Scenarios
Most enterprise applications use IP addresses from multiple carriers, which can cause issues such as cross-network latency, packet loss, and service unavailability. Global Traffic Manager (GTM) addresses this by returning the IP address of an application server on the same carrier network as the user's request. This provides access to the nearest server and accelerates connection speeds. If an application server on one carrier network fails, GTM promptly switches traffic to a server on another carrier network to minimize the impact of the failure and ensure service continuity.
Prerequisites
The Access Domain relies on a domain name within an Public Zone. Ensure that at least one domain name in the Public Zone has a DNS Server IP Address with a Available status.
NoteIf your service domain name does not use Alibaba Cloud DNS, you can still use GTM. After you generate an access domain name using a different domain name, add a CNAME record for the service domain name at your DNS provider and point the record to the GTM Access Domain.
If you use the subscription billing method, you must purchase a subscription instance in advance.
Solution overview
This solution achieves the following intelligent DNS resolution:
Source of DNS resolution request | Address Pool | Application server endpoint | Failover address |
Shift | Mobile | 1.1.XX.XX | 2.2.XX.XX, 3.3.XX.XX |
China Telecom | Telecom | 2.2.XX.XX | 1.1.XX.XX, 3.3.XX.XX |
China Unicom | Unicom | 3.3.XX.XX | 1.1.XX.XX, 2.2.XX.XX |
Global Default | Global | 1.1.XX.XX, 2.2.XX.XX, 3.3.XX.XX | If all addresses become unhealthy, a fallback policy is triggered to return all IP addresses. |
Architecture

Procedure
1. Configure Access Domain
On the Access Domain tab, click the Create Access Domain button.
In the dialog box, select Single Data Center for Multiple ISPs.
Click the Access Domain icon > Basic Configuration.
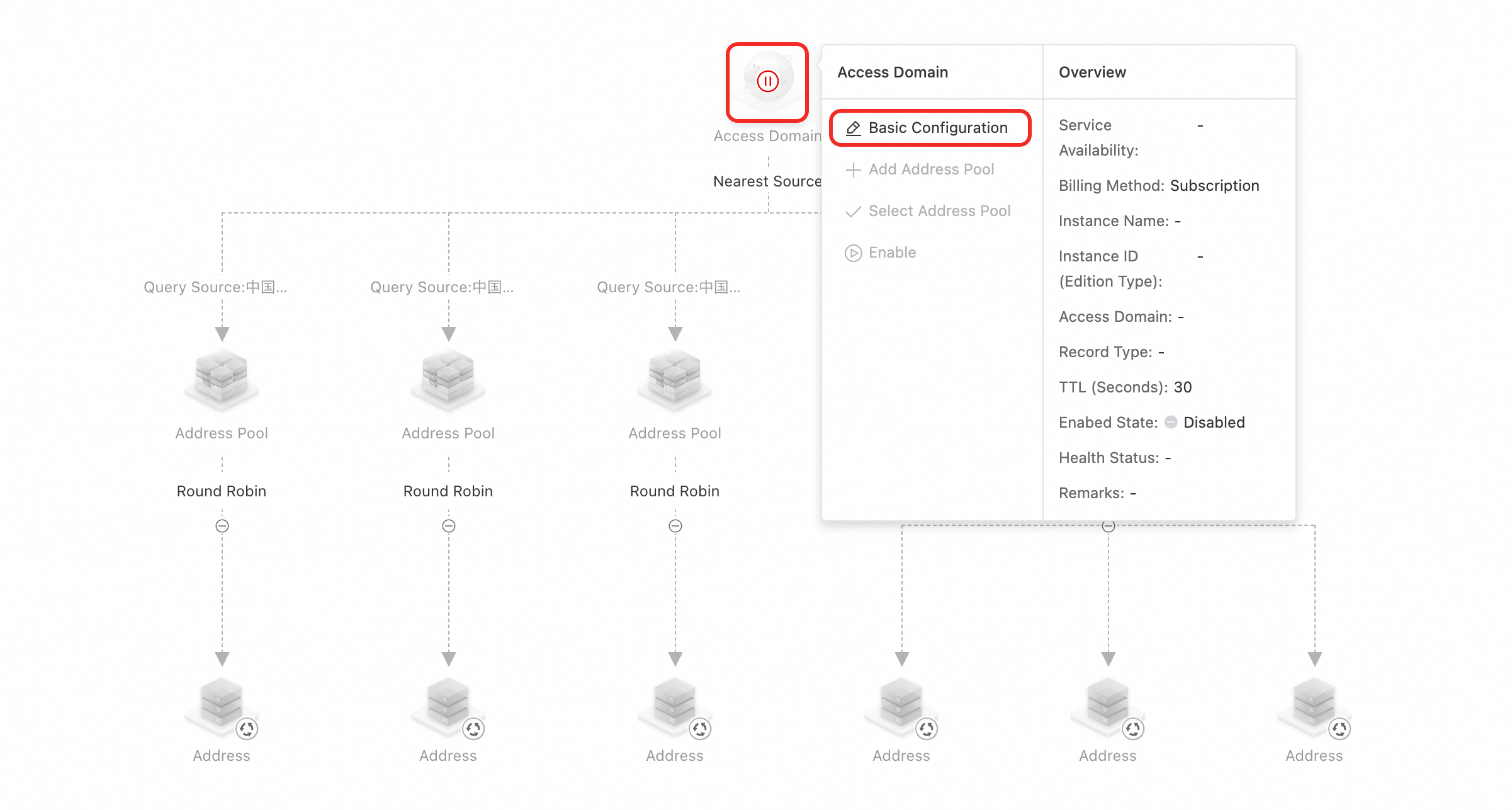
Complete the basic information and keep Enabed State set to Disabled. For more information, see Add Domain Name Configuration.
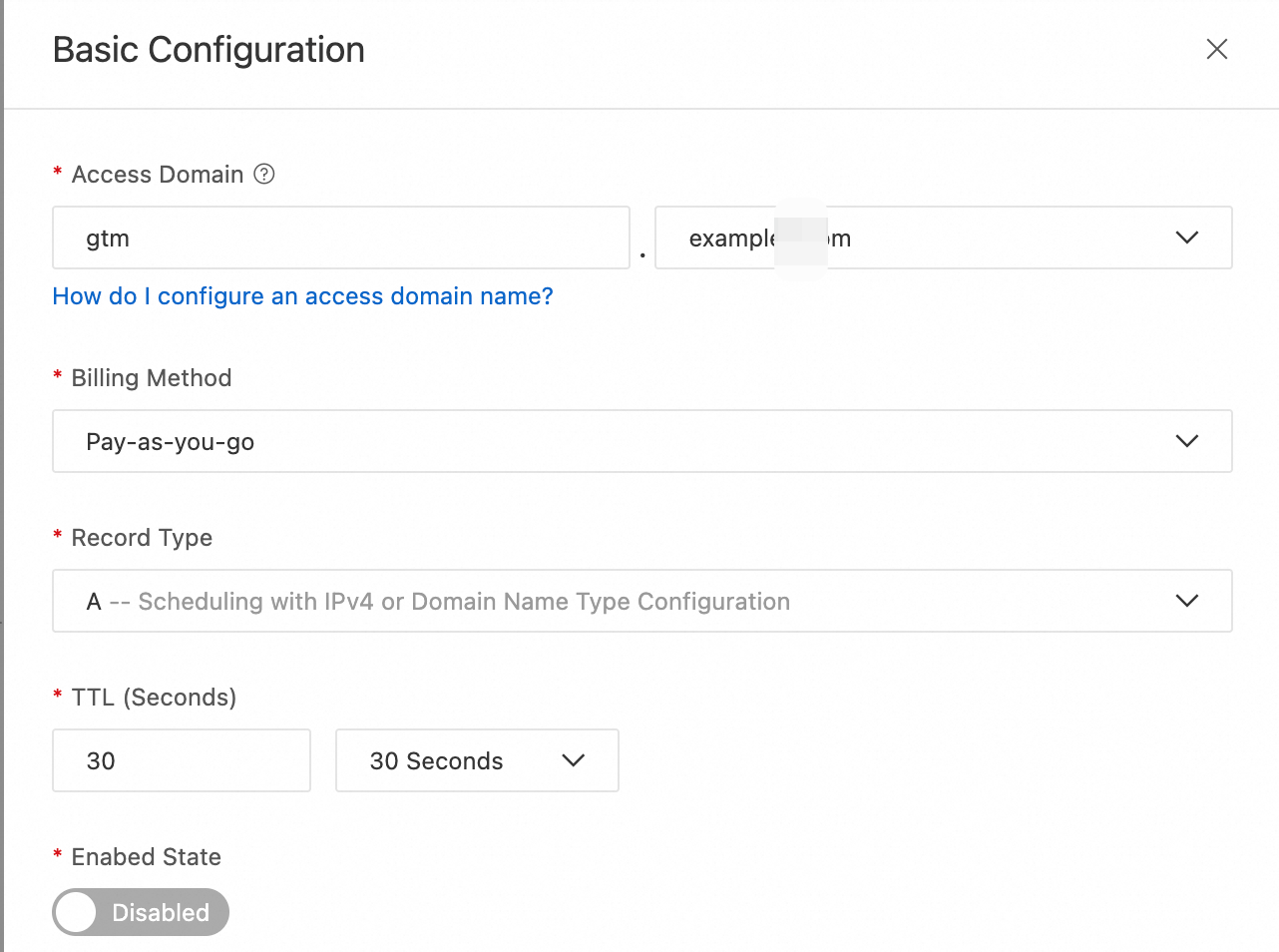
2. Configure address pools and addresses
On the Access Domain page, click the address pool icon > Basic Configuration.
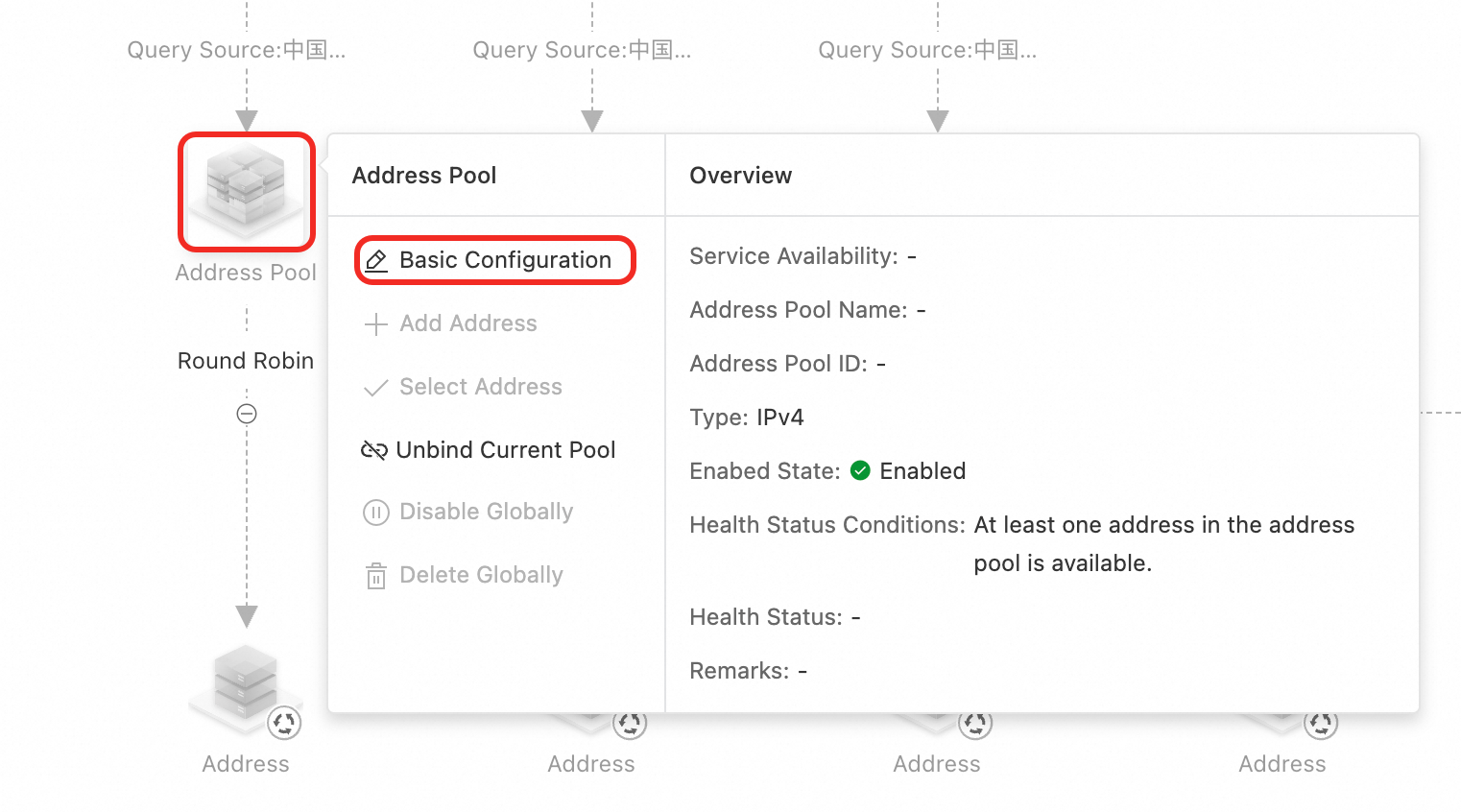
Name the four address pools Mobile, Telecom, Unicom, and Global. For more information, see Address Pool Configuration.
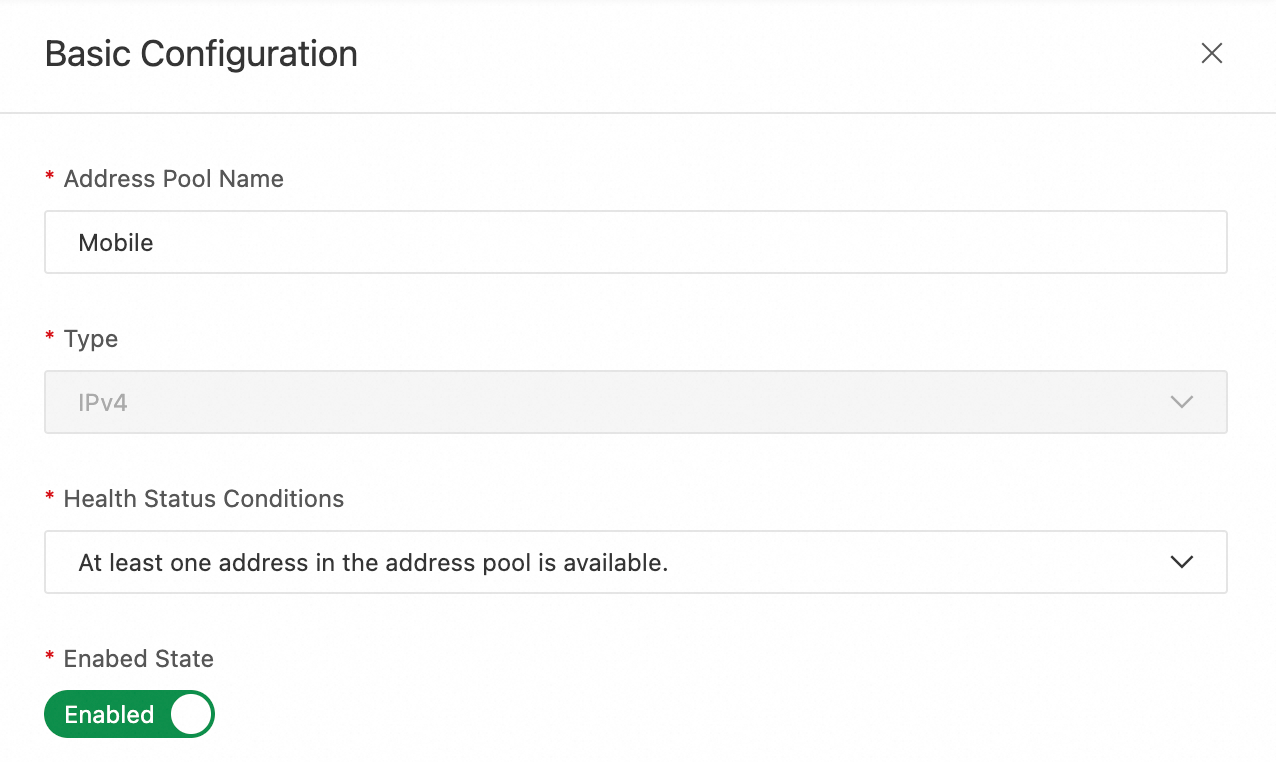
Click the address icon > Basic Configuration and add
1.1.XX.XXfor Mobile,2.2.XX.XXfor Telecom, and3.3.X.Xfor Unicom.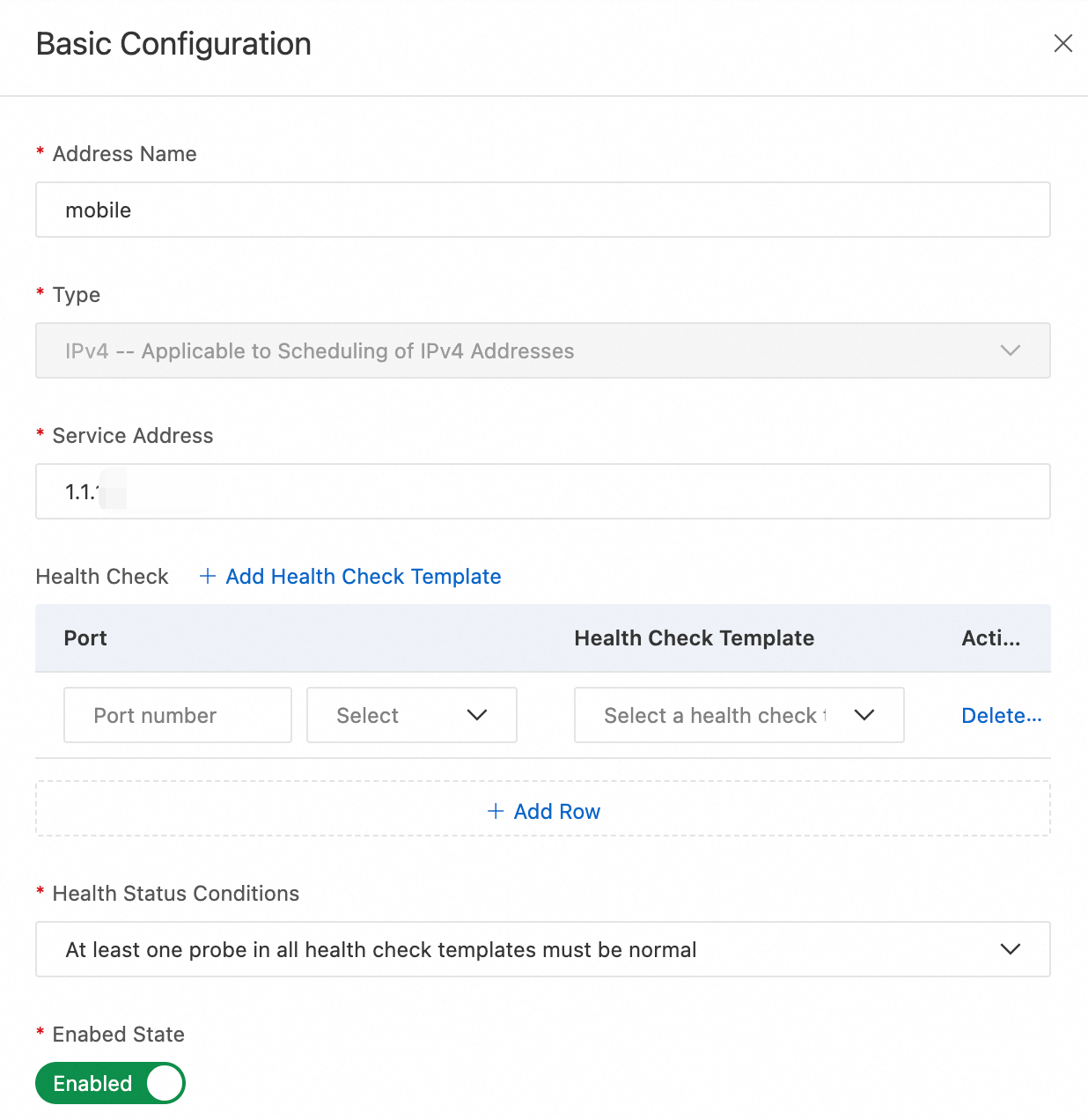
Click Global address pool > Select Address to add the three addresses that you previously created.
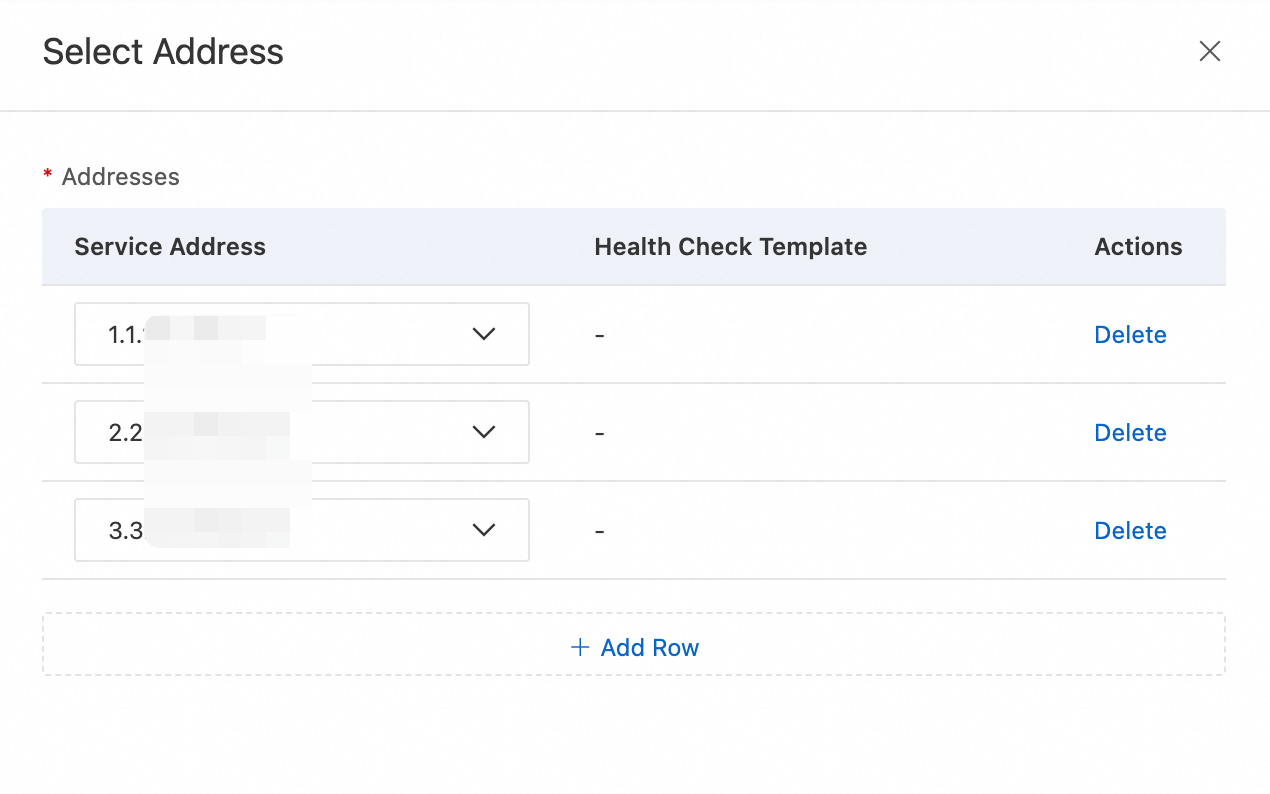
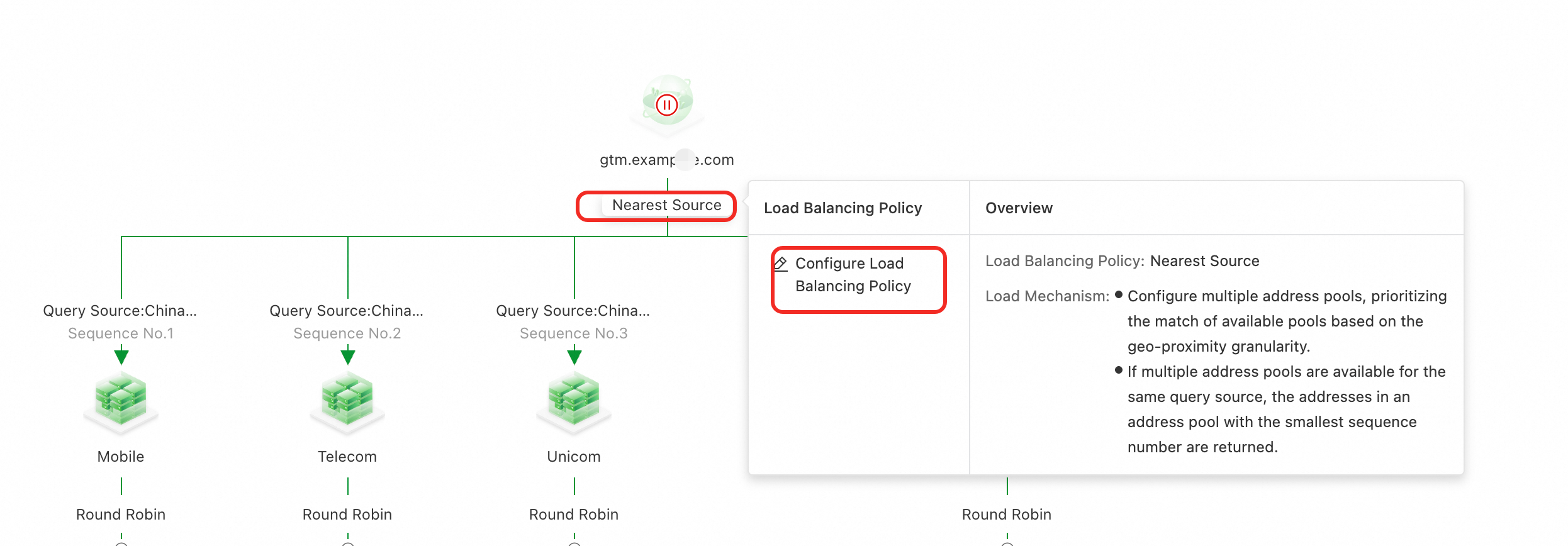
3. Configure load balancing policies
Because you selected a preset scenario, the Load Balancing Policy is already set to Nearest Source. If this is not the case, you can click the load balancing policy under Access Domain to configure it.
Because you selected a preset scenario, the Load Balancing Policy is selected by default. If this policy is not set, you can click Query Source above the address pool to complete the Query Source.
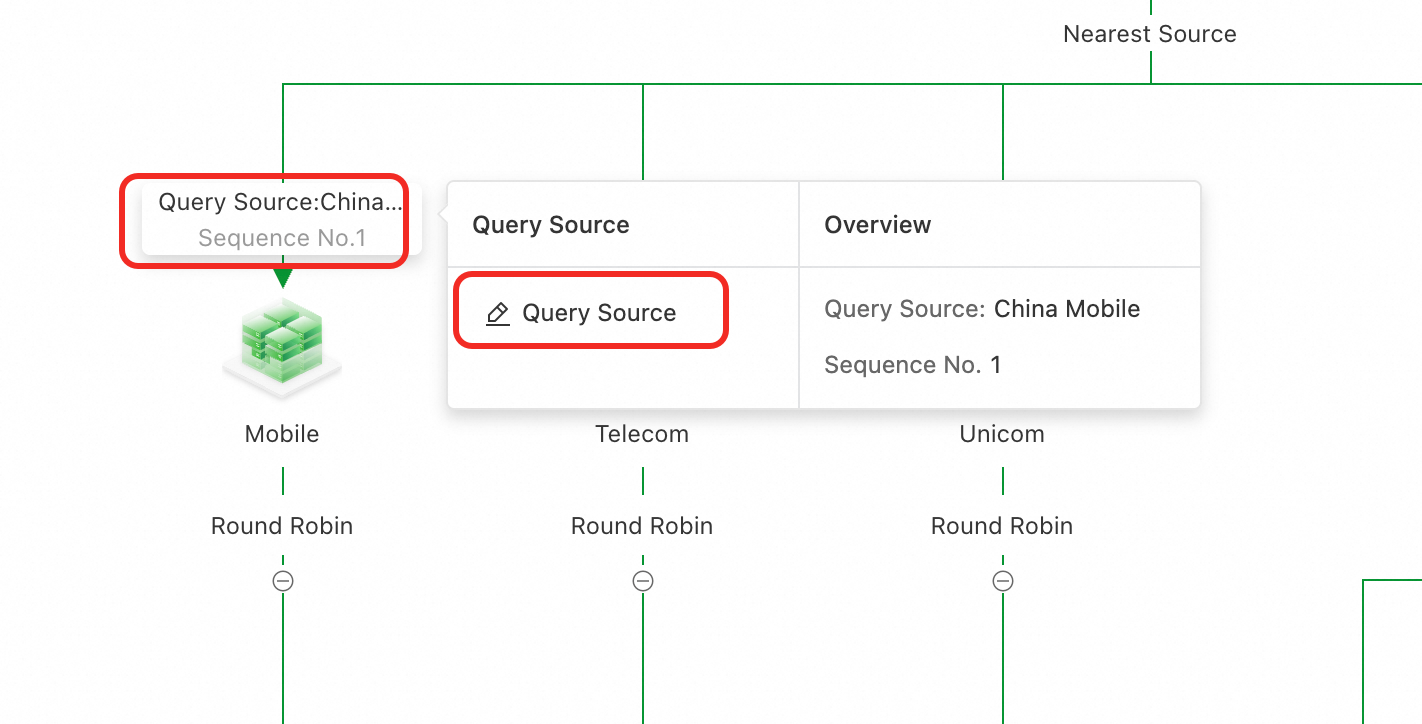
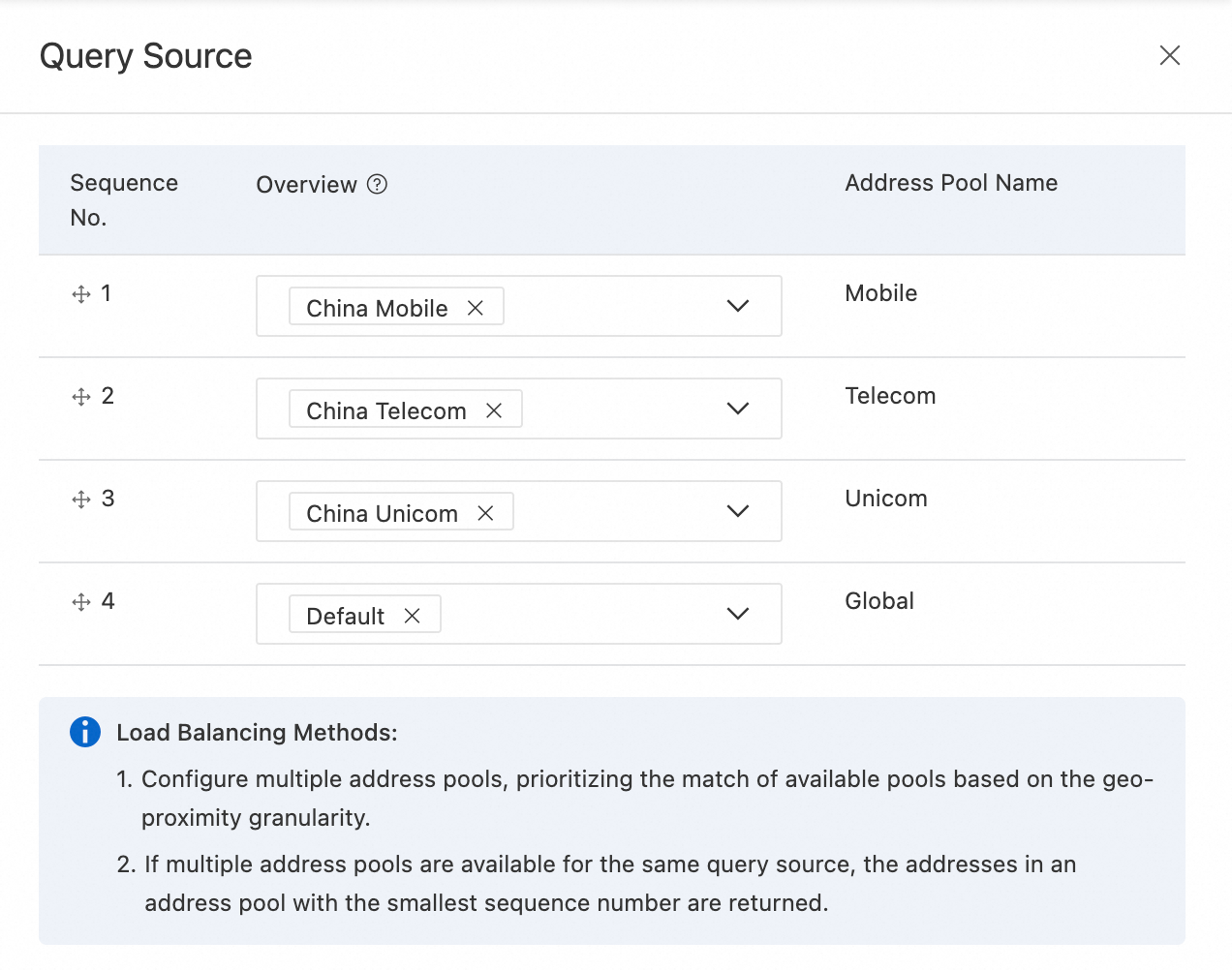
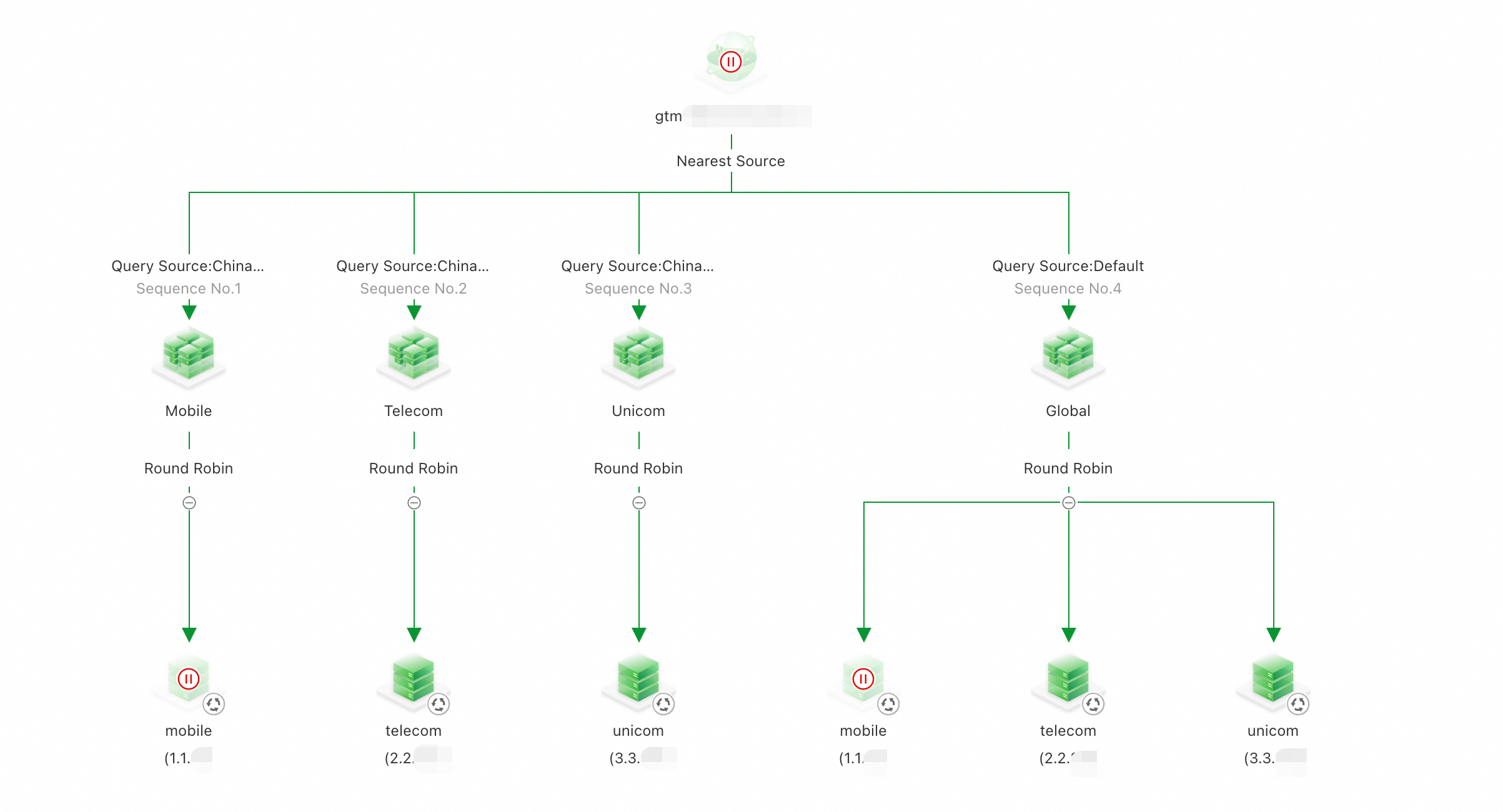
The complete configuration is as follows:
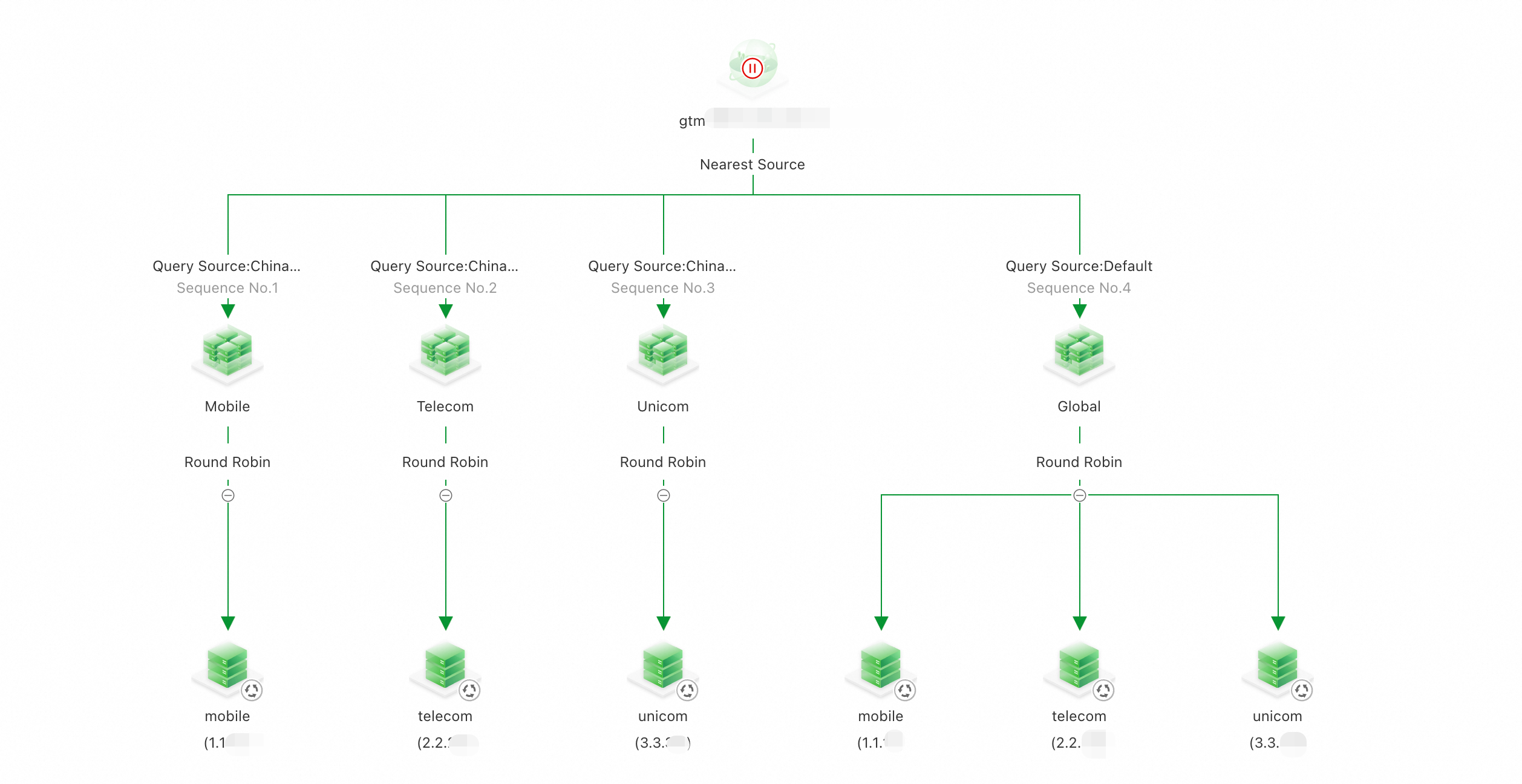
4. Enable Access Domain and ingest the stream
Click the Access Domain icon, and then click Enable for the Access Domain.
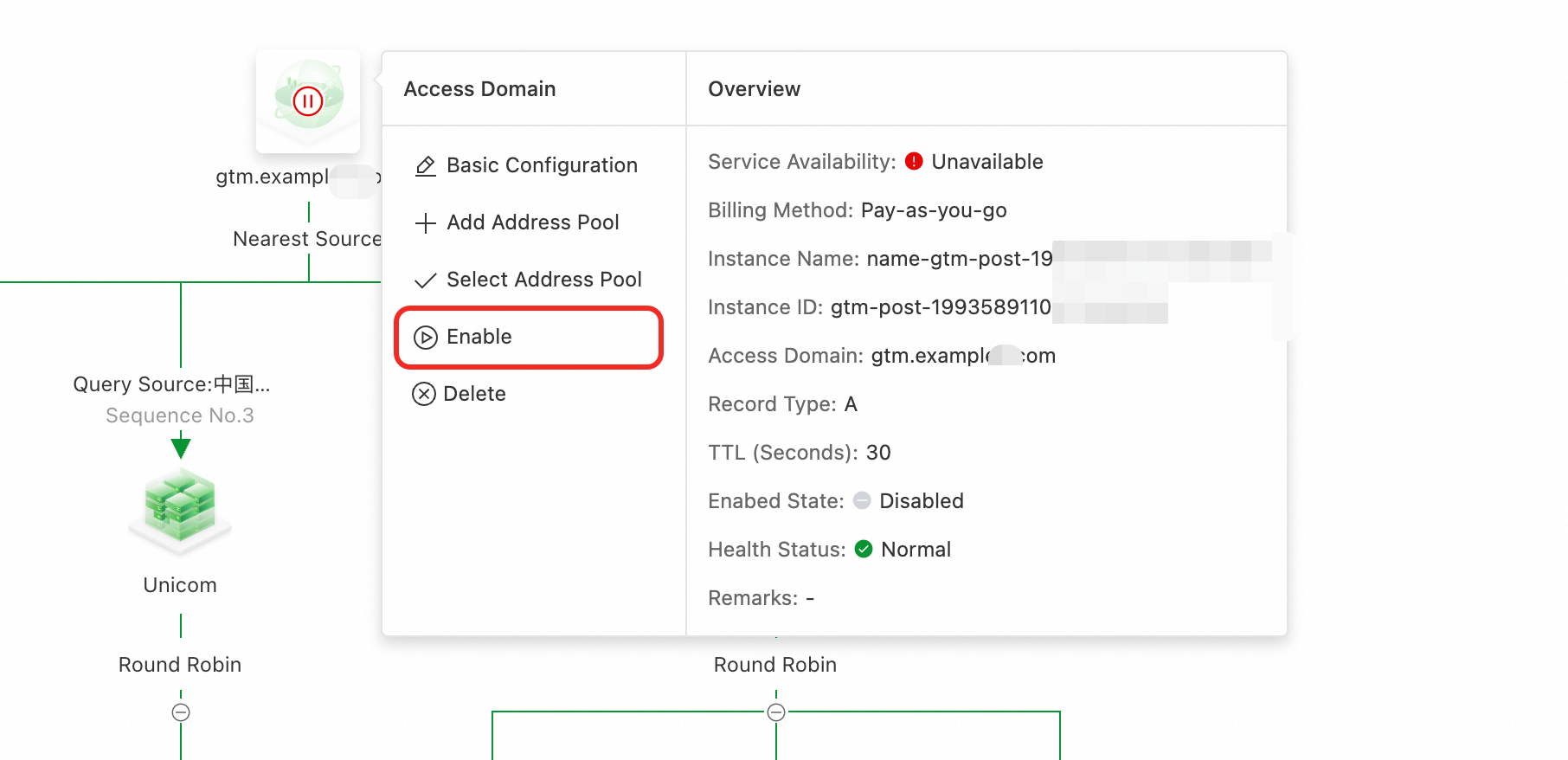 Important
ImportantIf a domain name record with the same name and type exists in the Public Zone, the system first uses the Global Traffic Manager (GTM) policy to intelligently schedule and resolve queries, enabling advanced features such as traffic load balancing or failover.
If you disable or delete a Access Domain, it will be resolved by the Public Zone.
You can use the Network Probe Tool to enter the Access Domain and verify that the network probe results from different carriers follow the Nearest Source principle.
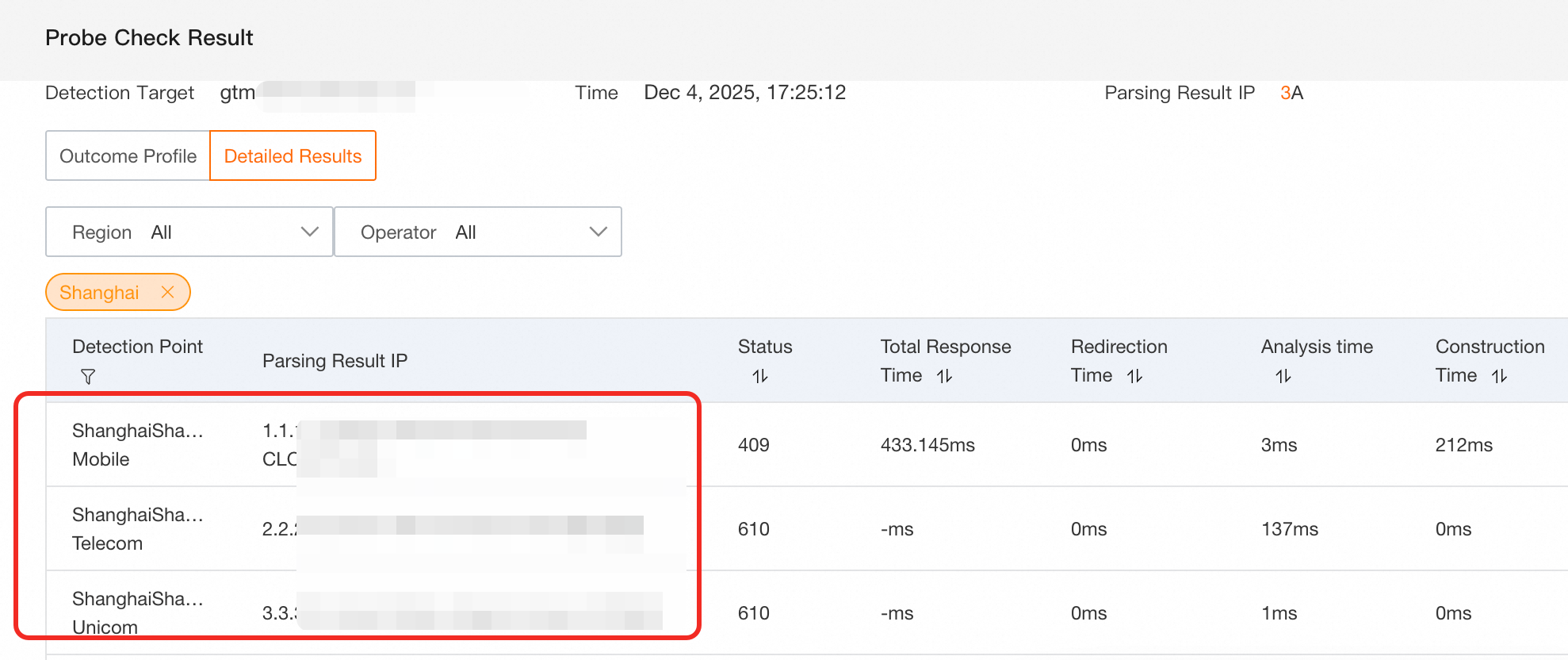
GTM uses the Nearest Source policy to return IP addresses.
After you verify the configuration of the Access Domain, go to the DNS provider for your business domain name and add a CNAME record that points to the Service Domain Name.
5. Verify failover
Scenario 1: The service address for the China Mobile line is abnormal
The probe results are shown in the following figure:
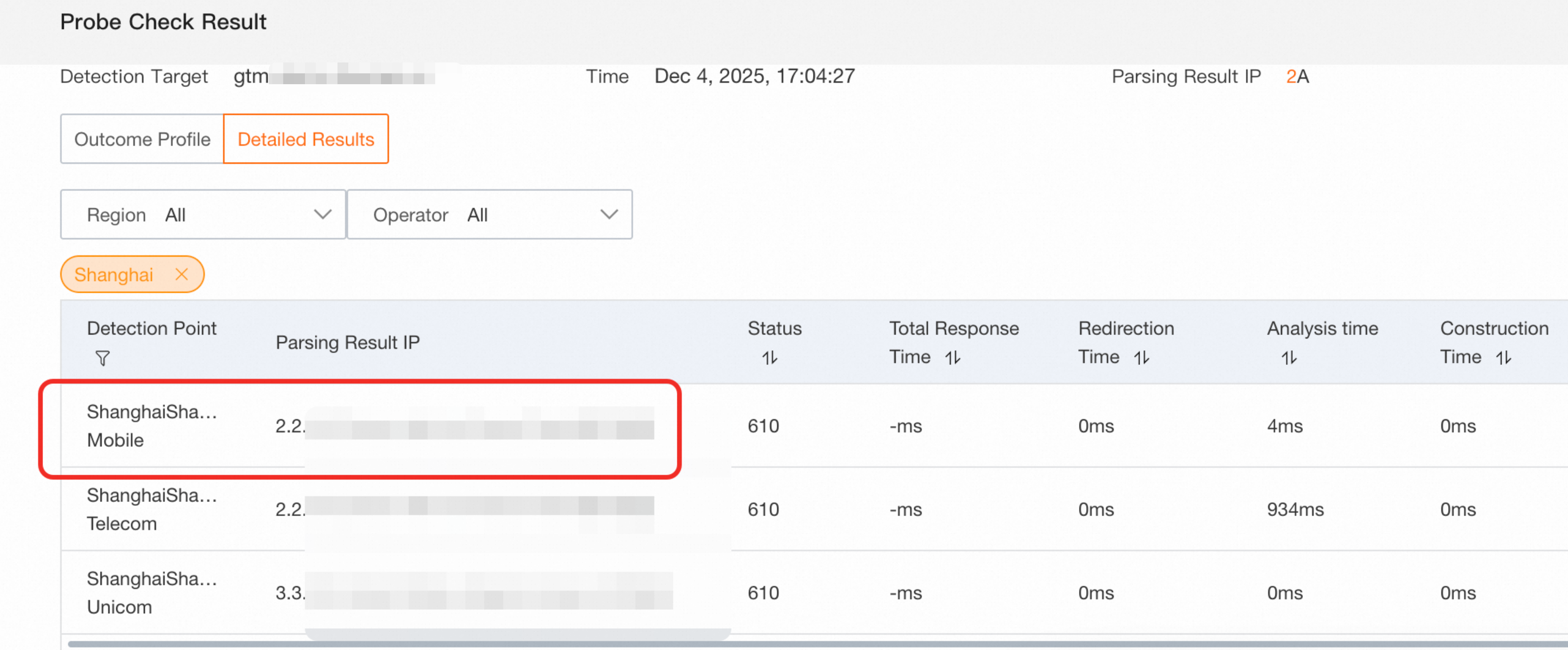
Because the endpoint for the China Mobile line is abnormal, resolution is switched to the first available IP address of the default line: telecom (2.2.XX.XX). The GTM switchover is successful, and other lines maintain the Nearest Source policy.
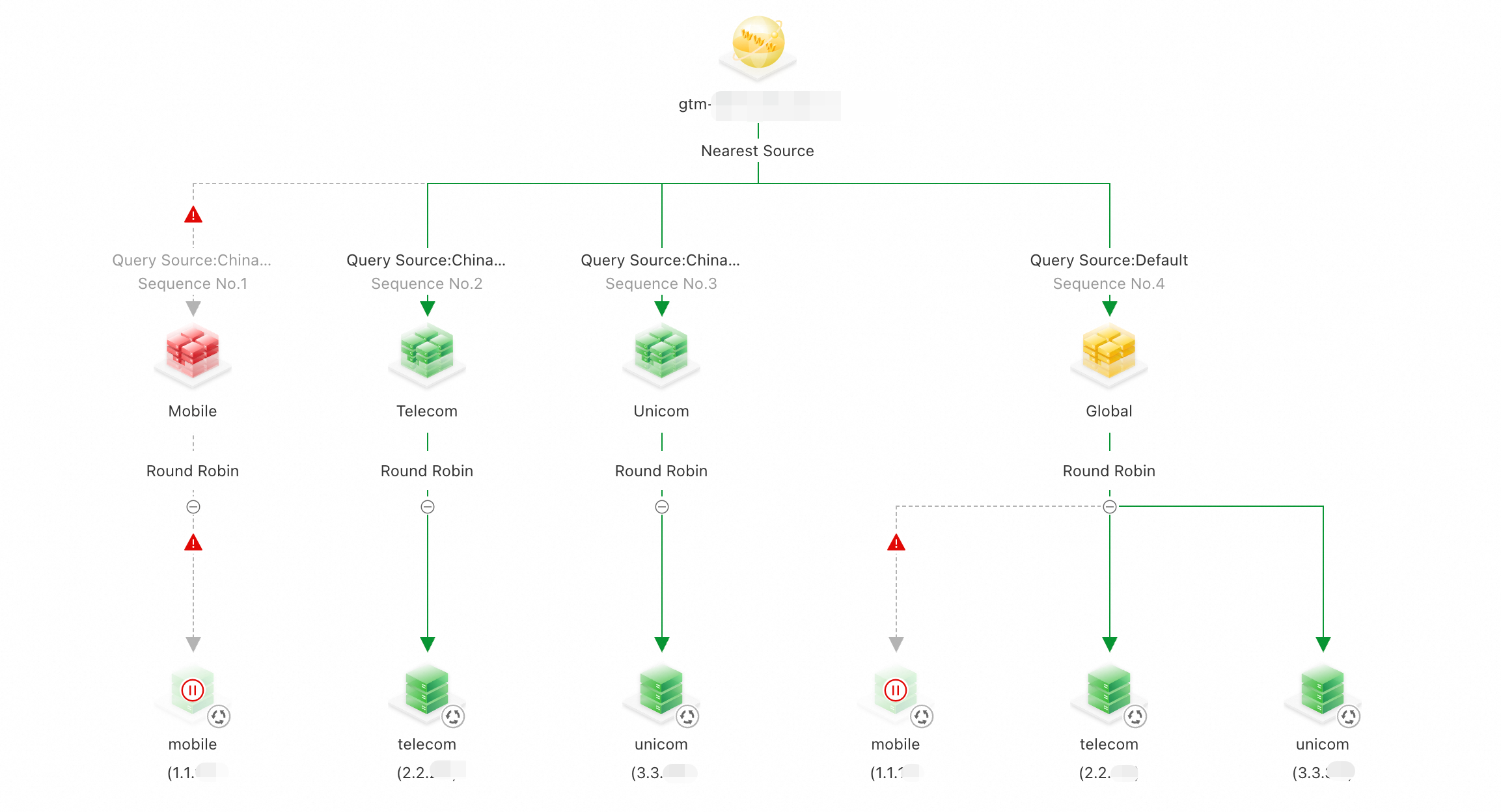
Scenario 2: The service addresses for both the China Mobile and China Telecom lines are abnormal
The probe results are shown in the following figure:
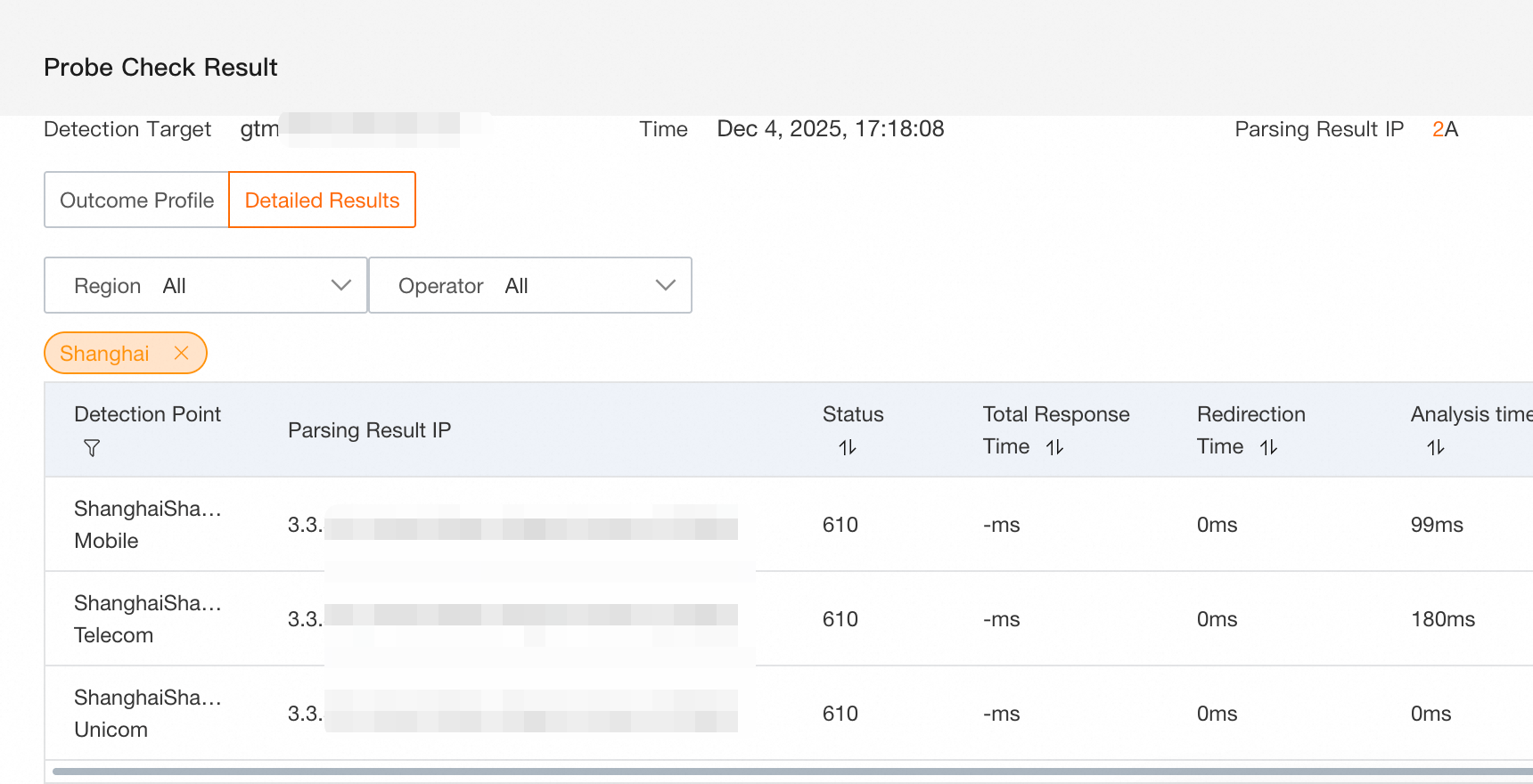
Because the endpoints for the China Mobile and China Telecom lines are abnormal, a GTM switchover successfully routes all traffic to the first available IP address of the default line, unicom (3.3.XX.XX), which uses the Nearest Source policy.