping <Domain name of the website>command to check whether the domain name of the website can be resolved as expected.The following figure shows a sample command output, which indicates that the domain name is resolved as expected.

Use a browser to re-access the website.
Delete the mappings of the website from the hosts file
Connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see Connection method overview.
Delete the domain name-to-IP address mappings of the website from the hosts file of the Windows operating system.
Open the
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostsfile and check whether the domain name-to-IP address mappings of the website exist in the file. If the domain name-to-IP address mappings of the website exist in the file as shown in the following figure, delete the mappings from the file and then save the file.
At the command prompt, run the
ping <Domain name of the website>command to check whether the domain name of the website can be resolved as expected.The following figure shows a sample command output, which indicates that the domain name is resolved as expected.

Use a browser to re-access the website.
Modify the private DNS (PrivateZone) record for the website
Perform the following troubleshooting steps:
Check whether the effective scope of the built-in authoritative zone that is associated with the domain name of the website covers the VPC in which the Windows instance resides. If the effective scope of the built-in authoritative zone does not cover the VPC in which the Windows instance resides, you must add the VPC to the effective scope of the built-in authoritative zone in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. For more information, see Configure the effective scope of a built-in authoritative zone.
Check whether the private DNS record meets your requirement to access the website. If the private DNS record does not meet your requirement to access the website, modify the private DNS record. For more information, see Modify DNS records.
Use a browser to re-access the website.
ImportantThe PrivateZone record is automatically read and updated every 1 minute in the operating system of the instance, with no other manual intervention required.