After you create a dedicated host, you can create one or more Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances on the dedicated host so that you can exclusively use all the physical resources of the ECS instances. This topic describes how to create ECS instances on a dedicated host.
Background information
ECS supports virtual private clouds (VPCs) and the classic network. However, you can create only ECS instances that use VPCs on a dedicated host. The ECS instances on a dedicated host have different features from those on a shared host. For more information, see Differences between ECS instances on a dedicated host and those on a shared host.
We recommend that you create pay-as-you-go ECS instances on a dedicated host and select a combination of billing methods to optimize your costs without compromising flexibility. For more information, see Resource billing for ECS instances on a dedicated host.
Procedure
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group to which the resource belongs.

Find the dedicated host on which you want to create ECS instances. Click Create Instance in the Actions column.
NoteThis topic introduces only the key parameters for creating ECS instances. For other parameters, use the default settings. For more information, see Create ECS instances.
On the Custom Launch page, create one or more ECS instances according to the following table.
Parameter
Description
Example
Dedicated Host
Select the dedicated host on which you want to create ECS instances and specify whether to associate the dedicated host.
If you select Associate with DDH, the ECS instances are deployed on the current dedicated host. If the resources of the dedicated host are insufficient, the ECS instances fail to be restarted.
If you do not select Associate with DDH, the ECS instances may be deployed on another dedicated host that belongs to your Alibaba Cloud account when the instances are restarted. For more information, see Functions and features.
Retain the default setting.
Billing Method
Select a billing method for the ECS instances based on the billing method of the dedicated host. You can select Subscription or Pay-as-you-go as the billing method of ECS instances that run on a subscription dedicated host.
For more information, see Resource billing for ECS instances on a dedicated host.
ImportantICP filings are unavailable for pay-as-you-go ECS instances.
Pay-as-you-go
Instance Type
Select appropriate instance types.
NoteThe region and zone of the ECS instances must be the same as those of the dedicated host. The available instance types depend on the type and available computing resources of the dedicated host. For more information about dedicated host types, see Dedicated host types.
ecs.i2.xlarge
Quantity
The number of instances to purchase.
1
Image
Select an appropriate image.
For more information, see Select an image.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2.1903 LTS 64-bit
System Disk/Data Disk
Configure a system disk and data disks based on your business requirements.
Retain the default setting.
Click Next:Networking and configure the parameters in the Networking step. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Network Type
Alibaba Cloud provides a default virtual private cloud (VPC). If you do not want to use the default VPC, you can create a VPC and a vSwitch in the region where you want to create ECS instances. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
VPC: ddh-vpc/vpc-bp1j4z1sr8****
vSwitch: test/vsw-bp155oak33****
Public IP Address
If you want to assign public IP addresses to the ECS instances, you must select Assign Public IPv4 Address. Then, select Pay-by-traffic or Pay-by-bandwidth as the metering method of the public bandwidth, and specify the bandwidth. The public IP addresses cannot be detached from the ECS instances. For more information on public bandwidth billing, see Public bandwidth.
If your instances do not need to access the Internet or your VPC-type instances use elastic IP addresses (EIPs) to access the Internet, you do not need to assign public IP addresses. You can associate an EIP with or disassociate an EIP from an instance at any time.
Retain the default setting.
Security Group
Alibaba Cloud provides a default security group. If you do not want to use the default security group, you can create a security group in the region where you want to create ECS instances. For more information, see Create a security group.
sg-20200622/sg-bp1542zl60b5q6hx****
Elastic Network Interface
If the selected instance type supports elastic network interfaces (ENIs), you can add ENIs and select vSwitches for the ENIs.
NoteBy default, the ENIs are released together with the ECS instances. You can also detach the ENIs from the instances by calling the DetachNetworkInterface operation or using the ECS console.
test
IPv6
Specify whether to use an IPv6 address based on your business requirements. For information about the instance families that support IPv6, see Overview of instance families.
Retain the default setting.
Click Preview to confirm the order.
Before the instances are created, make sure that all configurations, such as the use duration, meet your business requirements.
In the Configurations section, confirm the configurations of the ECS instances.
You can click
 to modify the configurations.
to modify the configurations. Configure the use duration of the ECS instances.
If the billing method of the ECS instances is Subscription, you must specify the duration and whether to enable auto-renewal.
NoteThe expiration date of the subscription ECS instances cannot be later than that of the subscription dedicated host.
If the billing method of the ECS instances is Pay-as-you-go, you can select Automatic Release and specify the time scheduled for the ECS instances to be automatically released.
Read ECS Terms of Service and select the check box.
In the lower part of the page, view the total fees of the ECS instances, confirm the order, and then complete the payment.
View the result
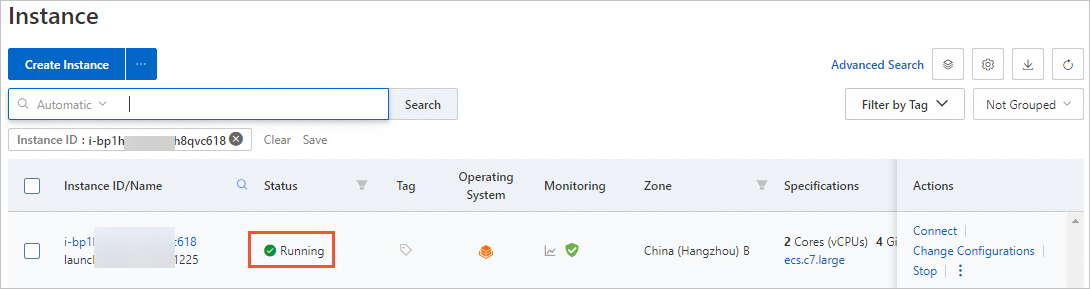
After the ECS instances are created, click Console to switch back to the ECS console. On the instances page, select the region where the created ECS instances reside. Then, you can view the instance IDs, public IP addresses, and private IP addresses of the created instances.
What to do next
If you did not set a logon password when you created an ECS instance, you can set a password for the instance later. For more information, see Reset the logon password of an instance.
You can build an FTP site on an ECS instance to upload files to the instance. For more information about how to deploy the FTP service, see Build an FTP site on an ECS instance.
If you have created data disks along with the ECS instances, you can use the data disks only after they are partitioned and formatted. For more information, see Initialize a data disk whose size does not exceed 2 TiB on a Linux instance or Initialize a data disk up to 2 TiB in size on a Windows instance.
 > Dedicated Hosts
> Dedicated Hosts