A PolarDB version number uses the format Major.Minor.Revision. Each part has a specific meaning:
Major Version (DB version): The primary identifier, such as 8.0. Different major versions contain significant feature differences.
Minor Version: A feature release within a major version, such as 8.0.1. You select a minor version when you create a cluster.
Revision: A patch release within a minor version, such as 8.0.1.1.0. A revision includes performance optimizations, security patches, and bug fixes.
Here is an example using PolarDB for MySQL version 8.0.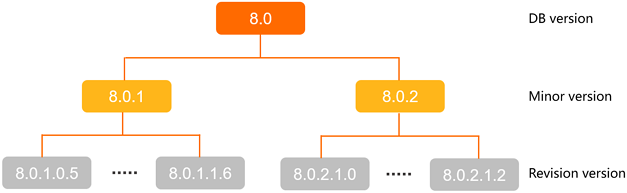
Note Upgrading from a lower version to a higher version does not require application changes. See Update engine versions for details.
Compatibility
MySQL versions
PolarDB for MySQL offers the following major versions:
PolarDB engine version | Compatible MySQL minor version |
8.0.2 | 8.0.18 and earlier |
8.0.1 | 8.0.13 and earlier |
5.7 | 5.7.28 and earlier |
5.6 | 5.6.16 and earlier |
Standards and protocols
SQL Standards: Supports ANSI/ISO SQL. To enable this, set the sql_mode parameter to ANSI. See Configure cluster and node parameters for details.
ODBC: Supports Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) versions 0 to 3.51.
JSON: Versions 5.7 and 8.0 support the native JSON data type like RFC 7159 and ECMA-262.
XML: Supports W3C and XPath standard XML functions.
Syntax for new features
PolarDB for MySQL includes advanced features that are not available in standard MySQL. To ensure that these features do not break downstream replication tools (like mysqldump or binlog synchronization), PolarDB automatically wraps new or modified SQL syntax in versioned comments.
Examples
Method 1: Execute the SHOW CREATE TABLE statement.
When you create a table with a PolarDB-specific feature like a GLOBAL index, the SHOW CREATE TABLE command reveals how compatibility is maintained.
CREATE TABLE `t1` (c1 int, KEY(c1) GLOBAL) ENGINE=InnoDB PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`) PARTITIONS 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
SHOW CREATE TABLE t1;
+-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| t1 | CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`c1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `c1` (`c1`) /*!99990 800020207 GLOBAL */
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
/*!50100 PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`)
PARTITIONS 4 */ |
Method 2: Use the mysqldump tool.
CREATE TABLE `t1` (c1 int, KEY(c1) GLOBAL) ENGINE=InnoDB PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`) PARTITIONS 4;
DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`);
--result
mysqldump --compact test t1
include/mysqlbinlog.inc
/*!50530 SET @@SESSION.PSEUDO_SLAVE_MODE=1*/;
/*!50003 SET @OLD_COMPLETION_TYPE=@@COMPLETION_TYPE,COMPLETION_TYPE=0*/;
DELIMITER /*!*/;
ROLLBACK/*!*/;
# [empty]
# original_commit_timestamp= MICROSECONDS-FROM-EPOCH (YYYY-MM-DD HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS TZ)
# immediate_commit_timestamp= MICROSECONDS-FROM-EPOCH (YYYY-MM-DD HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS TZ)
/*!80001 SET @@session.original_commit_timestamp= MICROSECONDS-FROM-EPOCH*//*!*/;
/*!80014 SET @@session.original_server_version= ORIGINAL_SERVER_VERSION*//*!*/;
/*!80014 SET @@session.immediate_server_version= IMMEDIATE_SERVER_VERSION*//*!*/;
SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= '#'/*!*/;
use `test`/*!*/;
SET TIMESTAMP=#/*!*/;
SET @@session.pseudo_thread_id=#/*!*/;
SET @@session.foreign_key_checks=1, @@session.sql_auto_is_null=0, @@session.unique_checks=1, @@session.autocommit=1/*!*/;
SET @@session.sql_mode=1168113696/*!*/;
SET @@session.auto_increment_increment=1, @@session.auto_increment_offset=1/*!*/;
/*!\C utf8mb4 *//*!*/;
SET @@session.character_set_client=255,@@session.collation_connection=255,@@session.collation_server=255/*!*/;
SET @@session.lc_time_names=0/*!*/;
SET @@session.collation_database=DEFAULT/*!*/;
/*!80011 SET @@session.default_collation_for_utf8mb4=255*//*!*/;
/*!80013 SET @@session.sql_require_primary_key=0*//*!*/;
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`c1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `c1` (`c1`) /*!99990 800020207 GLOBAL */
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
/*!50100 PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`)
PARTITIONS 4 */
/*!*/;
......
Method 3: Use binary log synchronization.
In this example, binary logs are synchronized from PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2.2.0 to MySQL 8.0.27.
Use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to synchronize binary logs from PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2.2.0 to MySQL 8.0.27. For more information, see From a PolarDB for MySQL cluster to an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
View the binary log synchronization result on PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2.2.0 and MySQL 8.0.27.
Sample result on PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2.2.0: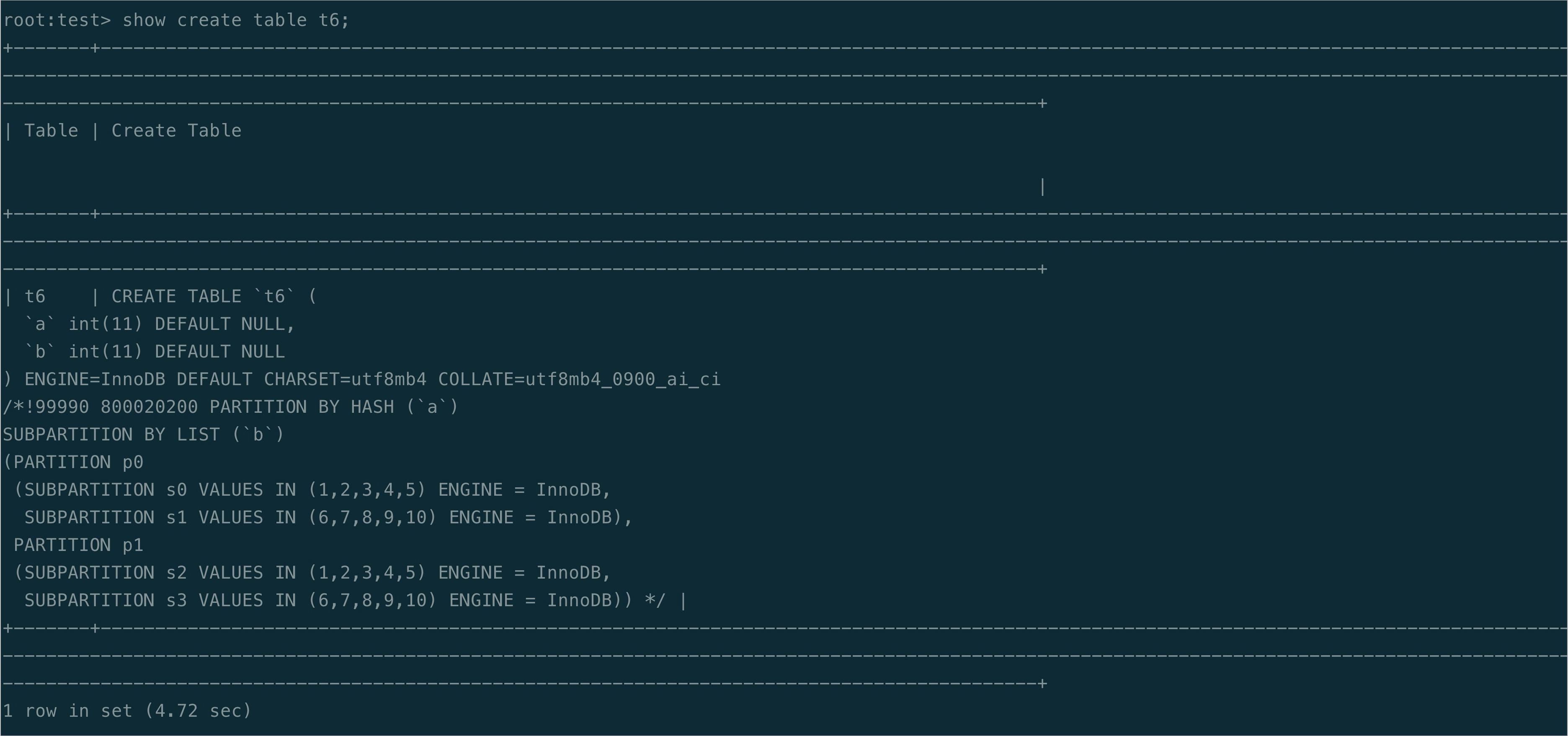
Sample result on MySQL 8.0.27: 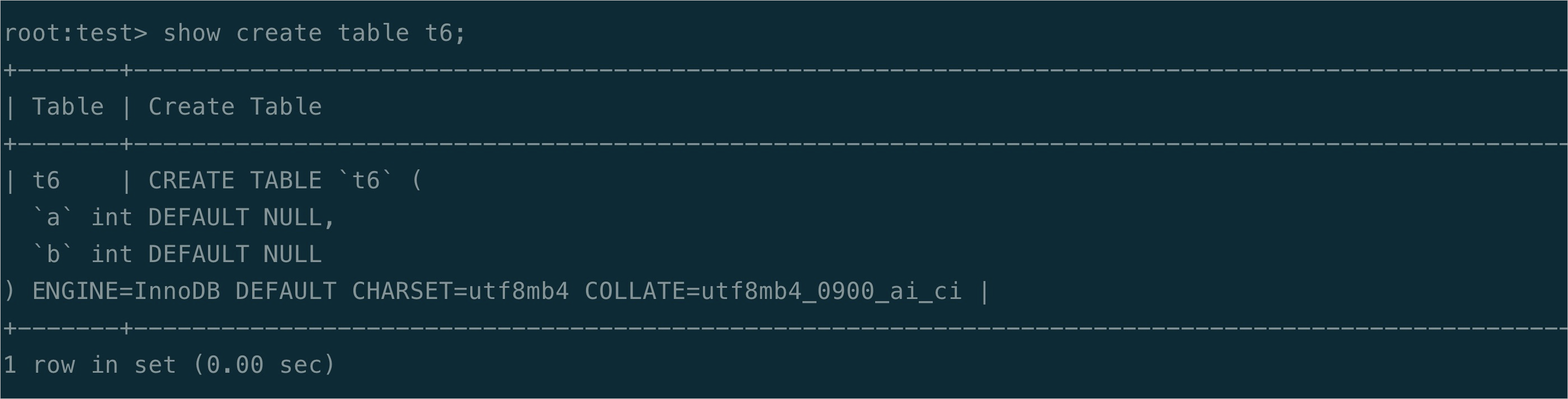 As shown in the preceding figures, the new features provided in PolarDB for MySQL do not appear in the MySQL result.
As shown in the preceding figures, the new features provided in PolarDB for MySQL do not appear in the MySQL result.
Note After data is synchronized from PolarDB for MySQL 8.0.2.2.0 to MySQL 8.0.27, the new features provided in PolarDB for MySQL are no longer available in MySQL.
DDL statements other than CREATE TABLE
Manually add comments to PolarDB for MySQL statements to ensure compatibility. Syntax:
/*!99990 800020200 Special new PolarDB Syntax SQL supported >= version 2.2.0 */
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`c1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `c1` (`c1`) /*!99990 800020207 GLOBAL */
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
/*!50100 PARTITION BY HASH (`c1`)
PARTITIONS 4 */
How to manage engine versions
Check your current version
You can find your cluster's engine version in two ways:
Console
Log on to the PolarDB console.
Navigate to the Basic Information page of your cluster, and check the value of the Kernel Version parameter.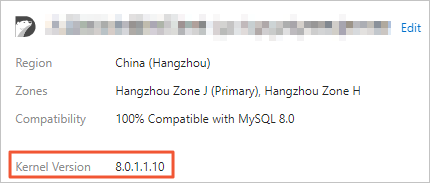
SQL Command
Connect to your cluster.
Run the following command to see the revision number:
show variables like '%polardb_version%';
Note: For version 5.6, use show variables like '%rds_release_date%'; instead.
Upgrade engine versions
Major version: To upgrade the major version, such as from 5.7 to 8.0, see Upgrade the Engine Version.
Minor versions: You cannot upgrade the minor version directly. To change minor versions, create a new cluster and migrate your data. Use the Data Transmission Service (DTS) for data migration.
Revision versions: To apply the latest patches and optimizations, see Upgrade revision versions.
Release notes
For a detailed list of new features, enhancements, and bug fixes in each version, see the following release notes:



 As shown in the preceding figures, the new features provided in
As shown in the preceding figures, the new features provided in