An HTTP(S) health check monitors target IP addresses using the HTTP(S) protocol. It checks web server metrics, such as network reachability, service availability, and first-packet latency. If a monitored IP address is detected as abnormal, the system automatically blocks it. When the IP address returns to a normal state, the system automatically unblocks it.
Parameters
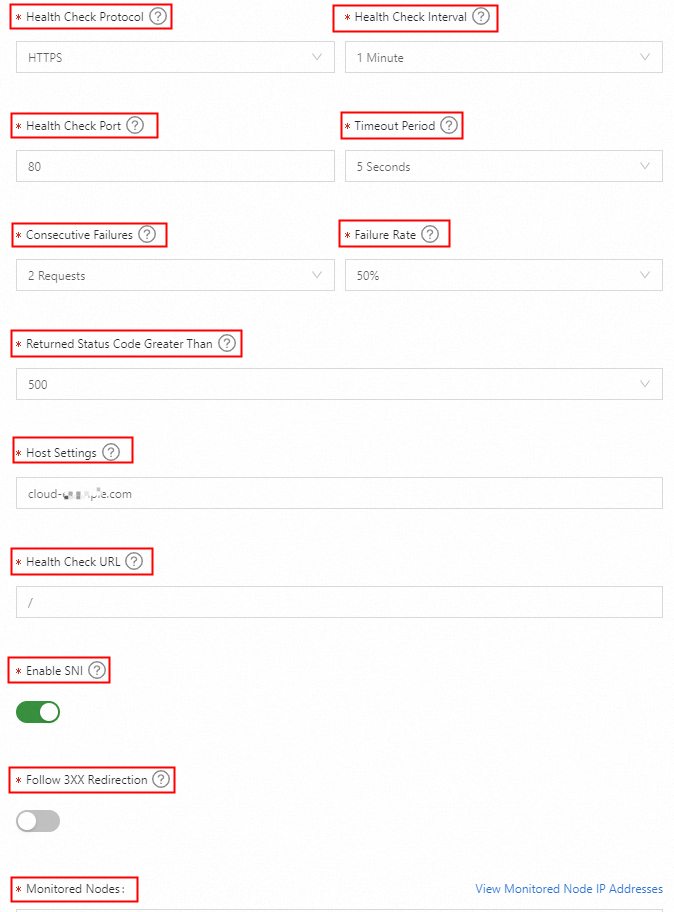
Check protocol
The protocol for the health check. Select HTTP(S) to monitor web server metrics of the target IP address, such as network reachability, service availability, and first-packet latency.
Health check interval
The time interval between HTTP(S) health checks. The default interval is 1 minute. The minimum interval is 15 seconds. This feature is available only to Ultimate Edition users.
Health check port
The port of the web server to check. The default port is 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS. You can also specify a custom port.
Timeout
The timeout period for a health check. During each check, the system sends an HTTP(S) packet and measures the response time. If no response is received within the specified timeout period, the check fails. You can select a value of 2, 3, 5, or 10 seconds.
Consecutive failures
The number of consecutive failed health checks required to mark the application service as abnormal. This setting helps prevent false alarms caused by temporary network jitter. You can select a value of 1, 2, or 3.
1: The application service is marked as abnormal after one failed health check.
2: The application service is marked as abnormal after two consecutive failed health checks.
3: The application service is marked as abnormal after three consecutive failed health checks.
Failure rate
The percentage of monitoring nodes that must report a failure before the application service is marked as abnormal. When the failure rate meets or exceeds this threshold, the service is considered abnormal. You can set the threshold to 20%, 50%, 80%, or 100%.
Return code greater than
During an HTTP(S) health check, the system uses the return code from the web server to determine if it is working correctly. If the return code is greater than or equal to the specified threshold, the application service is considered abnormal.
Greater than or equal to 400: Bad Request. If an HTTP(S) request contains invalid parameters, the web server returns a code of 400 or higher. If you set the alarm threshold to "Greater than or equal to 400", you must specify the exact URL access path in the URL Path field.
Greater than or equal to 500: Server Error. If the web server encounters an error, it returns a code of 500 or higher. The default alarm threshold is a return code of 500 or greater.
Host settings
The value for the Host field in the HTTP(S) request header. This field identifies the specific website to access. By default, this is the service domain name from the global configuration. You can modify this value if the target website has specific host requirements.
URL path
The URL path for the HTTP(S) health check. The default value is "/".
Enable SNI
If enabled, the host name is sent to the monitored object during the Transport Layer Security (TLS) negotiation.
Follow 3xx redirection
If enabled, the health check follows the redirection when the monitoring node receives a 3xx status code, such as 301, 302, 303, 307, or 308. If disabled, the health check does not follow the redirection.
Monitoring nodes
The geographic locations of the nodes that perform HTTP(S) health checks. The system provides the following default monitoring nodes:
Node type
Geographic location
BGP nodes
Zhangjiakou, Qingdao, Hangzhou, Shanghai, Hohhot, Shenzhen, Beijing
International nodes
China (Hong Kong), Germany, Singapore, California, Malaysia, Japan
Carrier nodes
Wuhan China Unicom, Dalian China Unicom, Nanjing China Unicom, Tianjin China Unicom, Qingdao China Telecom, Changsha China Telecom, Xi'an China Telecom, Zhengzhou China Telecom, Shenzhen China Mobile, Dalian China Mobile, Nanjing China Mobile
ImportantIf all addresses in the address pool are Alibaba Cloud addresses and you use a blackhole filtering policy for fault testing, select carrier nodes as the monitoring nodes. This is because blackhole filtering is an access control list (ACL) policy that takes effect on the Internet between the Alibaba Cloud network and carrier networks. Traffic between Alibaba Cloud IP addresses mostly flows within the Alibaba Cloud network, which can reduce the effectiveness of the health check.
Procedure
Log on to Alibaba Cloud DNS - Global Traffic Manager.
On the instance list page of Global Traffic Manager, find the target instance and click Configure in the Actions column.
If you have not configured Global Traffic Manager (GTM) for the instance, see Tutorials.
If you have already used the quick configuration wizard for the instance, click the Address Pool Configuration tab. Click the + icon next to the address pool to expand it. Then, click Modify next to Health Check. You can then edit the parameters for the HTTP(S) health check as described in this topic.