Data Management (DMS) allows you to manage the accounts of MongoDB databases and grant the accounts the permissions of different roles. The roles include Common operation role, Administrator action role, Instance-level role, Cluster administrator role, Backup and Recovery roles, and Super role.
Prerequisites
A MongoDB database is used.
You are a DMS administrator, a database administrator (DBA), or a regular user such as the owner of an instance. For more information, see System roles.
The database account and database password of the MongoDB database are obtained.
You are granted the permissions to create accounts such as the dbAdminAnyDatabase, userAdmin, or userAdminAnyDatabase permission if you want to create an account for the admin database. For more information about how to modify an account, see the Modify or delete an account section of this topic.
Create a database account
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
Log on to the MongoDB database. For more information, see Log on to a database instance.
ImportantIf your database instance is an ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instance, log on to the primary node of the instance.
In the left-side navigation pane of the DMS console, right-click the instance that you want to manage and select Account Management.
On the Database Accounts page, find the database for which you want to create a database account.
Click Create a database account in the upper-left corner and configure the following parameters.
Configure the information about the database account.
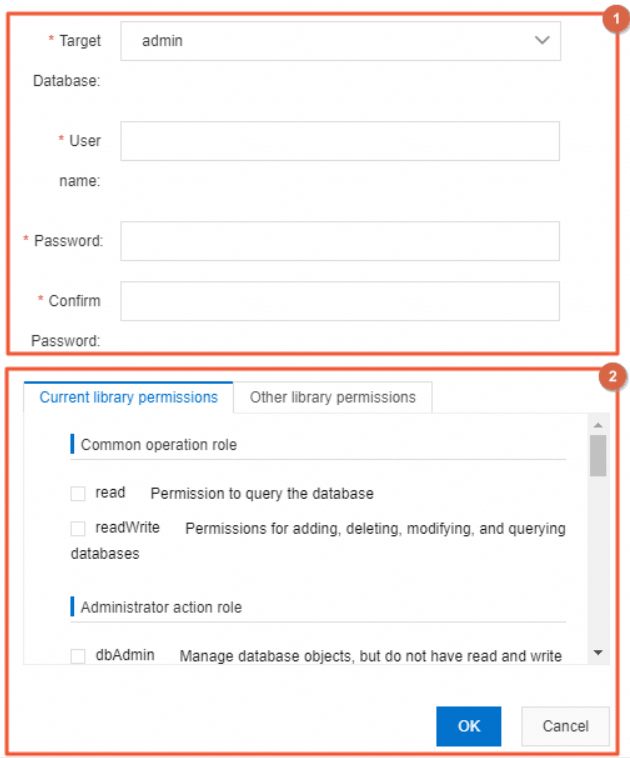
Parameter
Description
Destination Database
The database for which you want to create an account.
NoteIf you do not set the Destination Database parameter to admin, the account to be created is a regular account.
If you set the Destination Database parameter to admin, the account to be created is a privileged account.
Database Account
The username of the account.
The name cannot contain Chinese characters.
The name can contain letters, digits, and special characters.
The name can contain the following special characters:
! # $ % ^ & * ( ) _ + - =
Password
The password that is used to log on to the database.
we recommend that you set a password that is 8 to 32 characters in length and consists of three types of the following characters:
English letters (case-sensitive)
Digits
Special characters:
! # $ % ^ & * ( ) _ + - =
Confirm password
Enter the password again to confirm the password.
Grant permissions to the account.
NoteIf you set the Destination Database parameter to admin:
On the Current database permissions tab, you can grant the permissions of different roles to the account. The roles include Common operation role, Administrator action role, Instance-level role, Cluster administrator role, Backup and Recovery roles, and Super role. For more information, see the Permissions of different roles section of this topic.
On the Other database permissions tab, you can grant permissions on other databases in the instance to the account.
If you do not set the Destination Database parameter to admin:
On the Current database permissions tab, you can grant the permissions of only Common operation role and Administrator action role to the account. For more information, see the Permissions of different roles section of this topic.
You cannot grant permissions on other databases to the account on the Other database permissions tab.
Click OK.
NoteSQL statements can be generated based on the parameters that you configure. If the database instance is managed in Security Collaboration mode, the SQL statements may fail to be executed due to security rules. In this case, you can perform operations as prompted or contact a database administrator (DBA) or DMS administrator.
Modify or delete a database account
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the left-side instance list, right-click the database instance for which you want to manage a database account and select Database Accounts.
On the Database Accounts page, find the database account that you want to manage.
Click Edit or Delete in the Actions column.
Permissions of different roles
The following table describes the permissions of different roles. For more information, visit the MongoDB official website.
Role type | Permission | Description |
Common operation role | read | Allows a user to query data in the database. |
readWrite | Allows a user to insert, delete, update, and query data in the database. | |
Administrator action role | dbAdmin | Allows a user to manage data in the database, but not to read data from or write data to the database. |
userAdmin | Allows a user to create users for the database. | |
dbOwner | Allows a user to perform all operations on the database. | |
Instance-level role | readAnyDatabase | Allows a user to query data in all databases of the instance. |
readWriteAnyDatabase | Allows a user to insert, delete, update, and query data in all databases of the instance. | |
userAdminAnyDatabase | Allows a user to create users for all databases of the instance. | |
dbAdminAnyDatabase | Allows a user to manage data in all databases of the instance. | |
Cluster administrator role | hostManager | Allows a user to manage data in the database, but not to read data from or write data to the database. |
clusterMonitor | Allows a user to query clusters and replica sets. | |
clusterManager | Allows a user to manage and monitor clusters and replica sets. | |
clusterAdmin | Allows a user to perform all operations on clusters. | |
Backup and Recovery roles | backup | Allows a user to query data in all databases of the instance. |
restore | Allows a user to insert, delete, update, and query data in all databases of the instance. | |
Super role | Root | Allows a user to perform all operations on all resources in an instance. |