This topic describes how to use a data cache to deploy the QwQ-32B model. Before you deploy the QwQ-32B model, you can pull the model data and store it in a data cache. When you deploy the model, you can mount the model data to the elastic container instance that hosts the model. This way, Elastic Container Instance does not need to pull the model data but directly uses the data cache when the instance starts and accelerate the deployment of the model.
Why is Elastic Container Instance used to deploy QwQ-32B
Elastic Container Instance does not require O&M and can flexibly deploy applications and help you build elastic and cost-effective business. For more information, see Benefits.
Elastic Container Instance uses DataCaches and ImageCaches to save time of image pulls and model downloads, reduce network resource consumption, and improve system efficiency.
NoteThe deployment of a containerized large model inference service involves the following stages: create and start a container, pull the image, download the model file, and load and start the model. An extended period of time and a large amount of network traffic are required to pull the image and model of a large model inference service due to the large size of the image and model. Elastic Container Instance uses ImageCaches and DataCaches to save time of image pulls and model downloads.
Prerequisites
The virtual private cloud (VPC) that you use is associated with an Internet NAT gateway. An SNAT entry is configured for the NAT gateway to allow resources in the VPC or resources connected to vSwitches in the VPC to access the Internet.
If the VPC is not associated with an Internet NAT gateway, you must associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with the VPC when you create the DataCache and deploy the application. This way, you can pull data from the Internet.
Prepare a runtime environment
Recommended ECS instance types
We recommend that you use a GPU-accelerated Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance type that provides four NVIDIA A10 or higher GPU specifications, such as ecs.gn7i-4x.8xlarge, ecs.gn7i-4x.16xlarge, and ecs.gn7i-c32g1.32xlarge. For information about the GPU-accelerated ECS instance types that you can use to create elastic container instances, see Supported instance families.
NoteWhen you select an ECS instance type, make sure that the instance type is supported by the region and zone where the cluster resides. For more information, see Instance Types Available for Each Region.
Software requirements
The deployment of a large model depends on a large number of libraries and configurations. vLLM is a mainstream large model inference engine and used to deploy the inference service in this topic. Elastic Container Instance provides a public container image. You can directly use the public container image or perform secondary development based on the public container image. The image is stored at
registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/eci_open/vllm-openai:v0.7.2and about 16.5 GB in size.
Step 1: Create a data cache
Use the Elastic Container Instance console
Access ModelScope to obtain the ID of the model.
In this topic, the master version of QwQ-32B is used. Find the model that you want to use in ModelScope and copy the model ID in the upper-left corner of the model details page.
Log on to the Elastic Container Instance console.
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Cache.
Create a data cache for QwQ-32B.
Click Create Data Cache.
Configure the parameters that are used to create the data cache.
The following figure and table describe the sample parameter values that are used in this example. You must use the values provided in this topic for the Cache Data Source parameter. These provided values are fixed configurations for pulling the QwQ-32B model. You can specify other parameters based on your business requirements. For more information, see Create and manage a data cache.
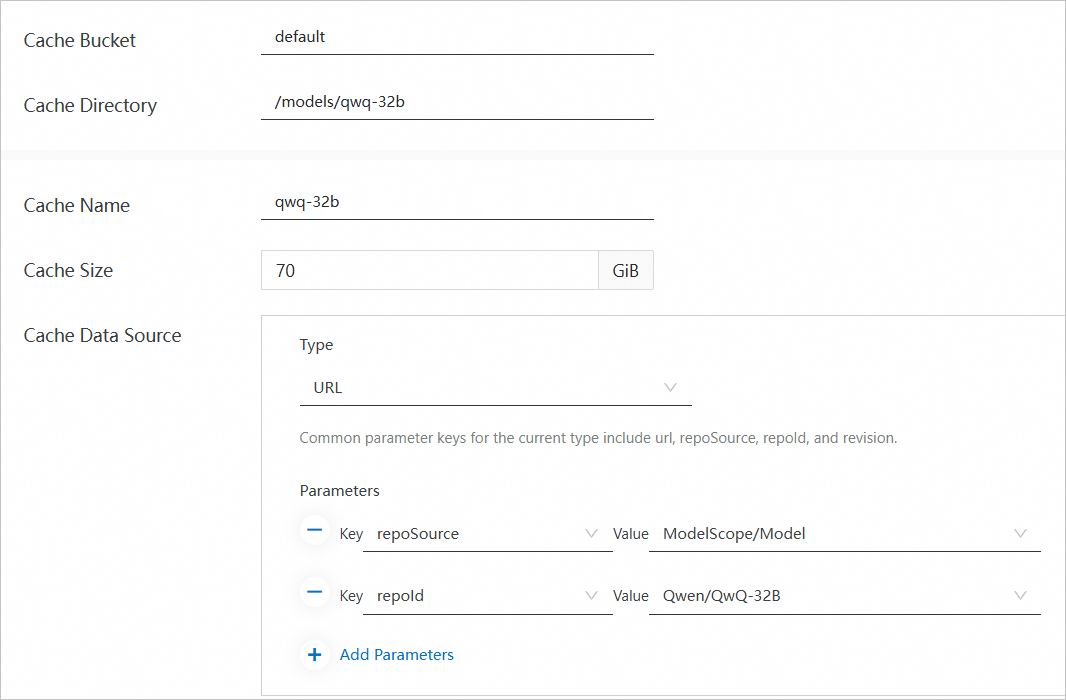
Parameter
Example
Cache Bucket
default
Cache Directory
/models/qwq-32b
Cache Name
qwq-32b
Cache Size
70 GiB
Cache Data Source
Type: URL
Parameters
repoSource: ModelScope/Model
repoId: Qwen/QwQ-32B
Click OK.
View the status of the data cache.
On the Data Cache page, refresh the page to view the status of the data cache. If the status becomes Available, the data cache is ready for use. Alibaba Cloud provides the hot load capability for QwQ-32B, which makes a data cache be created within seconds.
OpenAPI
Access ModelScope to obtain the ID of the model.
In this topic, the master version of QwQ-32B is used. Find the model that you want to use in ModelScope and copy the model ID in the upper-left corner of the model details page.
Create a data cache for QwQ-32B.
Call the CreateDataCache API operation to create a data cache. We recommend that you use Elastic Container Instance SDKs to create a data cache. For more information, see Overview.
The following code shows a sample SDK for Java. The system pulls the model data from ModelScope and stores the model data in the
/models/qwq-32bdirectory of the bucket named default.CreateDataCacheRequest request = new CreateDataCacheRequest(); request.setName("qwq-32b"); request.setBucket("default"); request.setPath("/models/qwq-32b"); request.setVSwitchId("vsw-2ze*********"); request.setSecurityGroupId("sg-2ze*********"); CreateDataCacheRequest.DataSource dataSource = new CreateDataCacheRequest.DataSource(); dataSource.setType("URL"); HashMap<String, String> options = new HashMap<>(); options.put("repoId", "Qwen/QwQ-32B"); options.put("repoSource", "ModelScope/Model"); dataSource.setOptions(options); request.setDataSource(dataSource);Query the status of the data cache.
Use the returned DataCache ID to call the DescribeDataCaches API operation and query the information of the DataCache. If the status of the DataCache that is indicated by DataCaches.Status is Available, the DataCache is ready for use.
Step 2: Deploy the QwQ-32B model inference service
You must specify the GPU driver version when you deploy the QwQ-32B model inference service. The console mode does not support the feature.
Use the data cache to create an elastic container instance and deploy QwQ-32B on the instance.
The following code shows the sample parameter values that are used when you call the CreateContainerGroup API operation to create the elastic container instance. The instance is created based on GPU-accelerated ECS instance types and is mounted with the QwQ-32B model. After the container is started, the container runs
vllm serve /models/QwQ-32B --port 8000 --trust-remote-code --served-model-name qwq-32b --tensor-parallel=4 --max-model-len 8192 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.95 --enforce-eagerto start the vLLM inference engine.NoteIn the following example, the system automatically creates an EIP and associates the EIP with the elastic container instance. If the VPC to which the elastic container instance belongs is associated with an Internet NAT gateway, you may not associate an EIP with the elastic container instance when you create the instance. After the instance is created, you can configure DNAT entries to allow external access to the instance.
{ "RegionId": "cn-beijing", "SecurityGroupId": "sg-2ze**************", "VSwitchId": "vsw-2ze**************", "ContainerGroupName": "qwq-32b-server", "InstanceType": "ecs.gn7i-4x.8xlarge,ecs.gn7i-4x.16xlarge,ecs.gn7i-c32g1.32xlarge", "DataCacheBucket": "default", "GpuDriverVersion": "tesla=535.161.08", "EphemeralStorage": 20, "Container": [ { "Arg": [ "-c", "vllm serve /models/QwQ-32B --port 8000 --trust-remote-code --served-model-name qwq-32b --tensor-parallel=4 --max-model-len 8192 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.95 --enforce-eager" ], "Command": [ "/bin/sh" ], "Gpu": 4, "Name": "vllm", "Image": "registry-vpc.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/eci_open/vllm-openai:v0.7.2", "VolumeMount": [ { "Name": "llm-model", "MountPath": "/models/QwQ-32B" }, { "Name": "dshm", "MountPath": "/dev/shm" } ] } ], "Volume": [ { "Type": "HostPathVolume", "HostPathVolume.Path": "/models/qwq-32b", "Name": "llm-model" }, { "Type": "EmptyDirVolume", "Name": "dshm", "EmptyDirVolume.Medium": "Memory", "EmptyDirVolume.SizeLimit": "30Gi" } ], "DataCacheProvisionedIops": 15000, "DataCacheBurstingEnabled": true, "AutoCreateEip": true }Check whether the application is deployed.
Use the returned instance ID to call the DescribeContainerGroupStatus API operation and query the status of the instance and the container. If the status of the instance that is indicated by Status and the status of the container that is indicated by ContainerStatuses.State are Running, the instance is created and the container is running.
Query the EIP of the elastic container instance.
Use the returned instance ID to call the DescribeContainerGroups API operation and query the instance details. You can obtain the EIP of the instance from the InternetIP parameter.
Step 3: Test the model inference service
Add an inbound rule to the security group to which the elastic container instance belongs and enable port 8000.
Send a request to the QwQ-32B model inference service.
In this example, an EIP is associated with QwQ-32B. Replace
XX.XX.XX.XXin the sample code with your actual EIP.curl POST http://XX.XX.XX.XX:8000/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "qwq-32b", "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "Briefly describe cloud computing in one sentence" } ], "temperature": 0.6, "max_tokens": 3000 }' \ --verboseExpected output:
{"id":"chatcmpl-7678099ec2b24852bc5b96b1227b0010","object":"chat.completion","created":1741747813,"model":"qwq-32b","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":" OK, the user asks me to briefly describe cloud computing in one sentence. I need to determine what the user needs. Maybe they need to quickly understand the basic concepts of cloud computing without going too deep into the technical details. So, I need to grasp the core features of cloud computing, such as resource virtualization, on-demand services, and elastic scaling. Then I need to make sure that the sentence is concise and easy to understand. \n\n Next, I have to think about the common definition of cloud computing. It usually refers to the provision of computing resources over the Internet, such as servers, storage, and databases, and use of computing resources and payment for computing resource on demand. It may also refer to elastic scaling, which is the automatic adjustment of resources according to demand. In addition, I think about the service models of cloud computing, such as IaaS, PaaS and SaaS, but they may not need to be mentioned in one sentence. They are too complicated. A deeper need that the user may not have spoken about is that they may want to understand the benefits of cloud computing, such as cost saving, flexibility, or how it differs from traditional IT. So these benefits need to be implied in the sentence. For example, keywords such as "no upfront investment required" or "flexible scaling" must be included. \n\n Then pay attention to avoid technical terms and make the sentence more common. For example, use "over the Internet" instead of "based on Internet infrastructure", or "on-demand access" instead of "on-demand self-service". Also make sure the sentence structure is smooth and the information is complete. \n \n I may also need to compare cloud computing with traditional methods. For example, users used to need to buy their own servers, but now they can rent cloud services. The comparison makes cloud computing more intuitive. But one sentence may not include the comparison, so I can use "no need to build your own infrastructure" to imply this. \n\n Check whether there are any missing key points: resource type (compute, storage, network), delivery method (Internet), on-demand service, elasticity, and pay-per-use. If all these are covered, it should be no problem. \n\n Finally, I need to combine the information into one sentence and make sure the information is accurate. For example: "Cloud computing is a model that provides on-demand access to scalable computing resources (such as servers, storage, and applications) through the Internet. Users can flexibly acquire and manage resources without building their own infrastructure, and pay according to actual usage." This should cover the main elements and be concise. \n</think>\n \n Cloud computing is a model that provides scalable computing resources (such as servers, storage, networks, and applications) over the Internet. Users can access and pay for the actual usage without the need to build their own infrastructure. ","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":15,"total_tokens":450,"completion_tokens":435,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}The content before
</think>represents the thinking process or inference steps before the model generates the final answer. These markers are not a part of the final output, but a record of the self-prompting or logical inference of the model before the model generates the answer.Extracted final answer:
Cloud computing is a model that provides scalable computing resources (such as servers, storage, networks, and applications) over the Internet. Users can access and pay for the actual usage without the need to build their own infrastructure.