The Real-Time Synchronization Nodes page of the DataWorks console displays all real-time synchronization tasks that are committed to and run by the scheduling system.
Go to the Real-Time Synchronization Nodes page
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Operation Center.
In the left-side navigation pane of the Operation Center page, click the
 icon next to Real-time Node O&M.
icon next to Real-time Node O&M. Select Real-Time Synchronization Nodes from the drop-down list. The Real-Time Synchronization Nodes page appears.
View real-time synchronization tasks in the task list
The task list displays real-time synchronization tasks that are run by the scheduling system. You can manage these tasks and perform O&M operations on these tasks. For example, you can view the basic information, properties, and running information of a real-time synchronization task. You can also start or undeploy a real-time synchronization task.
Area | Description |
1 | In this area, you can specify filter conditions to search for real-time synchronization tasks. You can specify the following filter conditions to search for tasks: Node Name Or ID, Task Status, Owner, Source Type, Source Name, Last Operated By, Destination Type, Destination Name, and Resource Group for Data Integration. Note When you search for tasks by task name, the search result is affected by other filter conditions that you specified. Only the tasks that meet all filter conditions are displayed. |
2 | In this area, you can view the following information about the real-time synchronization task that you want to query:
|
3 | In this area, you can perform the following operations on multiple tasks at a time:
|
View the details of a real-time synchronization task
Find the real-time synchronization task that you want to query and click the task name to go to the details panel of the task. In the details panel of the task, you can view the details of the task on the Progress, Logs, Database DDL Events, Statistics on Database DML Events, Failover, and Perform Diagnosis tabs.
Perform operations on a real-time synchronization task
Start a real-time synchronization task
Find the task that you want to start and click Start in the Actions column. In the Start dialog box, configure the parameters and click Confirm. The system starts to run the task.
If you select Reset site, you must configure the Time and Time zone parameters.
Stop a real-time synchronization task
Find the real-time synchronization task that you want to stop and click Stop in the Actions column. Then, click Stop in the message that appears to stop the task.
Undeploy a real-time synchronization task
Find the node that you want to undeploy and click Undeploy in the Actions column. Then, click Undeploy in the message that appears to undeploy the task.
View the alert rule settings of a real-time synchronization task
Find the task whose alert rule settings you want to view and click View Alert Settings in the Actions column. The Alert Events tab appears. On this tab, you can configure the Occurrence Time, Alert Level, and Rules parameters to view the alert events of the task.
Click Alert Rules to go to the Alert Rules tab. On this tab, you can view all the alert rules that are created for the task. You can view the metrics and status of an alert rule. You can also modify, pause, delete, or test an alert rule. If you want to create an alert rule, click Create Rule in the upper-right corner of the Alert Rules tab and configure the parameters. The following table describes the parameters.
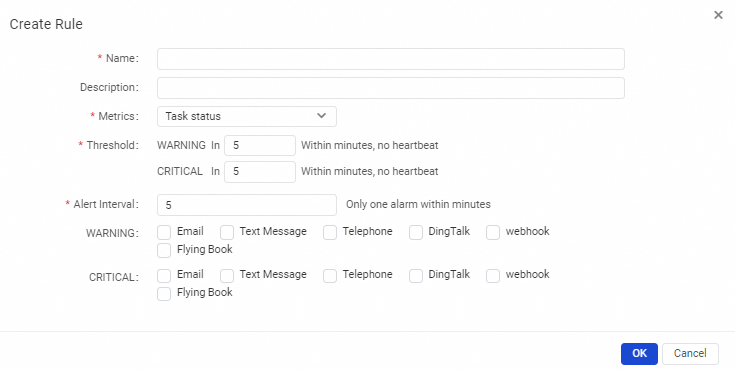
Parameter
Description
Required
Parameter
The name of the alert rule.
Yes
Description
The description of the alert rule.
No
Metrics
The type of metric that triggers an alert. The Metrics parameter and the Threshold parameter must be used in pairs. The value of the Threshold parameter varies based on that of the Metrics parameter. Valid values: Task status, Business delay, Failover, Not Supported by DDL Statements, DDL Notification, and Dirty Data.
Yes
Threshold
The thresholds for the metrics that are specified by the Metrics parameter.
If you set the Metrics parameter to Task status, you must specify the interval at which alerts are triggered.
If you set the Metrics parameter to Business delay, you must specify a duration for the business latency and another duration during which an alert can last after the duration for the business latency elapses.
If you set the Metrics parameter to Not Supported by DDL Statements, you need to only select an alert level.
For a task that is run in non-distributed execution mode, if you set the Metrics parameter to Failover, you must specify a duration and the maximum number of failovers that can be performed within the duration before an alert is triggered. For a task that is run in distributed execution mode, if you set the Metrics parameter to Failover, you must specify a duration and the maximum number of failovers that can be performed for a slice of the task within the duration before an alert is triggered.
Yes
Alert Interval
The minimum interval at which alerts are reported. Default value: 5. Minimum value: 1. Unit: minutes.
Yes
WARNING
The method used to receive a notification for a WARNING-level alert. Valid values: Email, Text Message, and DingTalk.
NoteEmail: If you want to use a RAM user to receive the notification, you must use an Alibaba Cloud account to add the email address of the RAM user in user information.
Text Message: If you want to use a RAM user to receive the notification, you must use an Alibaba Cloud account to add the mobile phone number of the RAM user in user information.
DingTalk: If you want to receive the notification by using a DingTalk chatbot, you must configure a DingTalk chatbot for your DingTalk group and add the keyword DataWorks for the DingTalk chatbot.
No
CRITICAL
The method used to receive a notification for a CRITICAL-level alert. Valid values: Email, Text Message, and DingTalk.
No
Receiver (Non-DingTalk)
The alert contact to whom alert notifications are sent.
Yes