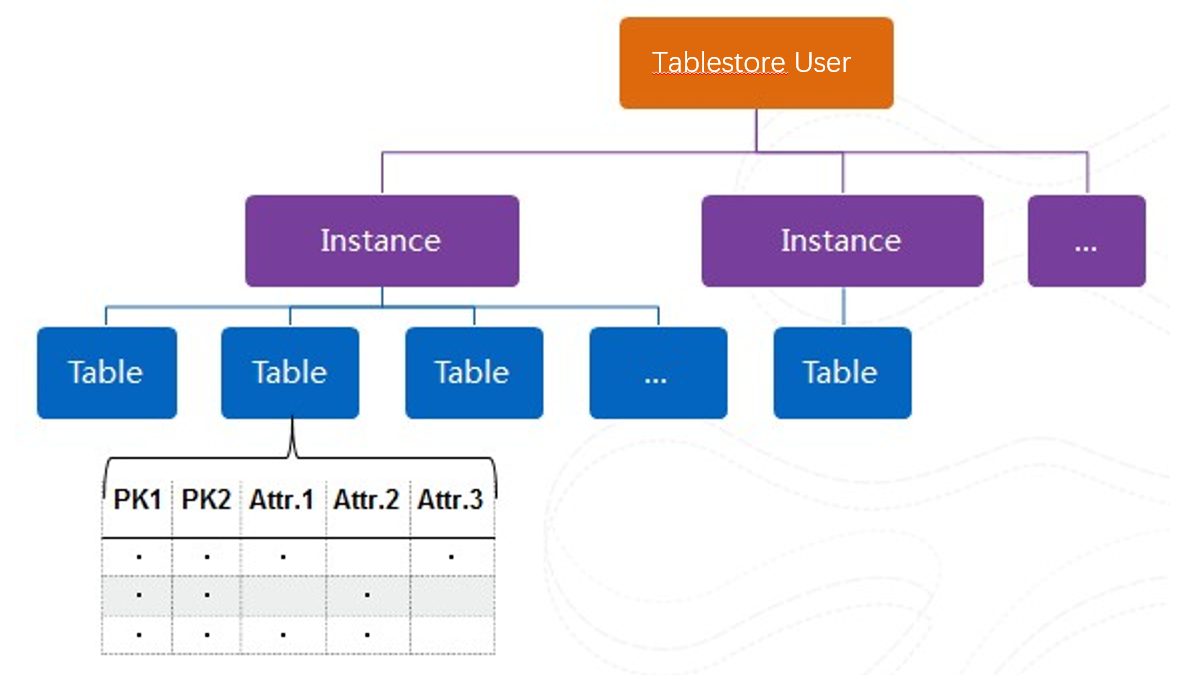
An instance is a logical entity used in Tablestore to manage tables. Each instance is equivalent to a database. Tablestore manages access to Tablestore from applications and measures resources at the instance level. After Tablestore is activated, you can create an instance in the Tablestore console and then manage and perform operations on tables and data in this instance.
Tablestore allows you to create up to 10 instances in each Alibaba Cloud account and up to 64 tables in each instance. Tables include data tables, secondary index tables, and time series tables. If you want to create more instances or tables, submit a ticket.
Instance types
Tablestore supports two instance types: high-performance instance and capacity instance. The two instance types support petabytes of data for a single table, but differ in costs and applicable scenarios. The following table compares the two instance types.
After you create an instance, you cannot change the type of the instance. Proceed with caution.
If you want to change the type of an instance, you can migrate data from the instance to another instance. You can use tools such as DataWorks to migrate data. For more information, see Synchronize data from one table to another table in Tablestore.
You are charged for high-performance storage usage, reserved read throughput, and metered read throughput when you use the search index feature regardless of the instance type. For more information, see Billable items of search indexes.
When you use the TimeSeries model, the following rules apply regardless of the instance type: You are charged for the metered read and write throughput that is consumed by read and write operations on data in time series based on the pricing for the throughput that is consumed by read and write operations on common data in capacity instances. You are charged for the metered read and write throughput that is consumed by read and write operations on metadata of time series based on the pricing for the throughput that is consumed by read and write operations on common data in high-performance instances. You are charged for the storage usage of metadata of time series based on the pricing for the storage usage of common data in high-performance instances. For more information, see Billable items of the TimeSeries model.
Instance type | High-performance instance | Capacity instance | |
Scenario | This instance type is suitable for online scenarios that require high concurrency and ultra-low read and write latency. | This instance type is suitable for offline scenarios that require cost-effective storage. This instance type is not suitable for online scenarios that are sensitive to access latency. | |
Billable item |
|
| |
Performance metric | Read performance | High | Medium |
Write performance | High | High | |
Concurrency | High | Medium | |
Instance naming conventions
The name of an instance must be unique within a region. The name can be the same across regions. The following items describe the naming conventions:
The name can contain only letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
The name must start with a letter.
The name cannot end with a hyphen (-).
The name is case-insensitive.
The name must be 3 to 16 characters in length.
The name cannot contain the following words:
ali,ay,ots,taobao, andadmin.
Instance types that are supported in each region
Region | High-performance instance | Capacity instance |
China (Hangzhou) | Supported | Supported |
China East 1 Finance | Supported | Not supported |
China (Shanghai) | Supported | Supported |
China East 2 Finance | Not supported | Supported |
China (Qingdao) | Not supported | Supported |
China (Beijing) | Supported | Supported |
China (Zhangjiakou) | Supported | Supported |
China (Hohhot) | Not supported | Supported |
China (Ulanqab) | Supported | Not supported |
China (Shenzhen) | Supported | Supported |
China (Guangzhou) | Supported | Not supported |
China (Chengdu) | Supported | Supported |
China (Hong Kong) | Supported | Supported |
Singapore | Supported | Not supported |
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur) | Supported | Supported |
Indonesia (Jakarta) | Supported | Supported |
Japan (Tokyo) | Not supported | Supported |
Philippines (Manila) | Supported | Not supported |
Thailand (Bangkok) | Supported | Not supported |
Germany (Frankfurt) | Supported | Supported |
UK (London) | Supported | Supported |
US (Silicon Valley) | Supported | Supported Important You cannot purchase capacity instances in the US (Silicon Valley) region. |
US (Virginia) | Supported | Supported |
UAE (Dubai) | Not supported | Supported |
SAU (Riyadh - Partner Region) | Supported | Not supported |