Configure an address pool. After you complete the basic configuration, you can add a new address or select an existing one.
Terms
Address pool: An address pool is a feature of Global Traffic Manager (GTM) that manages the addresses of application services. GTM uses address pools to direct users from different regions to the nearest application service for proximity-based access. An Access Domain can be configured with multiple address pools, and an address pool can be used by multiple Access Domain.
Create Address Pool
Click Address Pool > Create Address Pool.
On the Create Address Pool page, click the Address Pool icon > Basic Configuration.
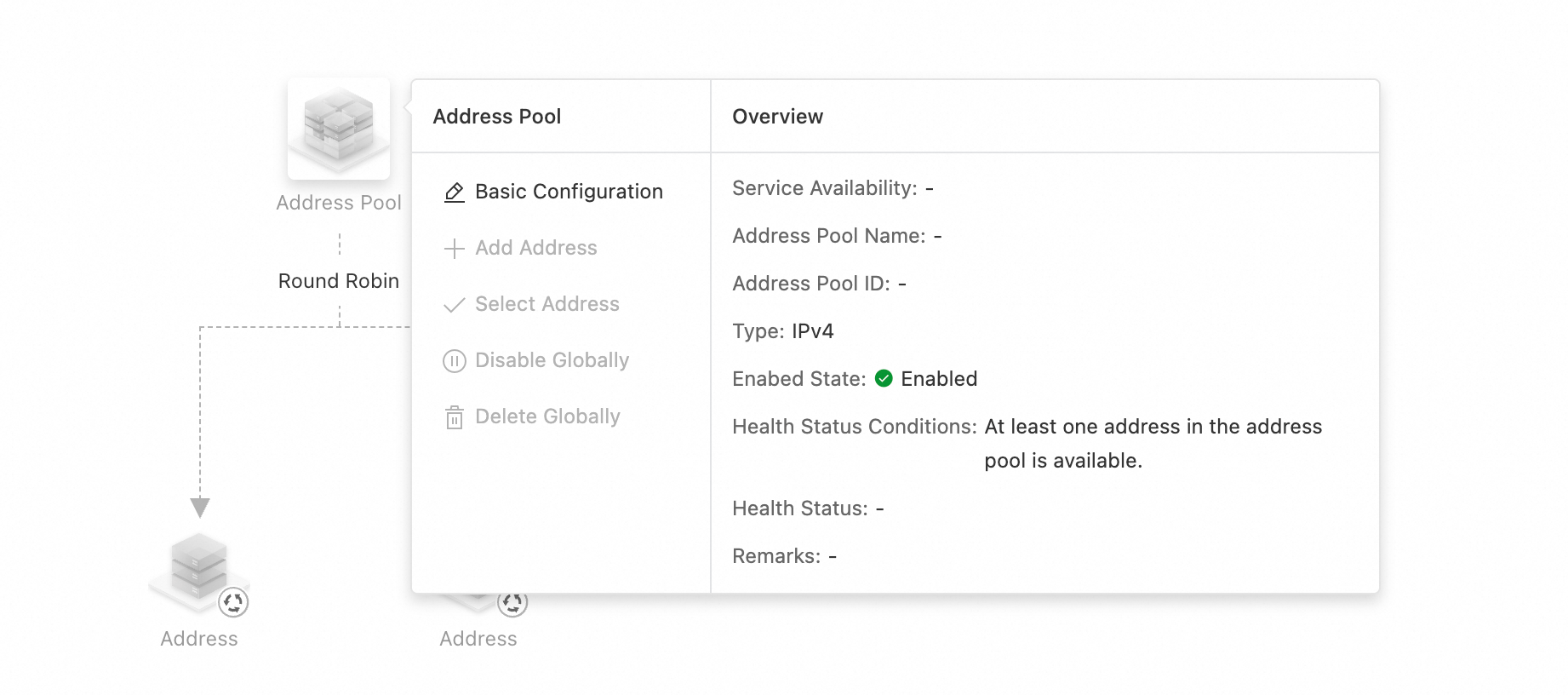
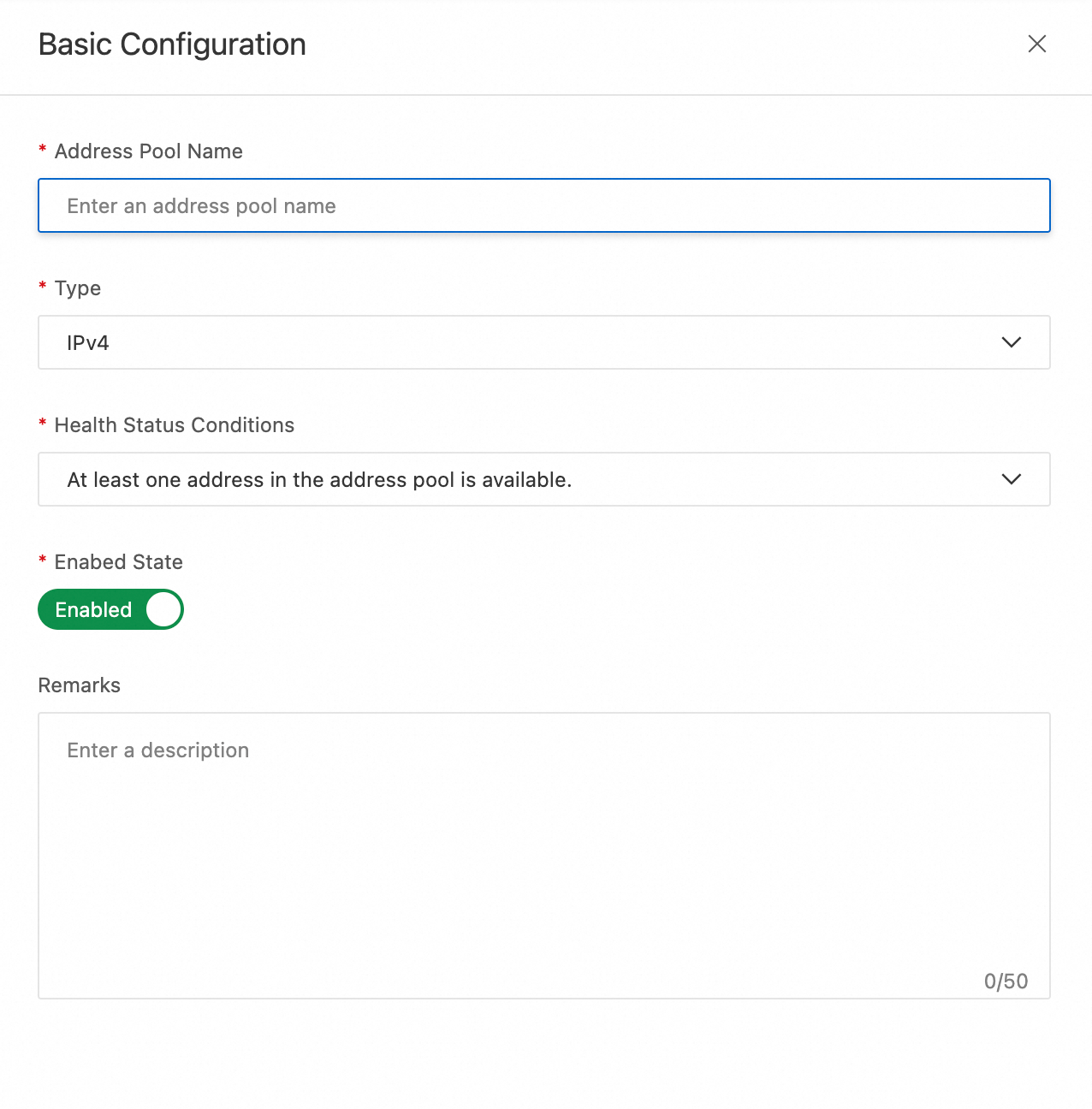
Complete the basic configuration.
Item
Description
Address Pool Name
Enter an easy-to-remember name for the address pool, such as `test`. Access policies use this name to identify the address pool.
Type
Options: IPv4, IPv6, and Zone name.
The record type of the Access Domain determines the available Type. The mappings are as follows:
Access Domain's Record Type
Address pool type
A
IPv4, Domain Name
AAAA
IPv6, Domain Name
CNAME
Domain Name
Health Status Conditions
A metric that determines whether the address pool is available. The options are:
At least one address in the address pool is available.
At least 30% of the addresses in the address pool are available.
At least 50% of the addresses in the address pool are available.
At least 70% of the addresses in the address pool are available.
All addresses in the address pool are available.
For more information about the determination rules, see Health status description.
Enabed State
Enabled by default. If set to Disabled, GTM will not return addresses from this address pool.
Remarks
Enter a description for the address pool. This helps you identify it later.
Configure addresses
You cannot add a duplicate address to an address pool.
You cannot add multiple addresses with the same endpoint to an address pool.
Address Pool add a new address
On the Access Domain configuration page, click the Address Pool icon > Add Address.
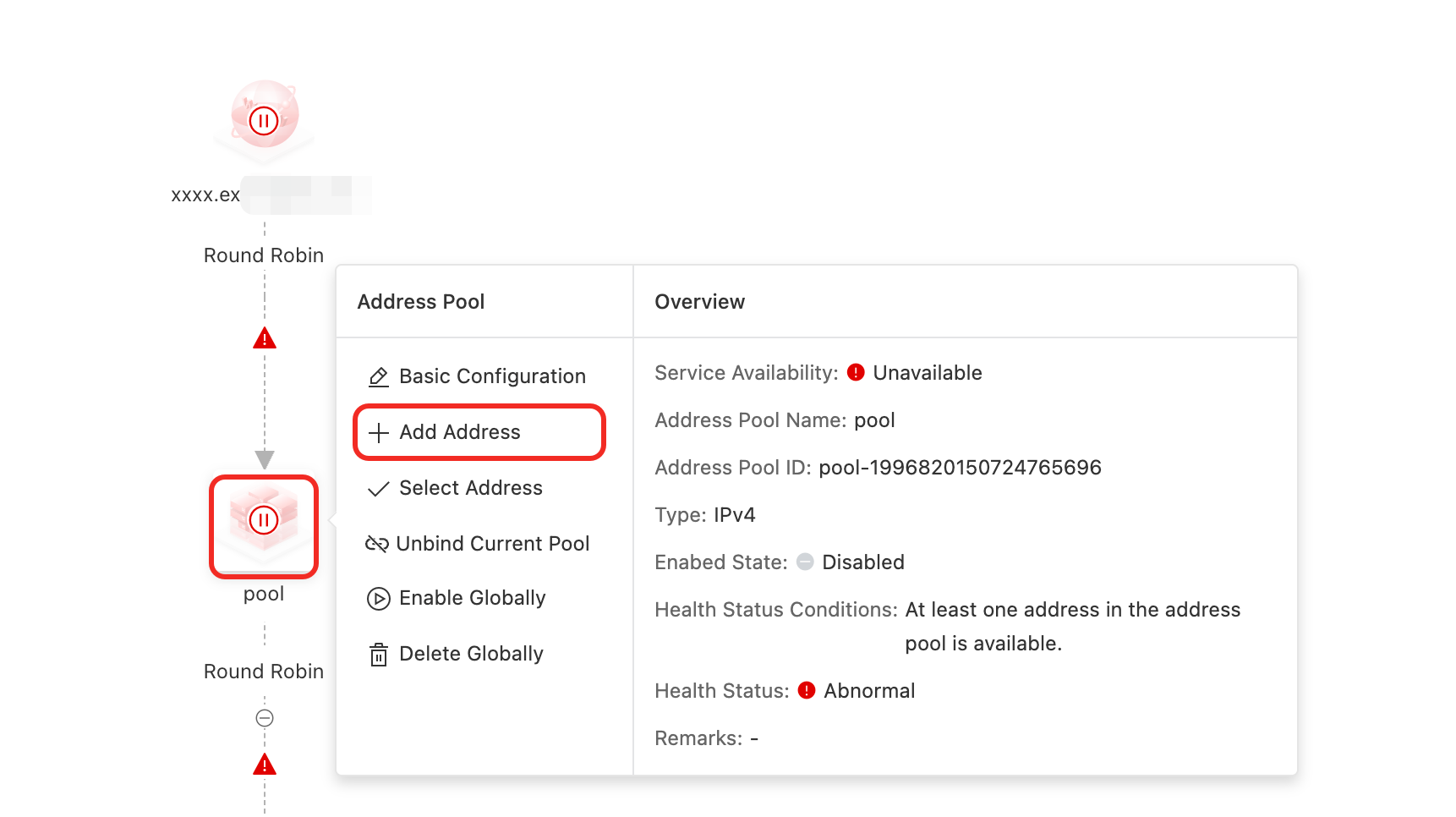
In the panel that appears, configure the parameters. For more information about the parameters, see 3. Address configuration.
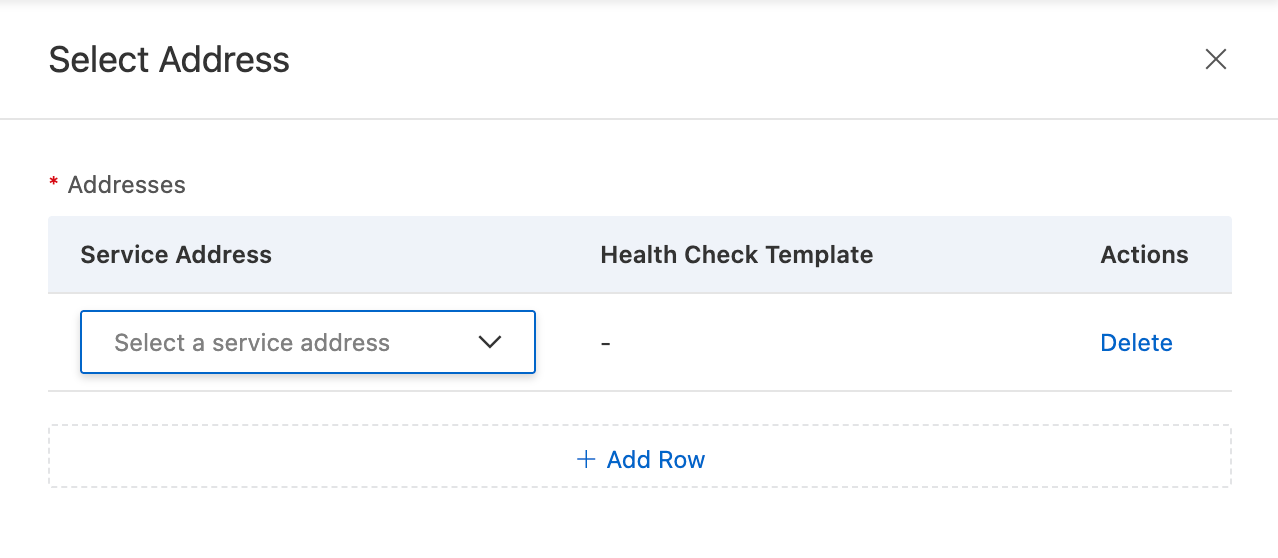
Address Pool: Select an existing address
On the Access Domain configuration page, click the Address Pool icon > Select Address.
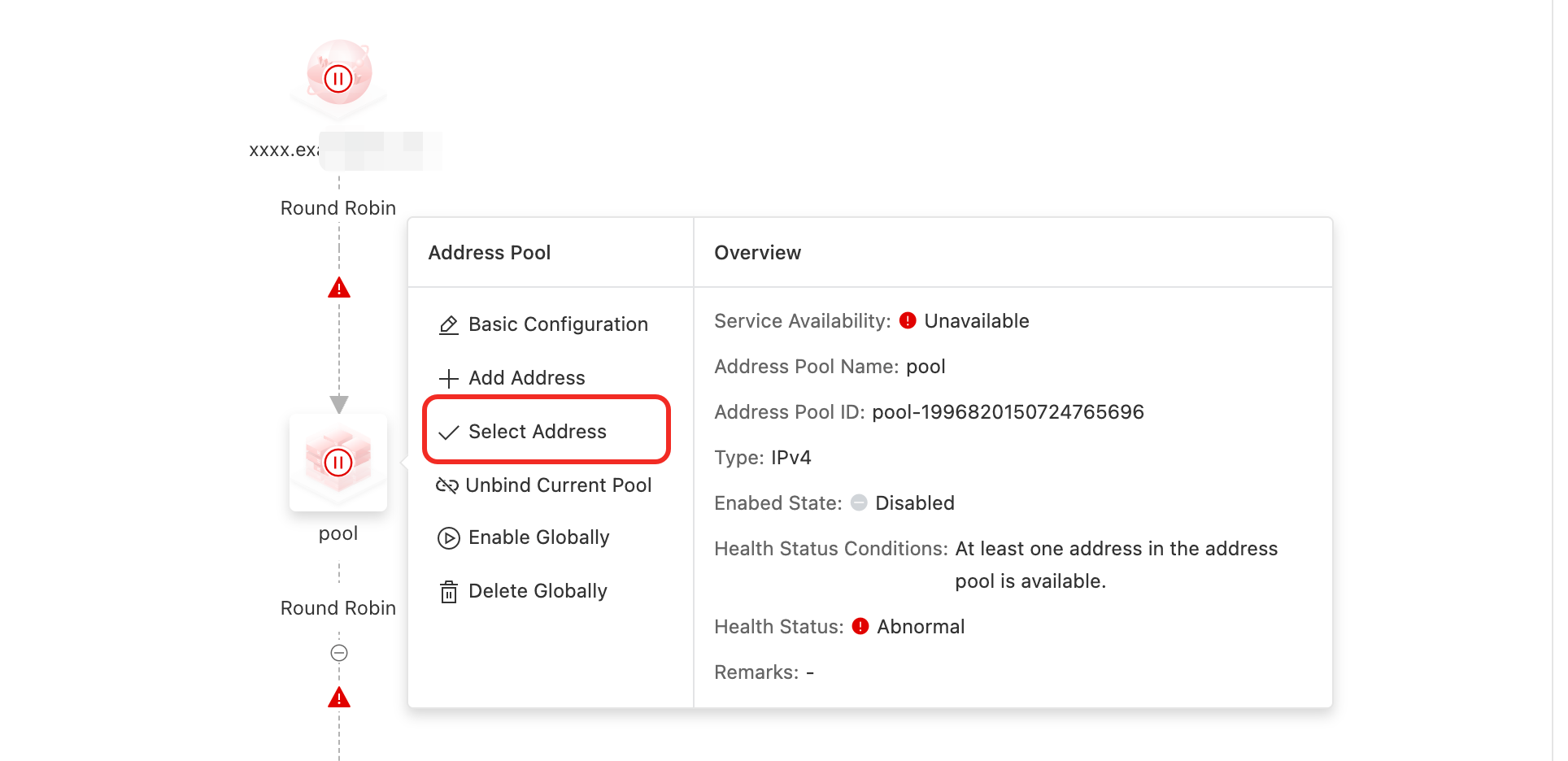
Select the addresses that you created. You can add multiple addresses at a time. The list displays only addresses that match the address pool type.
Manage address pools
Unbind Current Pool
Impact: This action removes the current address pool from the access domain. The address pool will no longer be used for DNS resolution for this domain. This operation does not affect other access domains that reference this address pool.
After you unreference an address pool, DNS queries may still resolve to the addresses in the pool. This is because the DNS records are cached on the local DNS servers of Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Before the DNS cache expires, the local DNS server returns the cached DNS record instead of requesting the latest record from Alibaba Cloud DNS. The change takes effect after the ISP refreshes its local cache. The time required for the change to take effect depends on the Time-to-Live (TTL) value of the cached DNS record. The change is expected to take effect in about 10 to 30 minutes.
On the Access Domain configuration page, click the Address Pool icon > Unbind Current Pool.
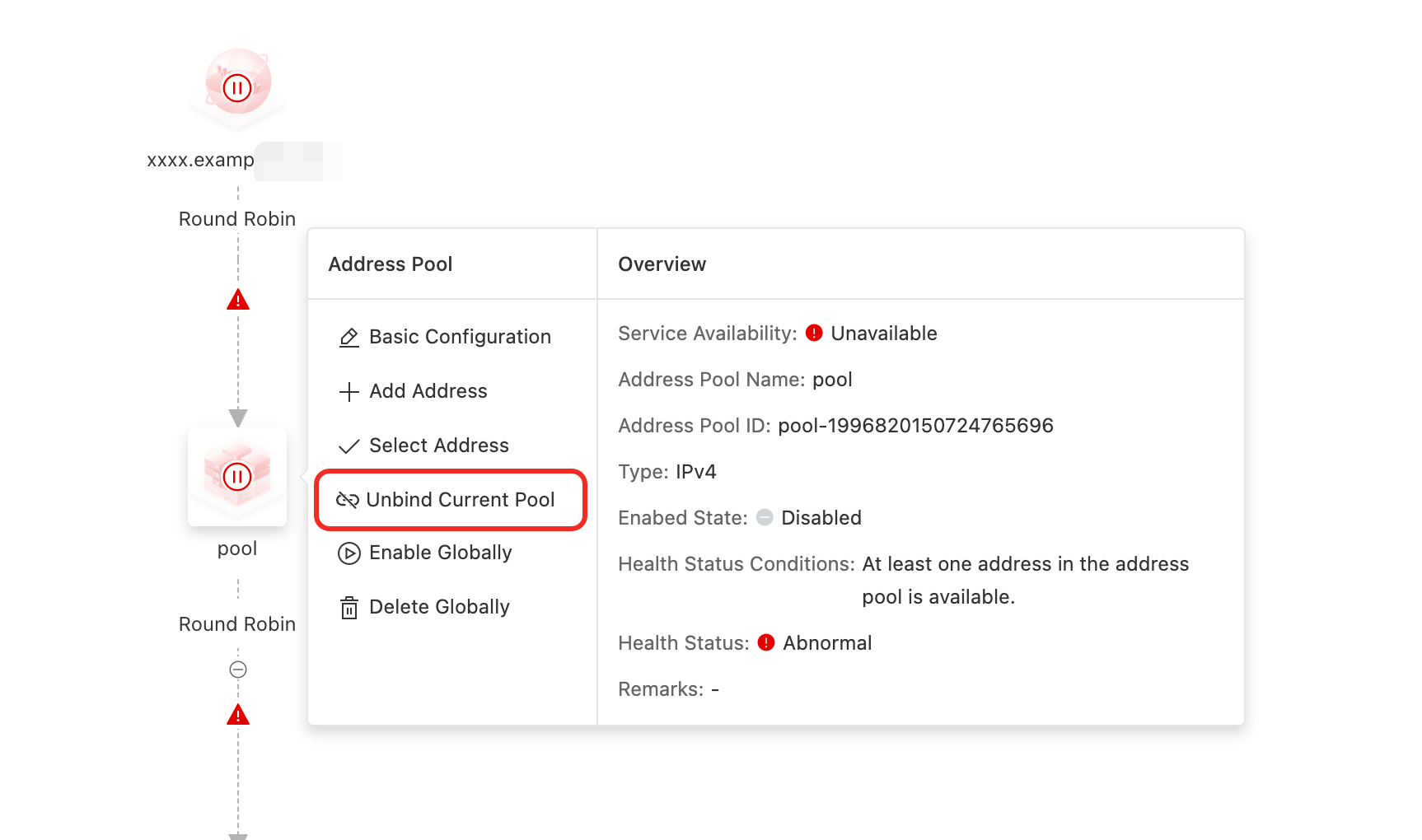
Confirming the operation in the second dialog box cancels the reference.
Enable Globally/Disable Globally/Delete Globally
Impact
Change Type | Impact |
Enable Globally | Ensure that the Address Pool is configured correctly and the Service Availability is set to Available. After you enable the address pool, it is used for DNS resolution. |
Disable Globally, Delete Globally | If an address is referenced by multiple Address Pool and is associated with multiple access domain names, disabling or deleting that address affects all associated access domain names. Important After an address is disabled or deleted, new GTM requests are no longer scheduled to it. However, DNS queries may still return the address because local ISP DNS servers maintain a cache. Until this cache expires, a local DNS server returns the cached DNS record instead of requesting the latest record from Alibaba Cloud DNS. The change takes effect after the local ISP cache expires. |
Procedure
On the Access Domain configuration page, click the Address Pool icon > Enable Globally / Disable Globally / Delete Globally.
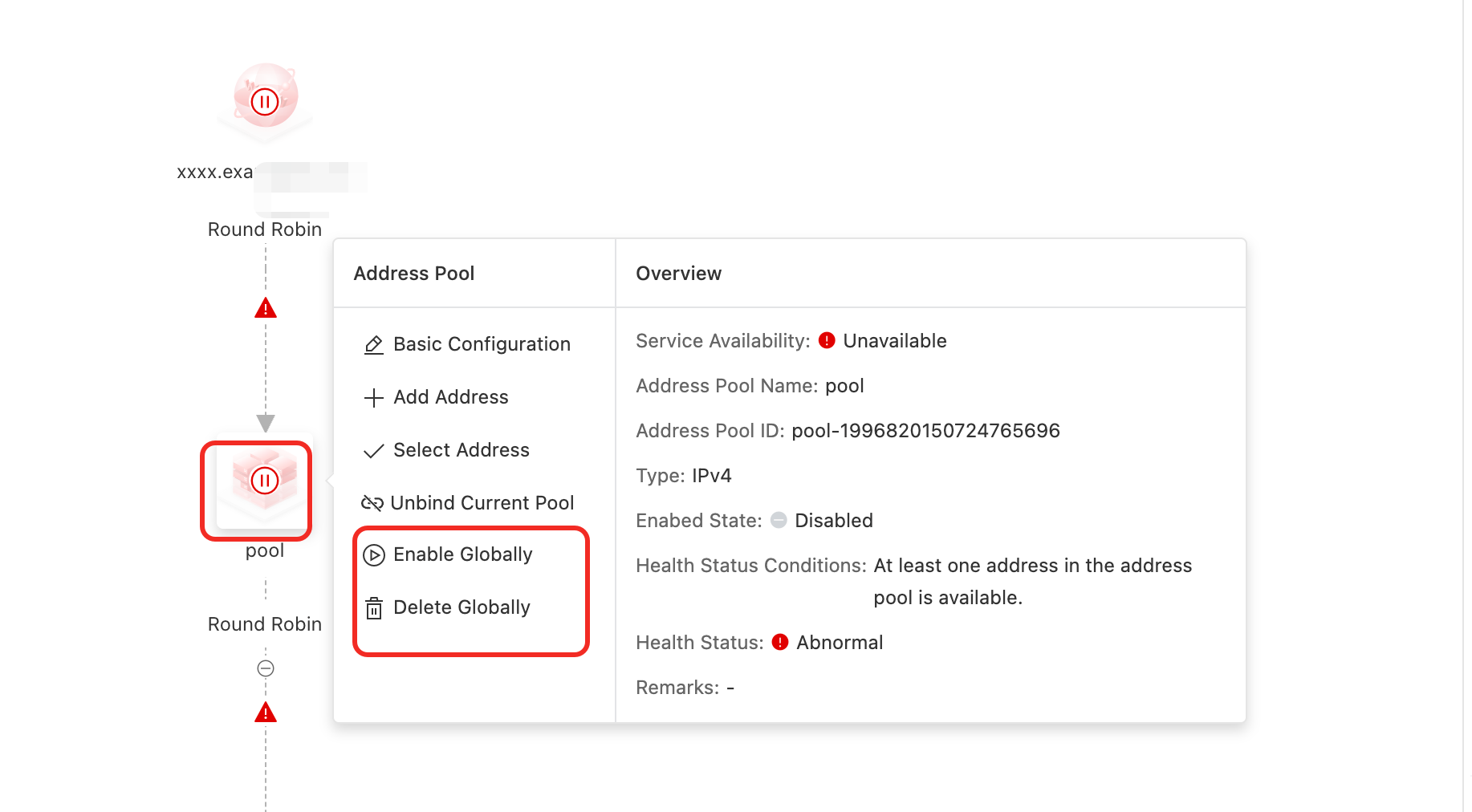
In the confirmation dialog box that appears, confirm the action.
Address Pool status description
Health Status description
Normal: All addresses in the Address Pool are available.
Warning: Some addresses in the Address Pool are unavailable. However, the number of unavailable addresses does not exceed the configured Health Status Conditions. In the Warning state, DNS queries resolve to the available addresses in the Address Pool, but not to the unavailable addresses.
Abnormal: The number of unavailable addresses in the Address Pool exceeds the configured Health Status Conditions. This sets the health status of the address pool to Abnormal. An abnormal address pool stops responding to DNS queries.
Service Availability description
The Service Availability is determined by the Enabed State and the Health Status. The logic is as follows:
Enabed State | Health Status | Service Availability |
Enabled | Normal or Warning | Available |
Enabled | Abnormal | Unavailable |
Disabled | Normal, Warning, or Abnormal | Unavailable |