If you plan to switch your legacy DataWorks resource groups to serverless resource groups, you must first assess the resource consumption of your existing tasks to ensure a smooth migration. Then, you can switch to a serverless resource group with sufficient capacity to handle your tasks. This topic explains how to estimate the required compute units (CUs), describes the potential impacts of the switch, and provides instructions on switching from legacy to serverless resource groups.
New resource groups
DataWorks provides exclusive resource groups for Data Integration, scheduling, and DataService Studio. However, these resource groups must be purchased and configured separately. To improve resource management and provide a unified user experience, DataWorks introduced serverless resource groups. A single serverless resource group can be used for data integration, task scheduling, and DataService Studio, which simplifies resource management and improves operational consistency.
Billing
Before you switch, review the billing details for legacy resource groups: Billing for legacy resource groups.
After you switch, review the billing details for serverless resource groups: Billing for serverless resource groups.
Procedure
Step 1: Query tasks in the resource groups to be switched
Data Integration
To switch data integration tasks on the Data Integration page:
Go to the Data Integration page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Integration.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Synchronization Task. In the Tasks section, click Expand. Filter the tasks by setting Resource Group to the data integration resource group that you want to switch.
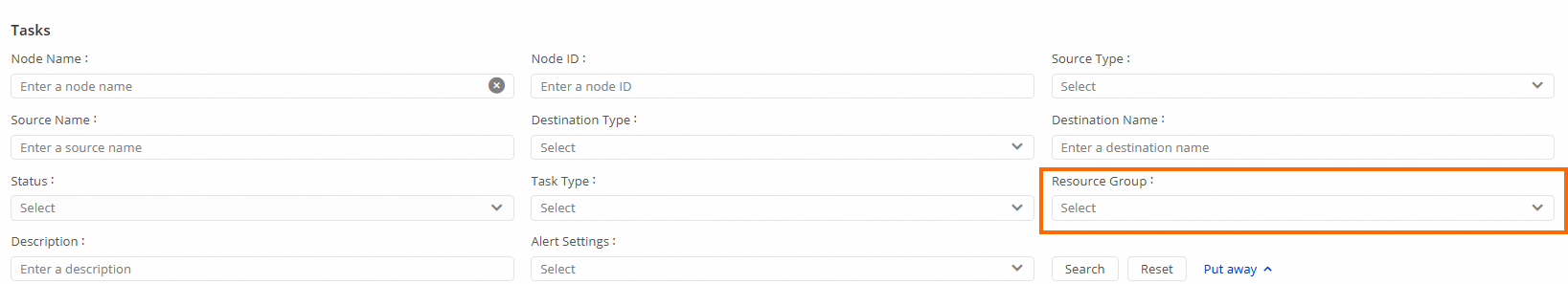
To switch data integration tasks on the new Data Studio page:
Go to the Workspaces page in the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select a desired region. Find the desired workspace and choose in the Actions column.
The Data Studio page appears by default. Click the
 icon next to Project Directory to perform batch operations on nodes.
icon next to Project Directory to perform batch operations on nodes.Filter the nodes by the resource group that you want to switch and select the Real-time Sync and Batch Sync node types.

To switch data integration tasks on the legacy Data Studio page:
Go to the DataStudio page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Development.
In the navigation pane on the left, click DataStudio. Find and right-click the target business flow, and then choose Batch Operation.
Set Node Type to Offline Synchronization and Real-time Synchronization. Set Resource Group for Data Integration to the resource group that you want to switch.
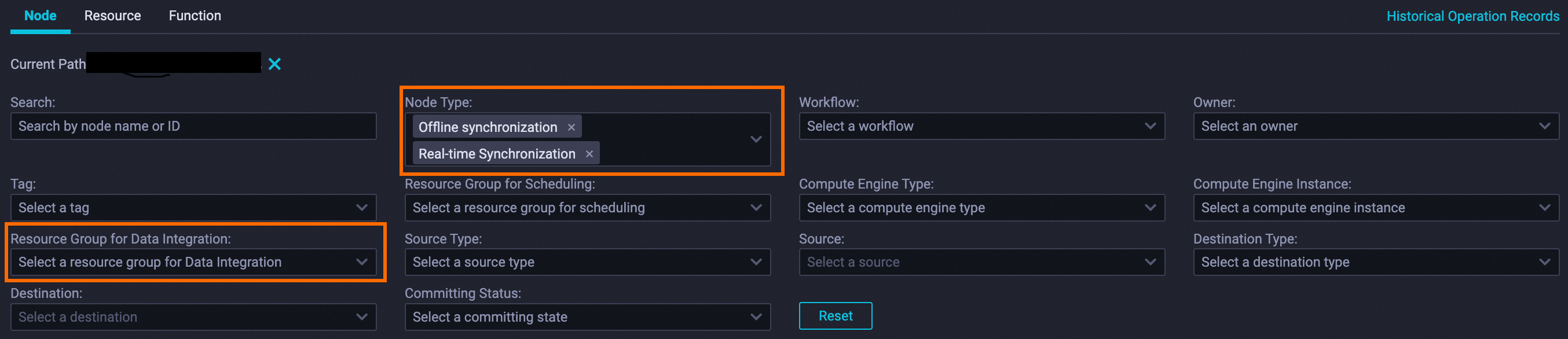
Scheduling tasks
Go to the Operation Center page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Operation Center.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Filter the tasks by setting Scheduling Resource Group to the scheduling resource group that you want to switch.
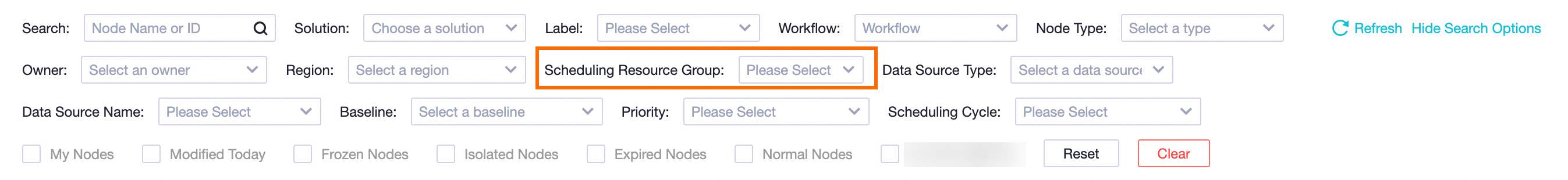
DataService Studio
Go to the DataService Studio page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to DataService Studio.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Service Development. Then, click the
 icon to go to the Batch Operations page. Filter the services by setting Resource Group to the DataService Studio resource group that you want to switch.
icon to go to the Batch Operations page. Filter the services by setting Resource Group to the DataService Studio resource group that you want to switch.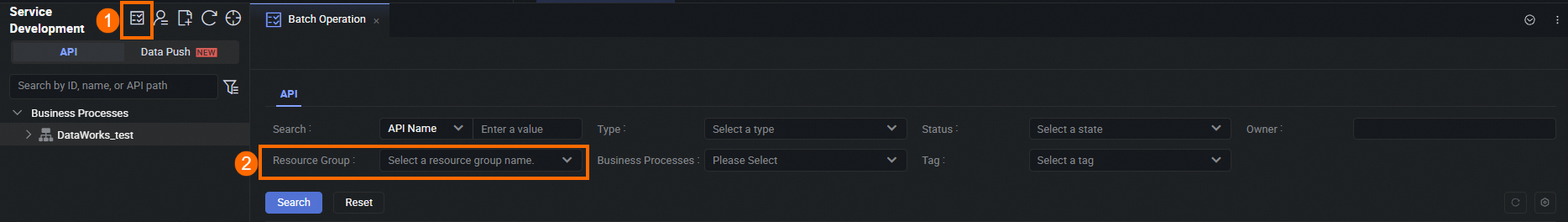
Step 2: Assess the specifications for serverless resource groups before the switch
After you switch to a serverless resource group, data computing tasks (such as PyODPS2 and EMR Hive) will incur computing fees.
Before you switch, assess the resource consumption of your existing tasks, including sync, scheduling, and DataService Studio tasks. This assessment helps you determine the required size of the serverless resource group and ensures that the resource group can handle your business workloads.
The following are the detailed assessment recommendations:
Data Integration
Offline synchronization
Concurrency configuration for offline synchronization tasks | Recommended specifications | Minimum specifications for running tasks |
<4 | 0.5 CU | 0.5 CU |
>=4 |
|
Real-time synchronization
Synchronization task type | Recommended specifications | Minimum specifications for running tasks | |
Real-time synchronization for MySQL | 1 database | 2 CU | Minimum specifications for running a real-time synchronization task: 1 CU |
2 to 5 databases | 2 CU | ||
6 or more databases | 2 CU | ||
Real-time synchronization for Kafka | 1 CU | ||
Other types of single-table real-time tasks | 1 CU | ||
Real-time synchronization for an entire database | - | Minimum specifications for running an entire-database synchronization task: 2 CU | |
Scheduling
A serverless resource group supports a maximum of 200 concurrently running instances. The CU specification of the serverless resource group can be ignored. The default number of concurrently running instances is 50. You can set the maximum number of concurrent scheduling tasks to 200 on the resource group details page.

DataService Studio
Maximum queries per second (QPS) | Minimum specifications | Service-level agreement (SLA) |
500 | 4 CU | 99.95% |
1000 | 8 CU | |
2000 | 16 CU |
Data compute
Each data compute task has a default number of CUs. For more information, see Task types and CU consumption.
Step 3: Purchase a serverless resource group
Based on your assessment, purchase a serverless resource group. For more information, see Use a serverless resource group.
Step 4: Switch to the serverless resource group
Switch the resource group for Data Integration
NoteAfter you switch to the serverless resource group, DataWorks automatically recommends the number of CUs based on the original task configuration. To manually set the number of CUs for the resource group, see the recommendations in Step 2: Assess the serverless resource group specifications before the switch.
Switch the resource group for scheduling tasks
NoteScheduling tasks run on the DataWorks resource group. A portion of the resource group quota is allocated for the CU configuration of compute-optimized tasks. Therefore, when you change the scheduling resource group, the resource group used for task computing also changes.
Switch the resource group for DataService Studio
NoteBefore you switch, you must set a quota for DataService Studio. If a quota is not set, you cannot select the serverless resource group during the switch. For more information about setting a quota for DataService Studio, see Allocate a CU quota to a task.
Next steps
After you switch to the serverless resource group, you can unsubscribe from the legacy resource group if it is no longer needed. For more information, see General reference: Unsubscribe from a subscription product.