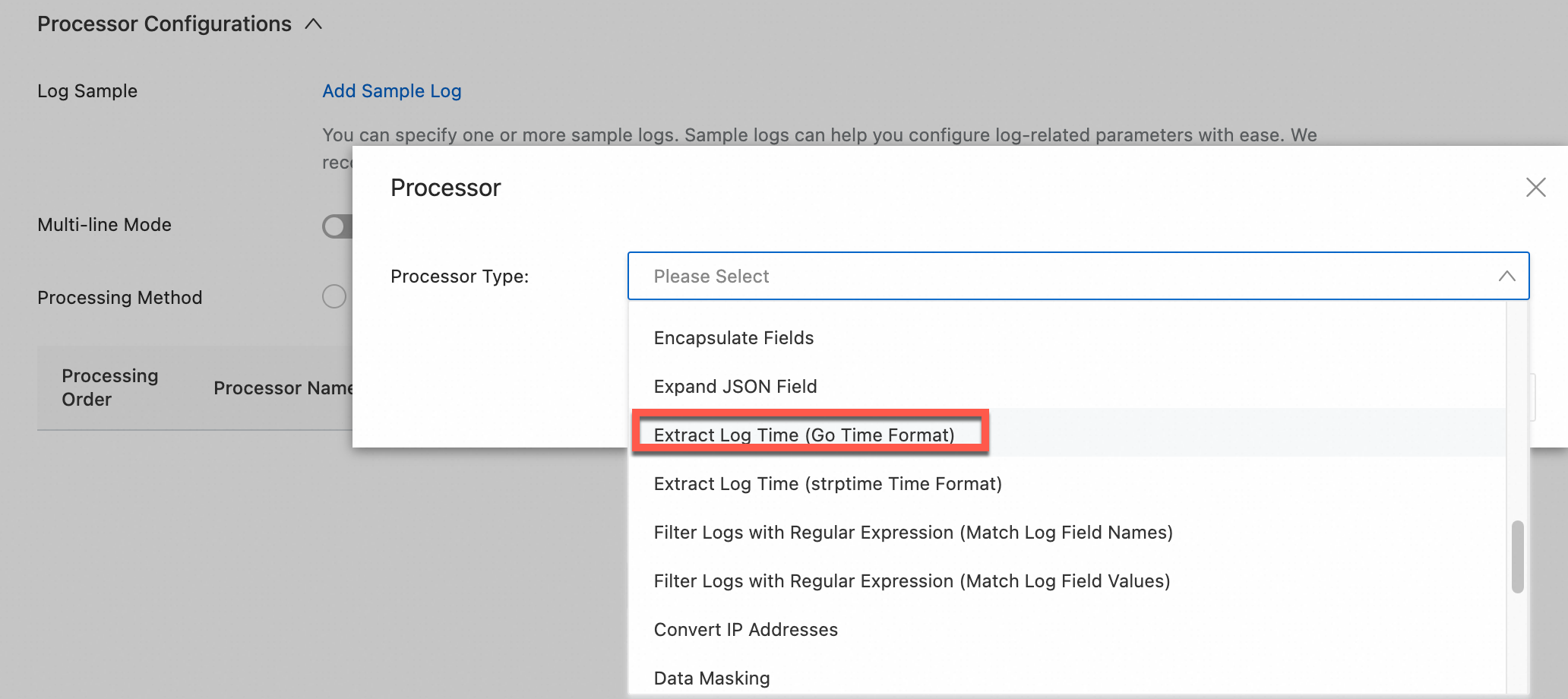
Time processing plugins parse, extract, and standardize the time field in logs.
Plugin effect example
The following table compares the data structure of a raw log after it is saved to Simple Log Service with and without the native time parsing plugin.
Raw Logs | Without using plugins | Using the time parsing plugin (native) |
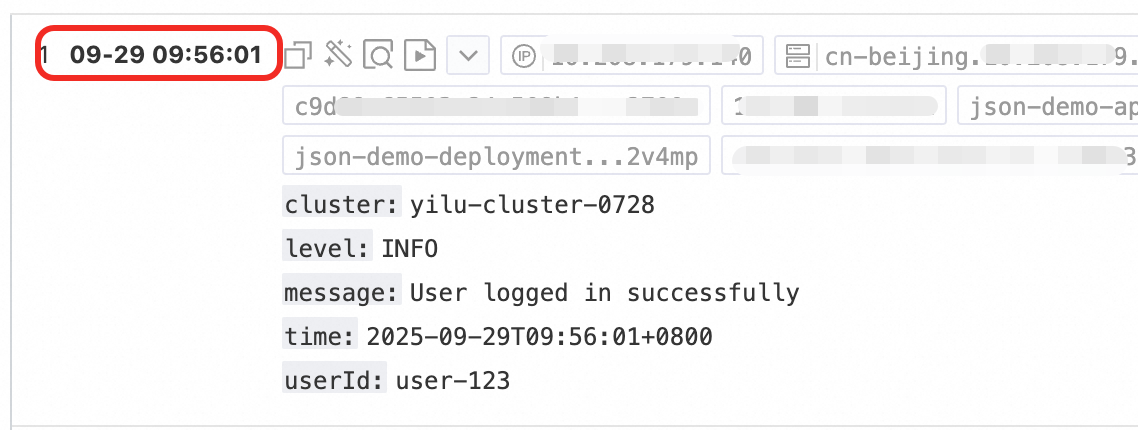
Second-level time: | Content: "{"level":"INFO","timestamp":"2025-09-29T09:56:01+0800","cluster":"yilu-cluster-0728","message":"User logged in successfully","userId":"user-123"}" |
|
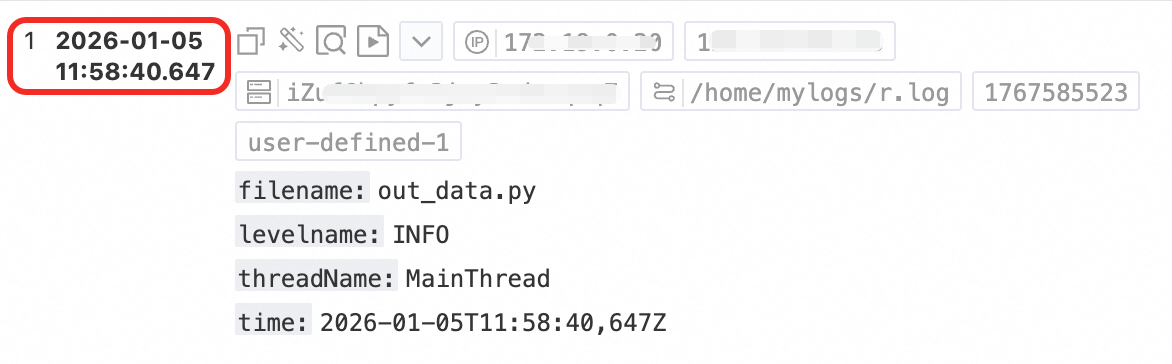
Millisecond time: | Content: "{"time":"2026-01-05T11:58:40,647Z", "filename":"out_data.py","levelname": "INFO", "threadName":"MainThread"}" |
|
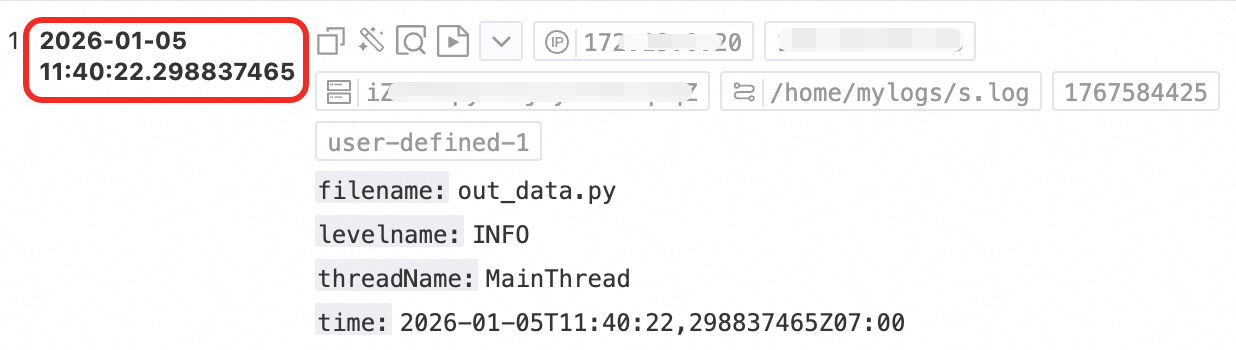
Nanosecond time: | Content: "{"time": "2026-01-05T11:40:22,298837465Z07:00","filename":"out_data.py","levelname":"INFO","threadName": "MainThread"}" | |
Overview of time processing plugins
Simple Log Service provides the following types of time processing plugins. You can select a plugin based on your requirements.
Plugin name | Type | Description |
Time parsing | Native | Parses and standardizes the time field in logs. |
Extract log time | Extension | Parses the raw time field and can set it as the log timestamp. |
Entry point
To use a Logtail plugin for log processing, add it when you create or modify a Logtail configuration. For more information, see Overview.
Differences between native and extension plugins
Native plugins are implemented in C++ and offer better performance.
Extension plugins are implemented in Go and offer a rich and flexible ecosystem. If your business logs are too complex to be processed by native plugins, you can use extension plugins.
Performance limits of extension plugins
When you use an extension plugin for log processing, LoongCollector consumes more resources (primarily CPU). If necessary, you can adjust the LoongCollector parameter settings for configuration management.
If the generation speed of raw data exceeds 5 MB/s, we recommend that you do not use overly complex plugin combinations to process logs. You can use extension plugins for simple processing and then use Data Transformation Overview for further processing.
Log collection limits
Extension plugins process text logs in line mode. This means file-level metadata, such as
__tag__:__path__and__topic__, is stored in each log entry.Adding an extension plugin affects tag-related features:
The context query and LiveTail features become unavailable. To use these features, you must add an aggregators configuration.
The
__topic__field is renamed to__log_topic__. If the aggregators configuration is added, both the__topic__and__log_topic__fields exist in the log. If you do not need the__log_topic__field, you can use the drop field plugin to delete it.Fields such as
__tag__:__path__no longer have native field indexes. You must create an index for them.
Time parsing plugin (native)
The time parsing plugin parses the time field of a log and sets the result as the value of the log's __time__ field.
Configuration description
Parameter Name | Description |
Source Field | The source field that stores the log content before parsing. The default value is content. Note When you use the regex parsing plugin, you can only set Source Field to time. Make sure that your regex parsing configuration includes time as an extracted field. |
Time Format | Set the time format that corresponds to the time content in the log. For example, if the time in the log is 10/Sep/2023:12:36:49, the corresponding time format is %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S. |
Time Zone | Select the time zone of the log's time field. If you do not select a time zone, the machine's time zone is used by default. This is the time zone of the environment where the Logtail process runs. |
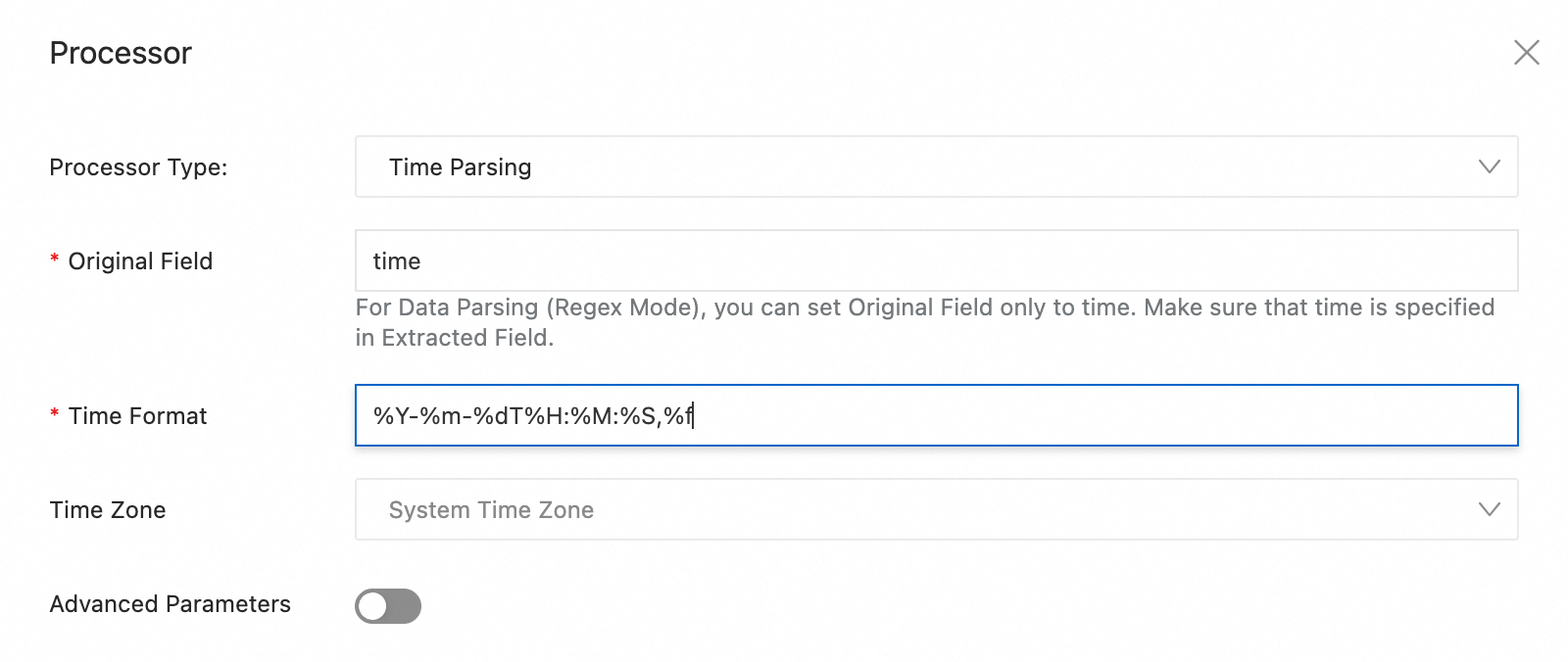
By default, log timestamps in Simple Log Service are accurate to the second. You only need to configure the time format to the second and do not need to configure milliseconds, microseconds, or other smaller units. If the time field in a raw log has millisecond, microsecond, or nanosecond precision that you want to retain, enable nanosecond precision as shown in the following example. For more information, see Log collection that supports nanosecond timestamps.
Raw log | Time parsing plugin configuration | Time format |
|
| %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S,%f |
Enable nanosecond precision support:
Go to the Logtail configuration page. In the section, turn on the Advanced Parameters switch and enter the following JSON content to enable nanosecond precision support:
{
"EnableTimestampNanosecond": true
}You must also enable the EnableTimestampNanosecond advanced parameter when you use extension plugins to parse nanoseconds or milliseconds.
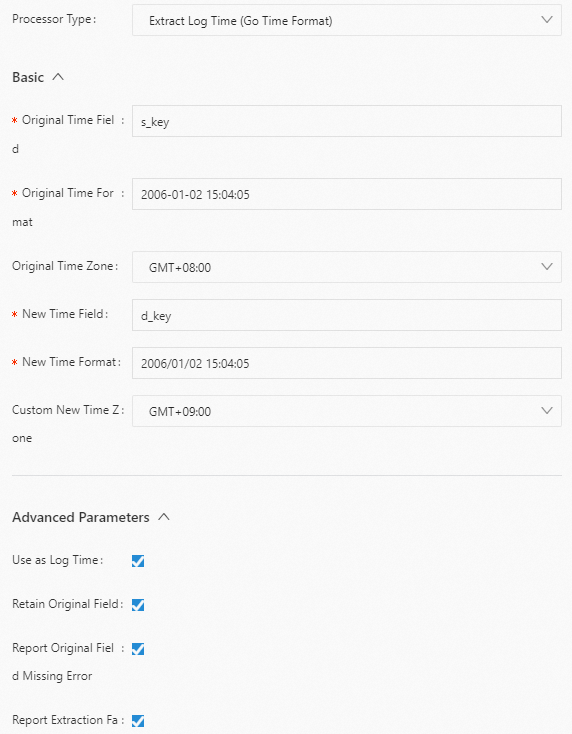
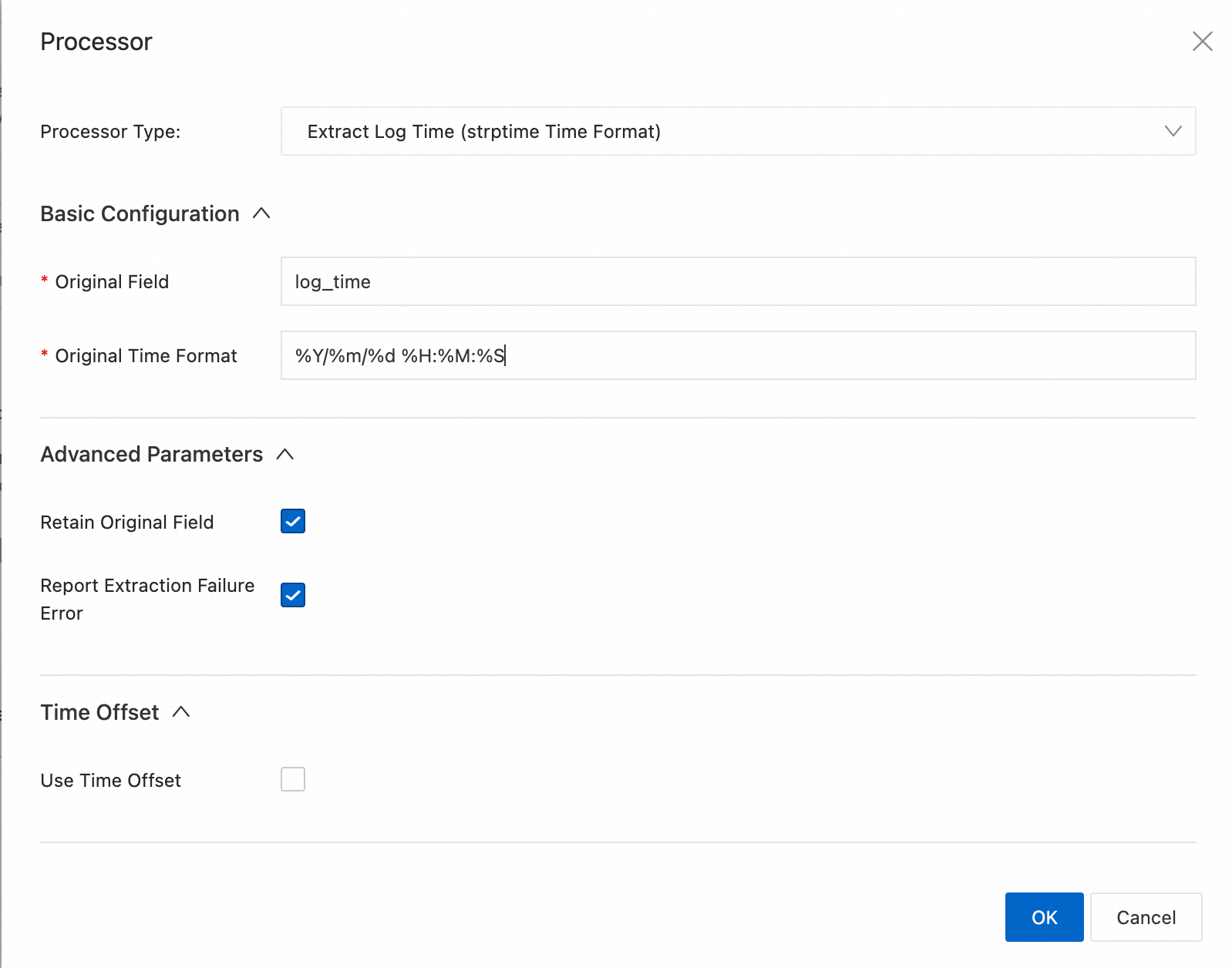
Extract Log Time plugin (extension)
You can use the processor_gotime plugin or the processor_strptime plugin to parse the time field in raw logs. This section describes the parameters and provides configuration examples for both plugins.
If the time field in the raw log has millisecond, microsecond, or nanosecond precision that you want to retain in Simple Log Service, see Log collection that supports nanosecond timestamps.
Go language time format (processor_gotime)
strptime time format (processor_strptime)
Common log time formats
For common log time formats supported by the processor_gotime extension plugin, see https://pkg.go.dev/time#pkg-constants. The following table lists the common log time formats supported by the native time parsing plugin (processor_parse_timestamp_native) and the processor_strptime extension plugin.
On a Linux server, Logtail supports all time formats provided by the strftime function. This means that Logtail can parse any log time string that can be formatted by the strftime function.
Time format | Description | Example |
%a | Abbreviated weekday name. | Fri |
%A | Full weekday name. | Friday |
%b | Abbreviated month name. | Jan |
%B | Full month name. | January |
%d | Day of the month as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 01 to 31. | 07, 31 |
%f | Fractional seconds (milliseconds, microseconds, or nanoseconds). | 123 |
%h | Abbreviated month name. Same as %b. | Jan |
%H | The hour in 24-hour format. | 22 |
%I | Hour (12-hour clock) as a zero-padded decimal number. | 11 |
%m | Month as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 01 to 12. | 08 |
%M | Minute as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 00 to 59. | 59 |
%n | A line feed. | Line feed |
%p | AM or PM. | AM, PM |
%r | 12-hour clock time. Same as %I:%M:%S %p. | 11:59:59 AM |
%R | Hour and minute. Same as %H:%M. | 23:59 |
%S | Second as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 00 to 59. | 59 |
%t | A tab character. | None |
%y | Year without century as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 00 to 99. | 04, 98 |
%Y | Year with century as a decimal number. | 2004, 1998 |
%C | Century as a decimal number. Range: 00 to 99. | 16 |
%e | Day of the month as a space-padded decimal number. Range: 1 to 31. A space is added before a single-digit number. | 7, 31 |
%j | Day of the year as a zero-padded decimal number. Range: 001 to 366. | 365 |
%u | Weekday as a decimal number, where Monday is 1. Range: 1 to 7. | 2 |
%U | Week number of the year, with Sunday as the first day of the week. Range: 00 to 53. | 23 |
%V | Week number of the year, with Monday as the first day of the week. Range: 01 to 53. If the week containing January 1 has four or more days in the new year, it is week 1. Otherwise, it is the next week. | 24 |
%w | Weekday as a decimal number, where Sunday is 0. Range: 0 to 6. | 5 |
%W | Week number of the year, with Monday as the first day of the week. Range: 00 to 53. | 23 |
%c | Standard date and time. | Tue Nov 20 14:12:58 2020 |
%x | Standard date without time. | Tue Nov 20 2020 |
%X | Standard time without date. | 11:59:59 |
%s | UNIX timestamp. | 1476187251 |
Examples
The following table shows common time standards, examples, and their corresponding time expressions.
Example | Time expression | Time standard |
2017-12-11 15:05:07 | %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S | Custom |
[2017-12-11 15:05:07.012] | [%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f | Custom |
2017-12-11 15:05:07.123 | %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f | Custom |
02 Jan 06 15:04 MST | %d %b %y %H:%M | RFC822 |
02 Jan 06 15:04 -0700 | %d %b %y %H:%M | RFC822Z |
Monday, 02-Jan-06 15:04:05 MST | %A, %d-%b-%y %H:%M:%S | RFC850 |
Mon, 02 Jan 2006 15:04:05 MST | %A, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S | RFC1123 |
2006-01-02T15:04:05Z07:00 | %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S | RFC3339 |
2006-01-02T15:04:05.999999999Z07:00 | %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%f | RFC3339Nano |
1637843406 | %s | Custom |
1637843406123 | %s | Custom (Simple Log Service processes it with second-level precision) |
References
You can configure a Logtail pipeline by calling the following API operations:
Configuring processing plug-ins in the console:
Collect container logs from a cluster using Kubernetes CRDs (standard output/file)