This topic describes how to create a workflow, create nodes in the workflow, and configure dependencies. After the workflow is created, you can use the data development feature to analyze and compute data in the workspace.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have created the business data table bank_data and the sink table result_table in the workspace. The business data table must contain data. For more information, see Create tables and upload data.
Background information
The DataWorks data development feature uses workflows to process data and manage dependencies. You can set node dependencies by dragging and dropping them within a workflow. You can create multiple workflows in a workspace. For more information, see Create a workflow.
Create a workflow
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Development.
On the page, move the pointer over the
 icon and click Create.
icon and click Create.In the Create Workflow dialog box, enter the Workflow Name and Description.
Click Create.
Create nodes and configure dependencies
Create a zero load node (start) and an ODPS SQL node (insert_data) in the workflow. Then, configure the dependency so that insert_data depends on start.
A zero load node is a control node that does not affect any data during workflow execution. It is used only for Operations and Maintenance (O&M) control over its descendant nodes.
If other nodes depend on a zero load node and an O&M engineer manually sets the zero load node to failed, its unexecuted descendant nodes will not be triggered. During O&M, this prevents incorrect upstream data from propagating.
In a workflow, the ancestor node of a zero load node is usually the workspace root node. The workspace root node uses the format
Workspace Name_root.DataWorks automatically adds an output for each node using the structure Workspace Name.Node Name. If two nodes in a workspace have the same name, you must modify the output of one of the nodes.
Create a zero load node as the root node to control the entire workflow. Design the workflow as follows:
Double-click the workflow name to go to the development panel. Click General > Zero-Load Node.
You can also drag the Zero-Load Node to the development panel on the right.
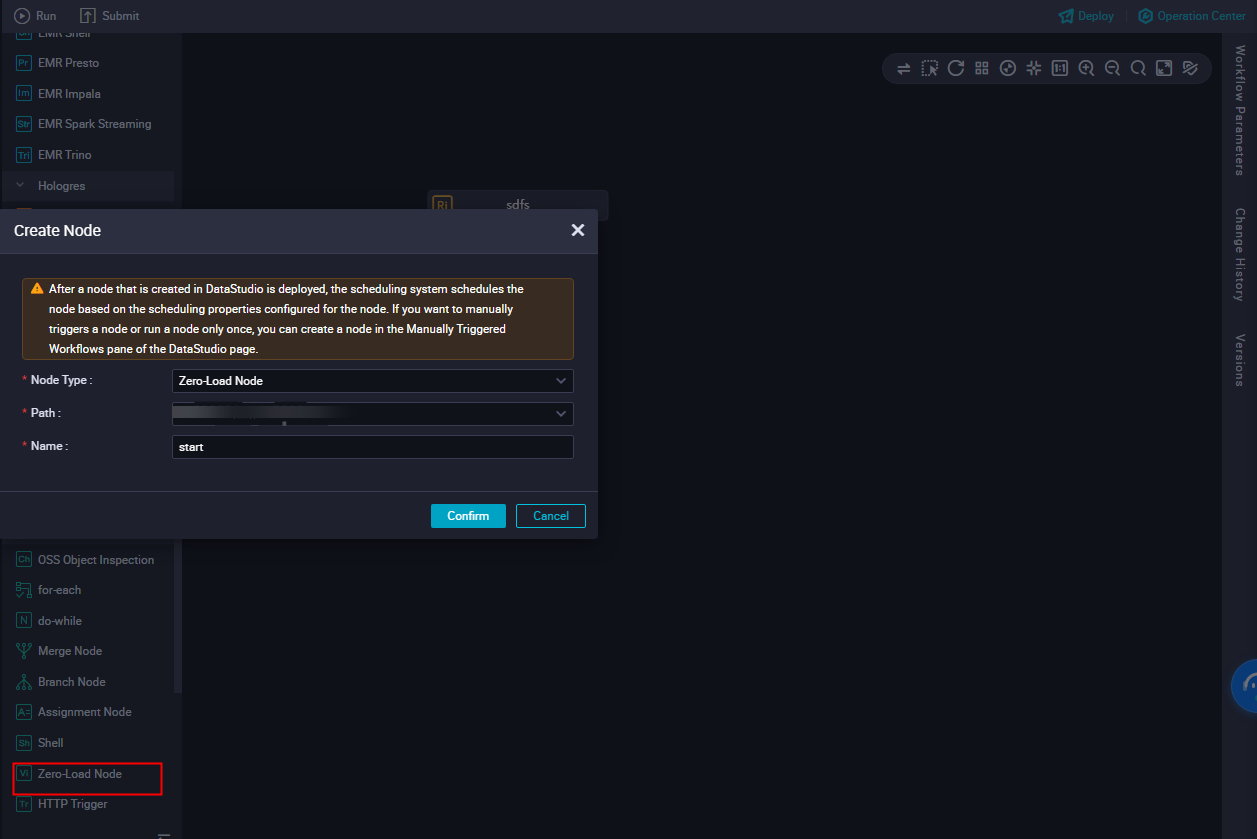
In the Create Node dialog box, select a Path, enter start for Name, and click Confirm.
Use the same method to create an ODPS SQL node and name it insert_data.
Drag a line to set the start node as the ancestor node of the insert_data node.
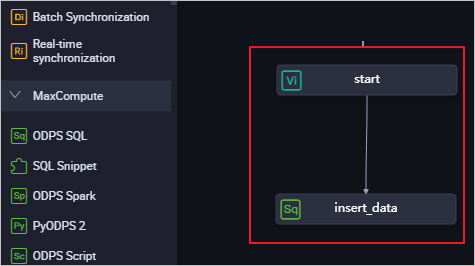
Configure the upstream dependency of the zero load node
In a workflow, a zero load node typically acts as the controller for the entire workflow and is the ancestor node of all other nodes in the workflow.
The root node typically serves as the upstream node of the zero load node:
Double-click the zero load node name to open the node's edit page.
On the right side of the node's edit page, click Properties.
In the Dependencies area, click Add Root Node to set the workspace root node as the ancestor node of the zero load node.

Save and commit the node.
ImportantConfigure the Rerun and Parent Nodes properties for the node before you commit it.
Click the
 icon in the toolbar to save the node.
icon in the toolbar to save the node.Click the
 icon in the toolbar.
icon in the toolbar.In the Submit dialog box, enter a change description.
Click Confirm.
Edit and run the ODPS SQL node
This section describes how to use SQL code in the insert_data ODPS_SQL node to query the number of single people with home loans at various education levels and save the results. These results can then be used by descendant nodes for further analysis or display.
Open the editor for the ODPS SQL node and enter the following code.
For more information about the syntax, see SQL overview.
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE result_table -- Insert data into the result_table table. SELECT education , COUNT(marital) AS num FROM bank_data WHERE housing = 'yes' AND marital = 'single' GROUP BY education;Right-click bank_data in the code and select Delete Input.
The bank_data table created in Create tables and upload data is not generated by a periodically scheduled node. If a node selects data from such a table, you can right-click the table name in the code editor and delete the input. You can also add a rule comment at the top of the code. This prevents the automatic parser from identifying this dependency.
 Note
NoteScheduling dependencies in DataWorks ensure that a node can obtain the table data that is regularly updated by its scheduled ancestor nodes. This ensures that downstream data retrieval is correct. Therefore, the platform cannot monitor tables that are not updated by the DataWorks scheduling system. If a node uses a select statement to query data from a table that is not generated by a periodically scheduled node, you must manually delete the ancestor node dependency that is automatically generated by the select statement.
Click the
 icon in the toolbar to save your code.
icon in the toolbar to save your code.Click the
 icon.
icon.After the code runs, you can view the run log and results at the bottom of the page.
Commit the workflow
After you run and debug the ODPS_SQL node insert_data, return to the workflow page.
Click the
 icon.
icon.In the Commit dialog box, select the nodes to commit, enter a change description, and choose whether to Ignore I/O Inconsistency Alerts.
Click Confirm.
After the workflow is committed, you can view the commit status of the nodes in the node list under Business Flow. If the
 icon appears to the left of a node name, the node is not committed. If the
icon appears to the left of a node name, the node is not committed. If the  icon is present, the node is committed.
icon is present, the node is committed.
What to do next
You have learned how to create and commit a workflow. You can continue to the next tutorial, where you will learn how to create a sync task to write data to different types of data sources. For more information, see Create a sync task.