Data Integration allows you to synchronize data from a database in a data source, such as an ApsaraDB for OceanBase, MySQL, Oracle, or PolarDB data source, to AnalyticDB for MySQL V3.0 in real time. This topic describes how to use DataWorks Data Integration to synchronize full and incremental data in a MySQL database to AnalyticDB for MySQL V3.0 in real time.
Prerequisites
A serverless resource group or an exclusive resource group for Data Integration is purchased.
A MySQL data source and an AnalyticDB for MySQL V3.0 data source are added to DataWorks. For more information, see Data source configuration.
Network connections between the resource group and data sources are established. For more information, see Overview of network connectivity solutions.
Procedure
1. Select a synchronization type
Go to the Data Integration page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Integration.
In the left-side navigation pane of the Data Integration page, click Synchronization Task. In the upper part of the Synchronization Task page, select a source type from the Source drop-down list and a destination type from the Destination drop-down list, and click Create Synchronization Task. On the page that appears, configure basic information for the synchronization task.
Source And Destination: Separately select
MySQLandAnalyticDB for MySQL (V3.0).New Node Name: Specify a name for the synchronization task based on your business requirements.
Synchronization Method: Select
Real-time migration of entire database.Synchronization Mode: Select Full initialization and Incremental synchronization.
2. Configure network settings and a resource group
In the Network and Resource Configuration section, select a resource group that you want to use to run the synchronization task, and configure the Task Resource Usage parameter.
In the Source section, select the added MySQL data source from the Name drop-down list. In the Destination section, select the added AnalyticDB for MySQL V3.0 data source from the Name drop-down list. Then, click Test Connectivity.
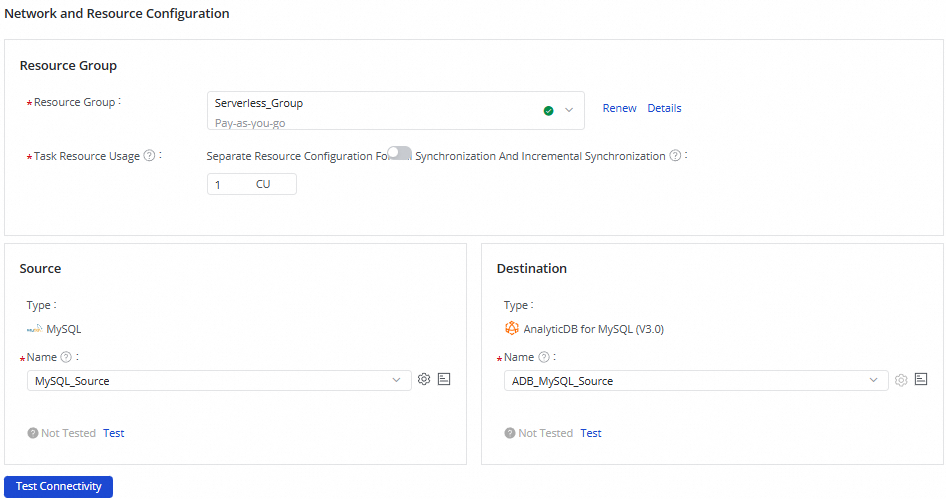
If the network connectivity test is successful, click Next.
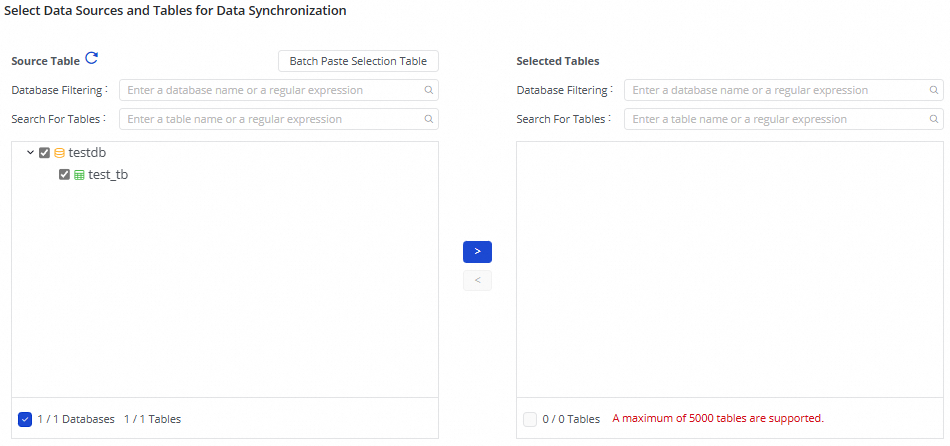
3. Select the tables from which you want to synchronize data
In this step, you can select the tables from which you want to synchronize data in the Source Table list and click the ![]() icon to move the selected tables to the Selected Tables list.
icon to move the selected tables to the Selected Tables list.
4. Configure settings related to destination tables
After you select the tables from which you want to synchronize data, the selected tables are automatically displayed in the Mapping Rules for Destination Tables section. The properties of the destination tables are waiting to be mapped. You must manually define mappings between the source tables and destination tables to determine the data reading and writing relationships. Then, you can click Refresh in the Actions column. You can directly refresh mappings between source tables and destination tables. You can also refresh mappings between source tables and destination tables after you configure settings related to destination tables.
You can select the rows in which source tables are displayed and click Batch Refresh Mapping Results. If the Customize Mapping Rules for Destination Table Names parameter is not configured, the mapping rule in the
${Source database name}_${Source table name}format is used for the related destination tables. If no tables with the same names as the source tables exist in the destination, the system automatically creates the tables in the destination.You can click Edit in the Customize Mapping Rules for Destination Table Names column to configure mapping rules for destination table names based on your business requirements.
You can concatenate a built-in variable and a specific string into a destination table name. You can edit built-in variables. For example, when you create a mapping rule, you can add a suffix to a variable that indicates a source table name to form a destination table name.
a. Modify data type mappings for fields
Default mappings exist between data types of source fields and data types of destination fields. You can click Edit Mapping of Field Data Types in the upper-right corner of the Mapping Rules for Destination Tables section to configure data type mappings between source fields and destination fields based on your business requirements. After the configuration is complete, click Apply and Refresh Mapping.
b. Modify the schema of a destination table to add fields to the table and assign values to the fields
If a destination table is in the To Be Created state, you can perform the following steps to add fields to the table and assign values to the fields:
Add fields to one or more destination tables.
Add fields to a single destination table: Find the destination table to which you want to add fields and click the
 icon in the Destination Table Name column. In the dialog box that appears, add fields.
icon in the Destination Table Name column. In the dialog box that appears, add fields. Add fields to multiple destination tables at a time: Select the destination tables to which you want to add fields at a time, click Batch Modify in the lower part of the page, and then click Destination Table Schema - Batch Modify and Add Field.
Assign values to the fields. You can perform one of the following operations to assign values to the fields:
Assign values to the fields that are added to a single destination table: Find the destination table in which you want to assign values to newly added fields and click Configure in the Value assignment column. In the Additional Field dialog box, assign values to the fields.
Assign values to the fields that are added to multiple destination tables at a time: Select the destination tables in which you want to assign values to newly added fields, click Batch Modify in the lower part of the page, and then click Value assignment to assign values to the same fields in the selected destination tables at a time.
NoteYou can click the
 icon to switch the value assignment method and assign constants and variables to the fields that are added to a destination table.
icon to switch the value assignment method and assign constants and variables to the fields that are added to a destination table.
c. Configure DML processing rules
Data Integration provides default DML processing rules. You can also configure DML processing rules for destination tables based on your business requirements.
Configure DML processing rules for a single destination table: Find the destination table for which you want to configure DML processing rules and click Configure in the Configure DML Rule column to configure DML processing rules for the table.
Configure DML processing rules for multiple destination tables at a time: Select the destination tables for which you want to configure DML processing rules, click Batch Modify in the lower part of the page, and then click Configure DML Rule.
5. Configure alert rules
To prevent the failure of the synchronization task from causing latency on business data synchronization, you can configure different alert rules for the synchronization task.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Configure Alert Rule to go to the Alert Rule Configurations for Real-time Synchronization Subnode panel.
In the Configure Alert Rule panel, click Add Alert Rule. In the Add Alert Rule dialog box, configure the parameters to configure an alert rule.
NoteThe alert rules that you configure in this step take effect for the real-time synchronization subtask that will be generated by the synchronization task. After the configuration of the synchronization task is complete, you can refer to Run and manage real-time synchronization tasks to go to the Real-time Synchronization Task page and modify alert rules configured for the real-time synchronization subtask.
Manage alert rules.
You can enable or disable alert rules that are created. You can also specify different alert recipients based on the severity levels of alerts.
6. Configure advanced parameters
You can change the values of specific parameters configured for the synchronization task based on your business requirements. For example, you can specify an appropriate value for the Maximum read connections parameter to prevent the current synchronization task from imposing excessive pressure on the source database and data production from being affected.
To prevent unexpected errors or data quality issues, we recommend that you understand the meanings of the parameters before you change the values of the parameters.
In the upper-right corner of the configuration page, click Configure Advanced Parameters.
In the Configure Advanced Parameters panel, change the values of the desired parameters.
7. Configure DDL processing rules
DDL operations may be performed on the source. You can click Configure DDL Capability in the upper-right corner of the page to configure rules to process DDL messages from the source based on your business requirements.
For more information, see Configure rules to process DDL messages.
8. View and change resource groups
You can click Configure Resource Group in the upper-right corner of the page to view and change the resource groups that are used to run the current synchronization task.
9. Run the synchronization task
After the configuration of the synchronization task is complete, click Complete in the lower part of the page.
In the Synchronization Task section of the Data Integration page, find the created synchronization task and click Start in the Operation column.
Click the Name/ID of the synchronization task in the Tasks section and view the detailed running process of the synchronization task.
Perform O&M operations on the synchronization task
View the running status of the synchronization task
After you complete the configuration of the synchronization task, you can go to the Tasks section of the Synchronization Task page, and view all synchronization tasks that are created in the current workspace and the basic information of each synchronization task.
You can click Start or Stop in the Operation column to start or stop the synchronization task. You can also click More in the Actions column and select Edit or View to modify the synchronization task or view information about the synchronization task.
You can click Running Details in the Operation column to view the running details of a synchronization task. You can also click different sections on the running details page of the synchronization task to view the related information.
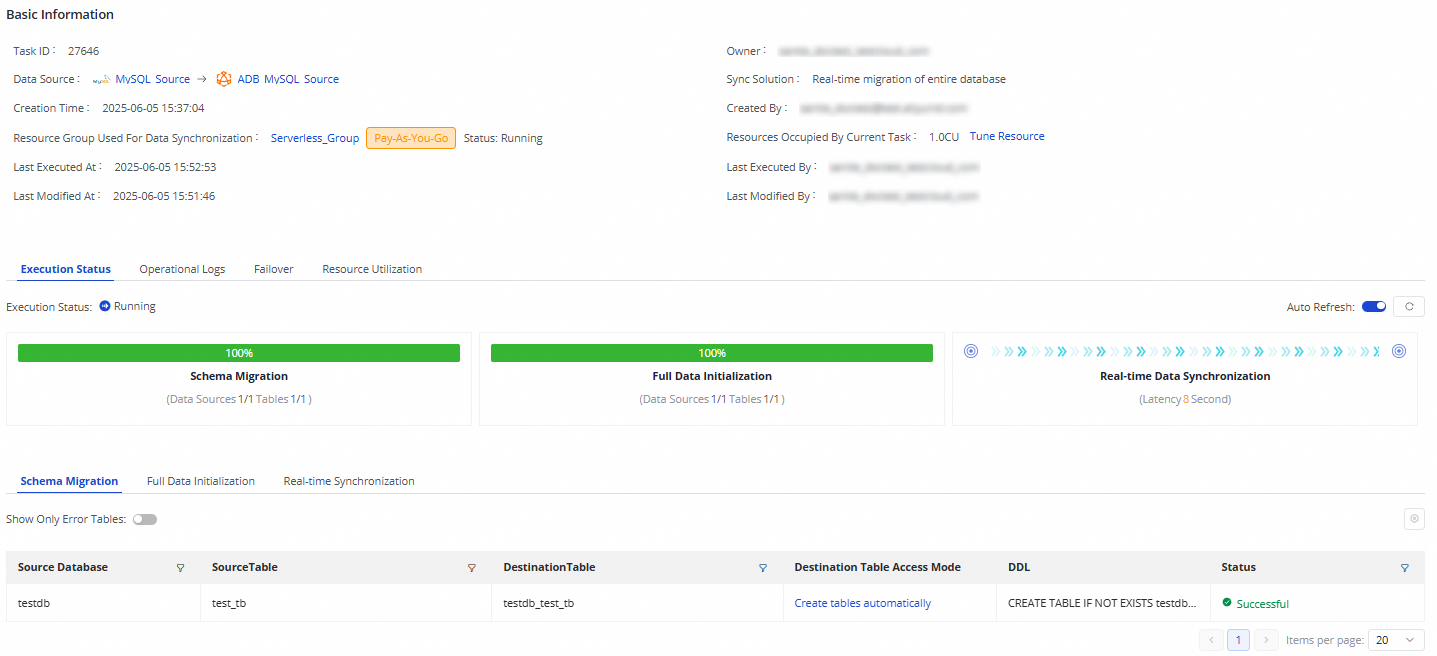
The synchronization task has the following stages:
Schema Migration: This tab displays information such as whether the destination table is a newly created table or an existing table. For a newly created table, the DDL statement that is used to create the table is displayed.
Full Data Initialization: This tab displays information such as the source tables and destination tables involved in batch synchronization, the synchronization progress, and the number of data records that are synchronized.
Real-time Synchronization: This tab displays statistical information about real-time synchronization, including the synchronization progress, DDL records, DML records, and alert information.
Rerun the synchronization task
In some special cases, if you add tables to or remove tables from the source, or change the schema or name of a destination table, you can click More in the Operation column of the synchronization task and then click Rerun to rerun the task after the change. During the rerun process, the synchronization task synchronizes data only from the newly added tables to the destination or only from the mapped source table to the destination table whose schema or name is changed.
If you want to rerun the synchronization task without modifying the configuration of the task, click More in the Actions column and then click Rerun to rerun the task to perform full synchronization and incremental synchronization again.
If you want to rerun the synchronization task after you add tables to or remove tables from the task, click Complete after the change. In this case, Apply Updates is displayed in the Actions column of the synchronization task. Click Apply Updates to trigger the system to rerun the synchronization task. During the rerun process, the synchronization task synchronizes data from the newly added tables to the destination. Data in the original tables is not synchronized again.