This topic describes how to access Data Lake Formation (DLF) from EMR Serverless Spark via PVFS.
Version requirements
This feature requires esr-3.5.0, esr-2.9.0, esr-4.6.0, and later.
Create a DLF catalog
See Get started with DLF.
Connect a DLF catalog to a Spark workspace
You can associate your DLF catalog with a new or existing EMR Serverless Spark workspace.
New workspaces
See Create a workspace.
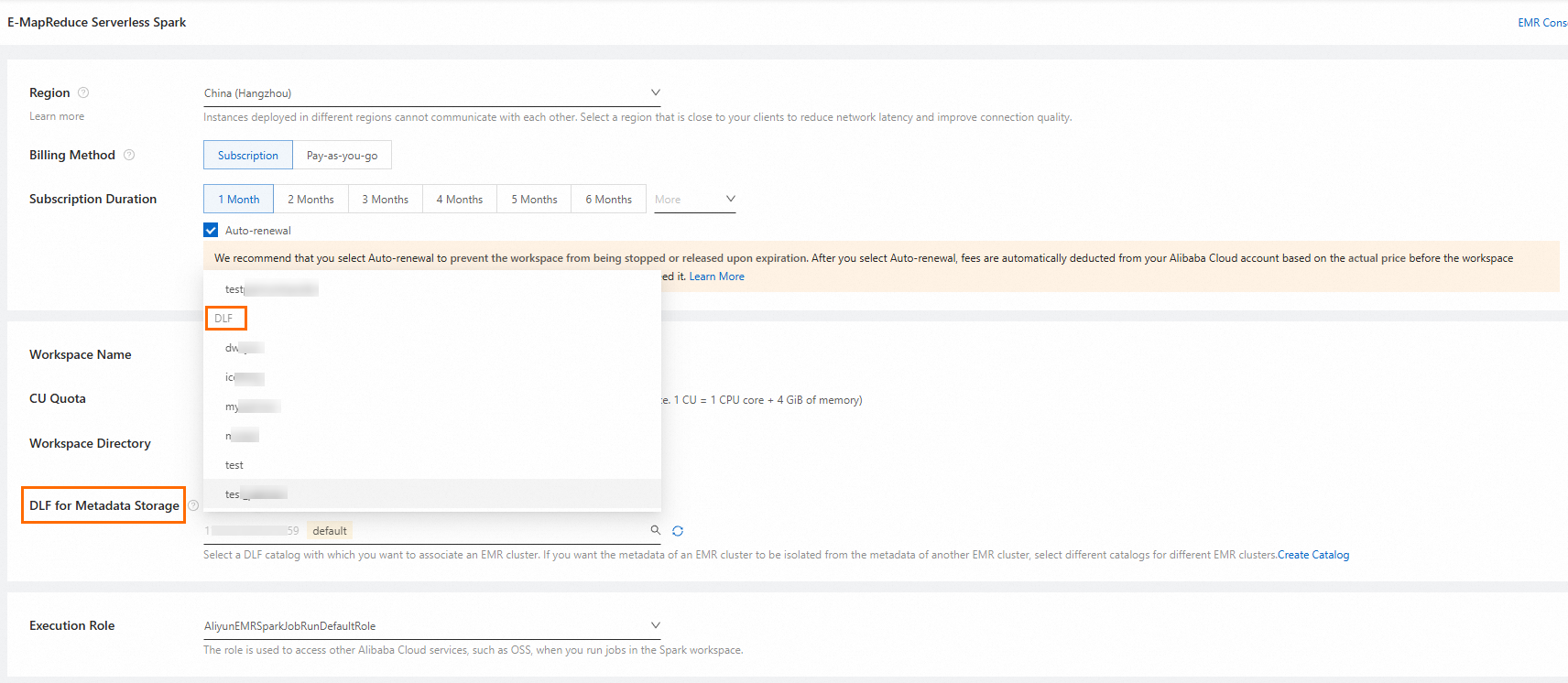
When creating a workspace, enable DLF for Metadata Storage and select your DLF catalog.
Existing workspaces
Navigate to the Catalog page of your Spark workspace and add a DLF catalog.
All DLF catalogs in a Spark workspace must be of the same version. You can either add DLF-Legacy catalogs or only the latest DLF catalogs. If your Spark workspace already has a DLF-Legacy catalog and you wish to use the latest DLF catalog, you have two options:
Remove the DLF-Legacy catalog before adding the latest DLF catalog. Before removing the legacy catalog, ensure no running Spark jobs are using its data.
Create a new Spark workspace and add the latest DLF catalog here.
Access DLF from EMR Serverless Spark
Log on to the DLF console.
In the left navigation menu, choose Catalogs. Click the name of your catalog associated with your EMR Serverless Spark workspace. In the default database, create an Object table named
object_table.Click the
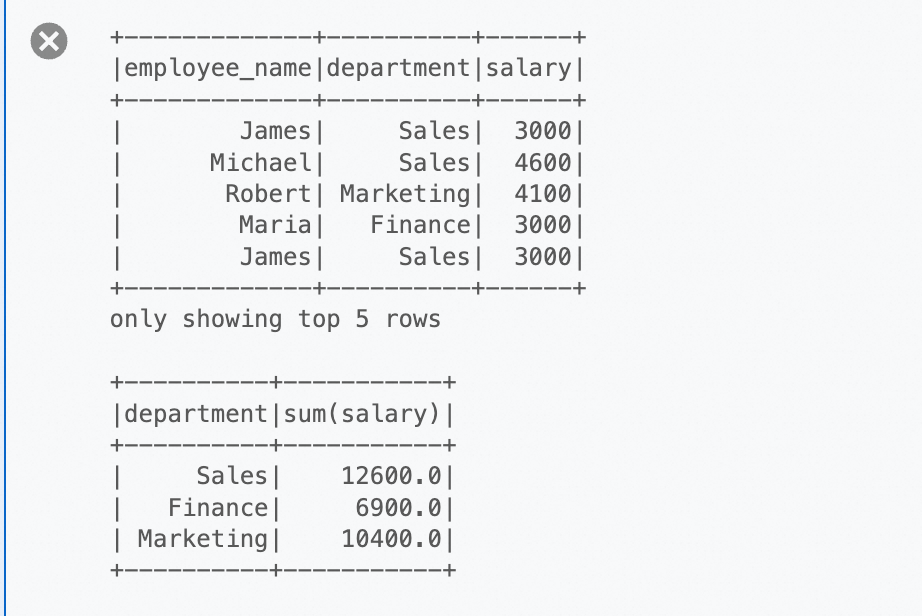
object_tabletable to open its details page. Select the File List tab.Click Upload File and upload the employee.csv file.
Go to the EMR console. In the left navigation pane, choose . Click your Spark workspace name.
In the left navigation menu of the page that appears, choose Development.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon. In the New dialog box, enter a name, set Type to Notebook, and click OK.
icon. In the New dialog box, enter a name, set Type to Notebook, and click OK.Copy and paste the following code to access the sample file.
# Replace catalog_name with your actual catalog name. df = spark.read.option("delimiter", ",").option("header", True).csv("pvfs://catalog_name/default/object_table/employee.csv") # Show the first 5 rows. df.show(5) # Perform an aggregate by calculating the total salary for each department. sum_salary_per_department = df.groupBy("department").agg({"salary": "sum"}).show()