This topic introduces how to use cross-node parameters through two typical scenarios.
Scenarios
Cross-node parameters have two typical application scenarios:
A financial enterprise needs to convert currencies for daily scheduled tasks and settle daily investment returns in US dollars. The daily closing exchange rates are extracted from the business system and synchronized to an offline table. Multiple scheduled tasks involve currency conversion, which requires the exchange rate corresponding to the data timestamp. You can write a program to read the exchange rate as an output node task and output the exchange rate as a cross-node parameter. The node tasks that need the exchange rate can then reference this cross-node parameter as input nodes.
A retail distribution enterprise needs to query a supplier's service daily to confirm whether the product catalog has changed. If changes are detected, the latest catalog data needs to be pulled in full (which is costly because of the large data volume). If no changes are detected, the previously pulled data continues to be used. You can write a program to detect whether the product catalog has changed in an output node task and output the update status of the product catalog as a cross-node parameter. At the same time, you can set the node that pulls and synchronizes the product catalog as an input node, which is scheduled based on the value of the cross-node parameter (conditional scheduling).
Example 1: Exchange rate conversion
Data structure
Exchange rate table exchange_rate_table, the table schema and sample data are as follows.
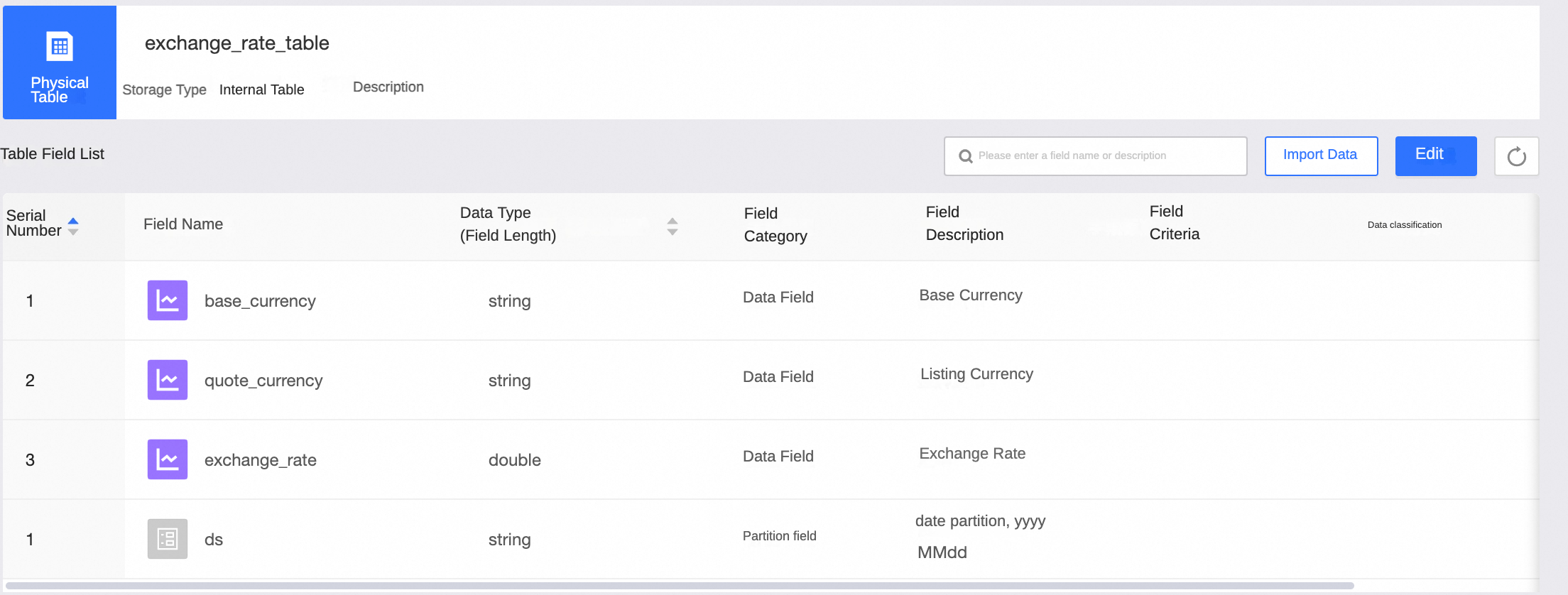
Output node
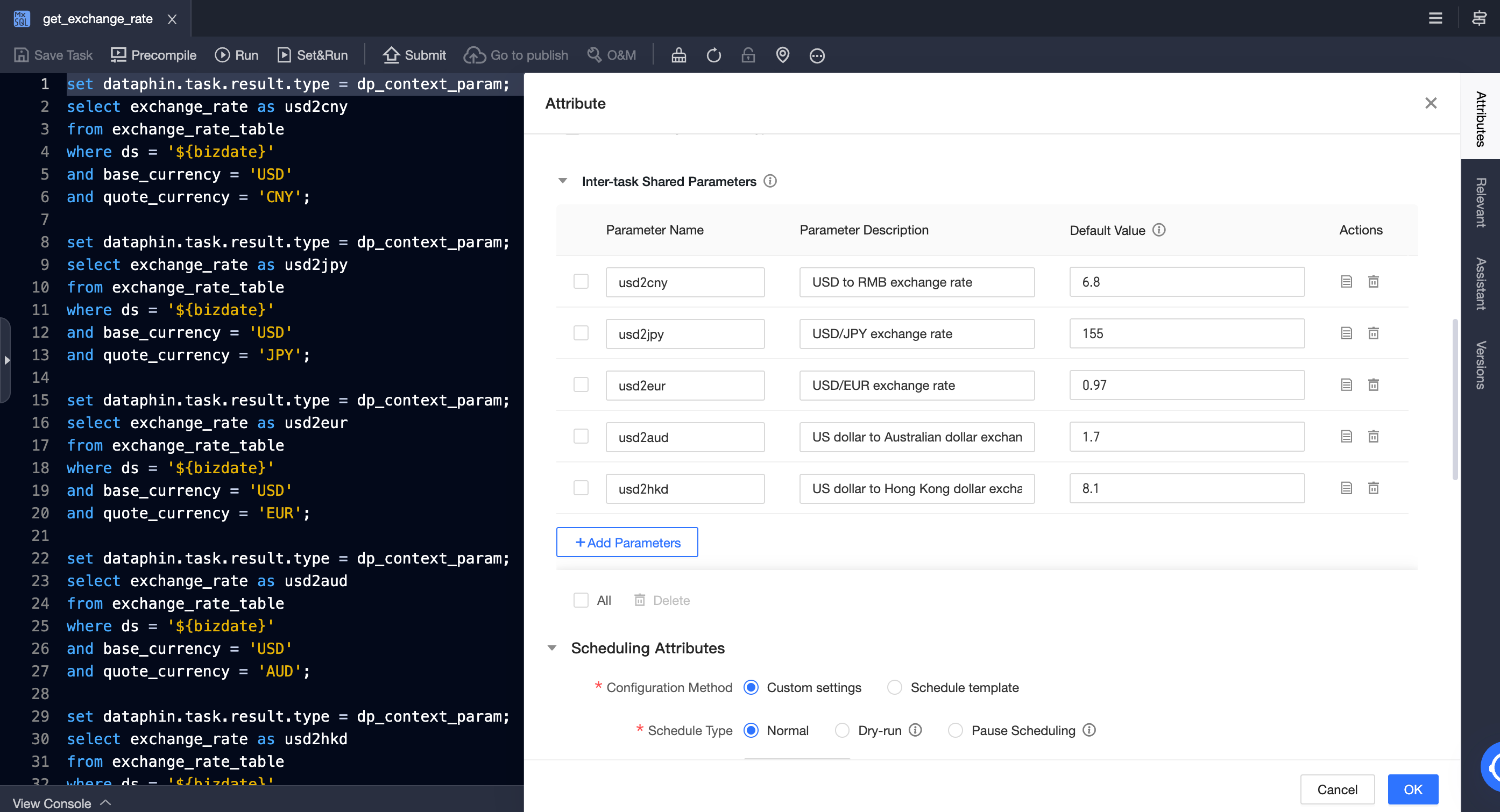
Create a MAX_COMPUTE_SQL task
get_exchange_rate, and define the cross-node output parameterusd2cny.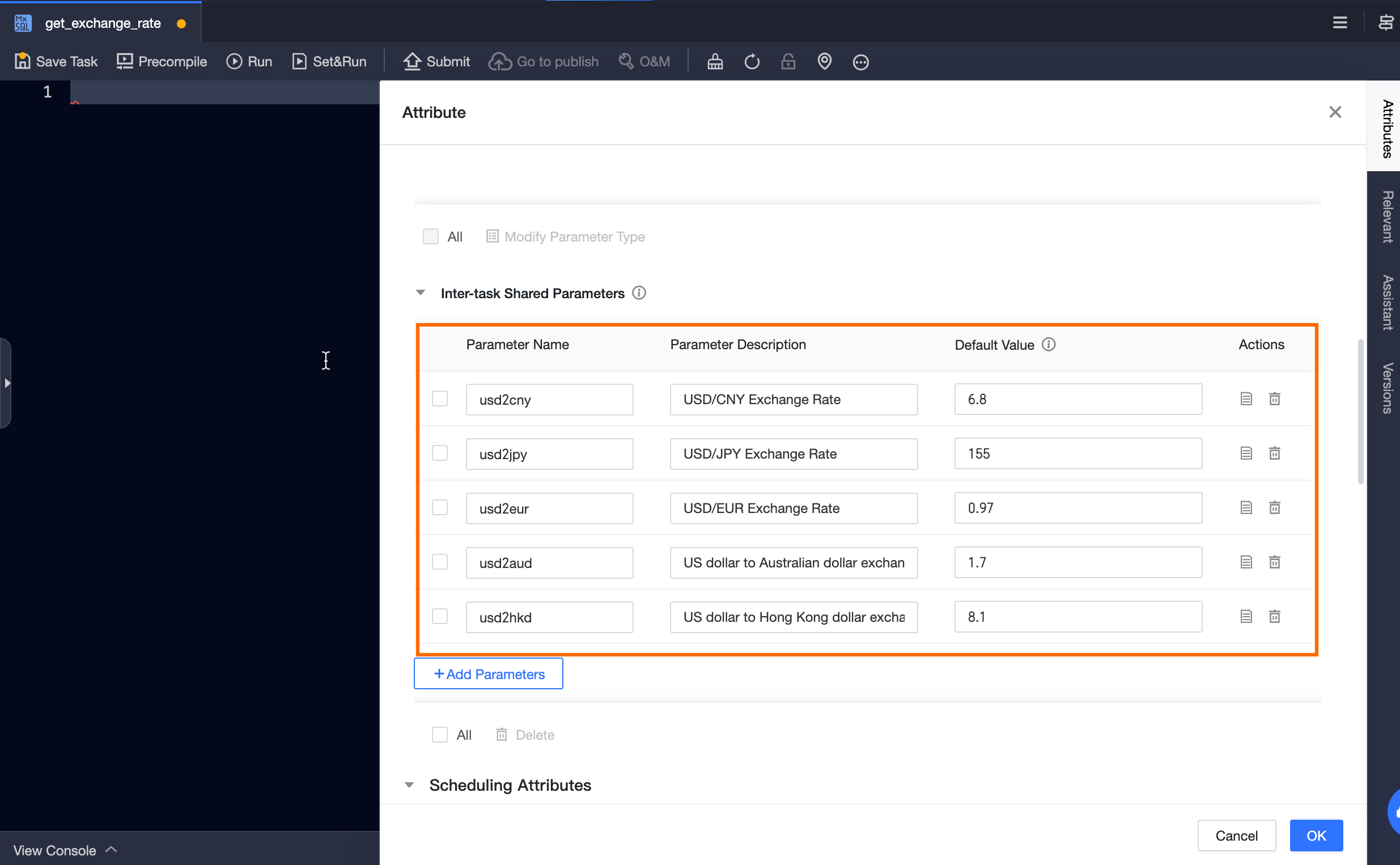
In the task editor, right-click and select Set Cross-node Parameters.
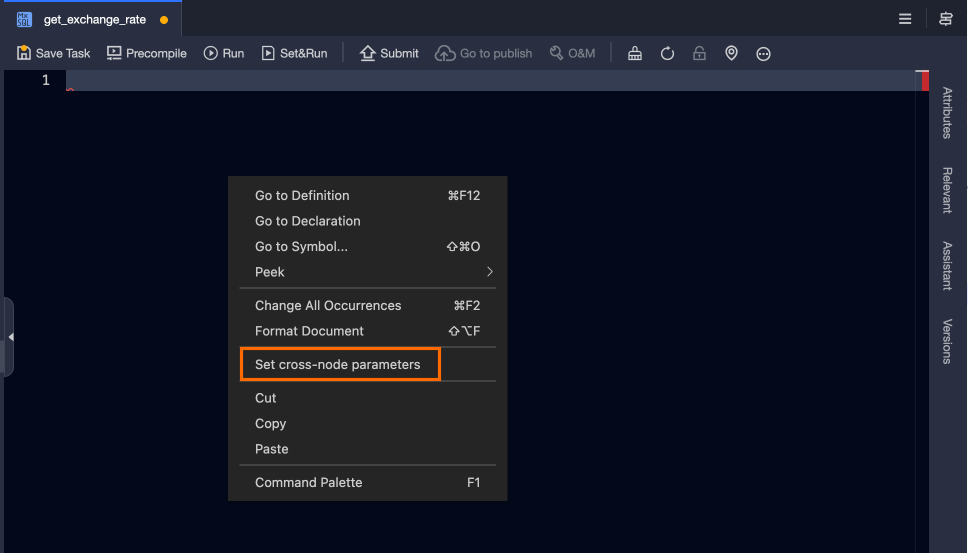
The task editor will automatically prompt the defined cross-node output parameters.
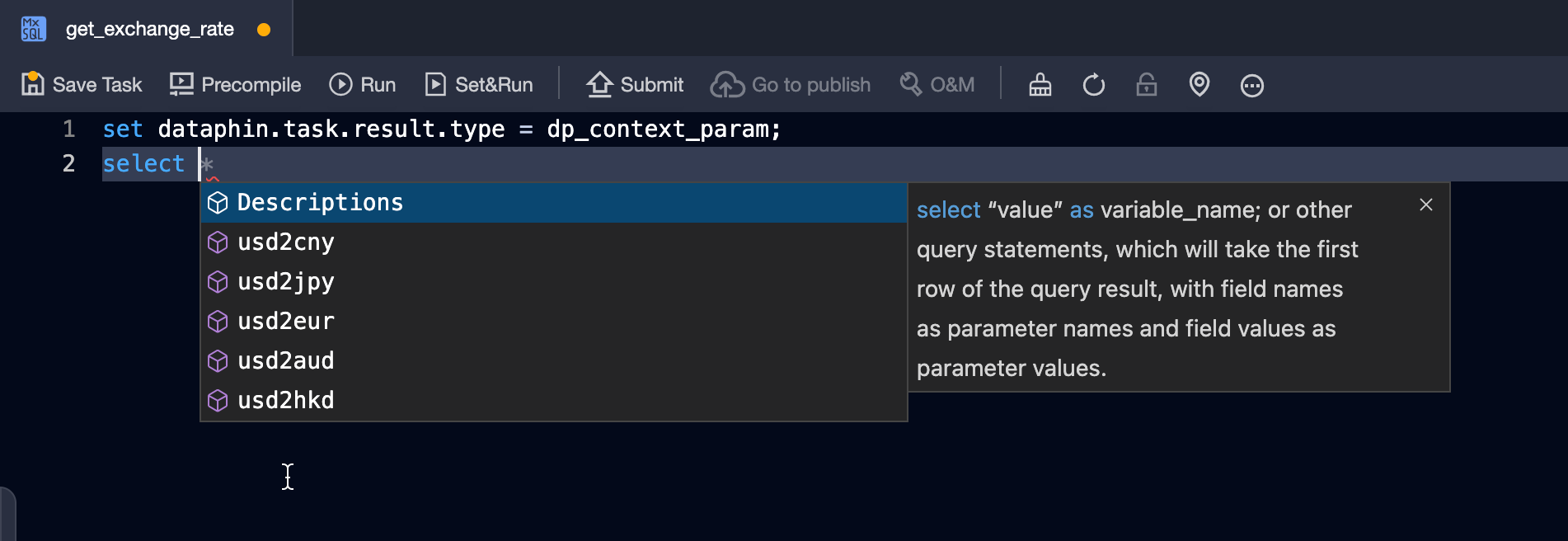
Set the alias of a field to the name of the cross-node output parameter. The system will automatically assign the value of the corresponding field in the first row of the query result to the cross-node parameter.
NoteFor SQL tasks, if multiple statements output cross-node parameters, the
setstatement before each statement cannot be omitted.There are two SQL writing methods in this example:
One separate SQL for each cross-node parameter.
Using a single statement.
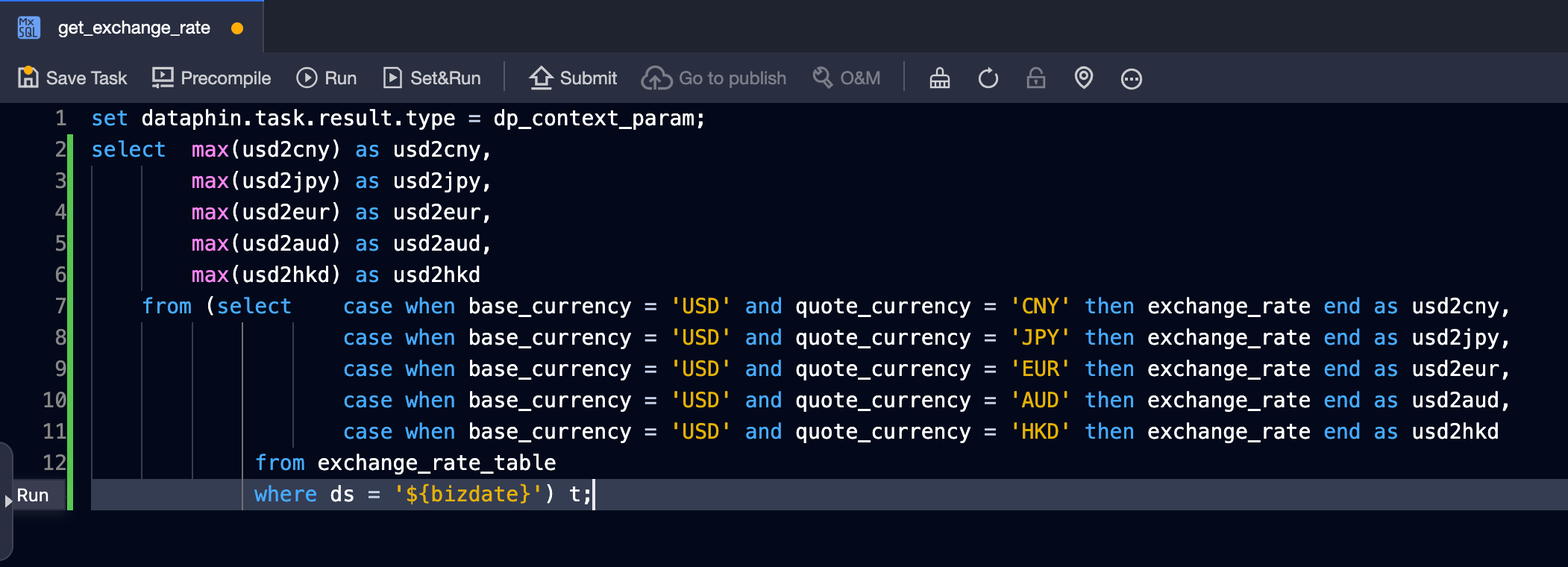
Submit the task.
Input node
Create an SQL task
exchange_usd_to_cnywith the following sample code. At the same time, add the output nodeget_exchange_rateas an upstream node.-- Convert 10000 USD to CNY, JPY, EUR, AUD, and HKD select 10000 * ${usd2cny_rate}, 10000 * ${usd2jpy_rate}, 10000 * ${usd2eur_rate}, 10000 * ${usd2aud_rate}, 10000 * ${usd2hkd_rate};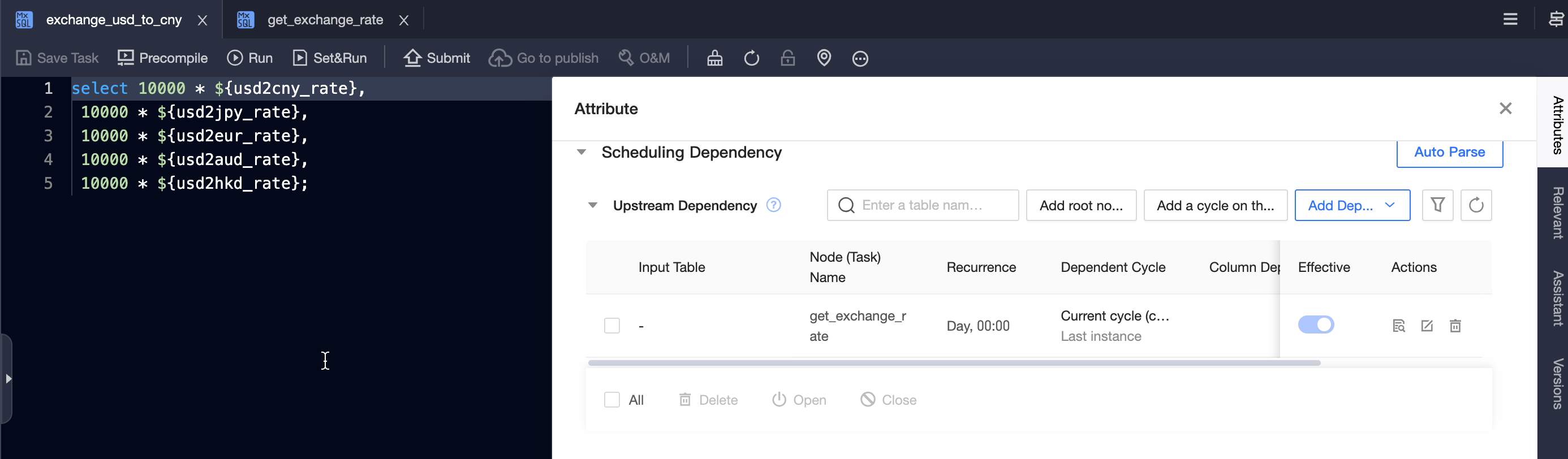
Change the type of the identified variable parameters to Cross-node Variable.
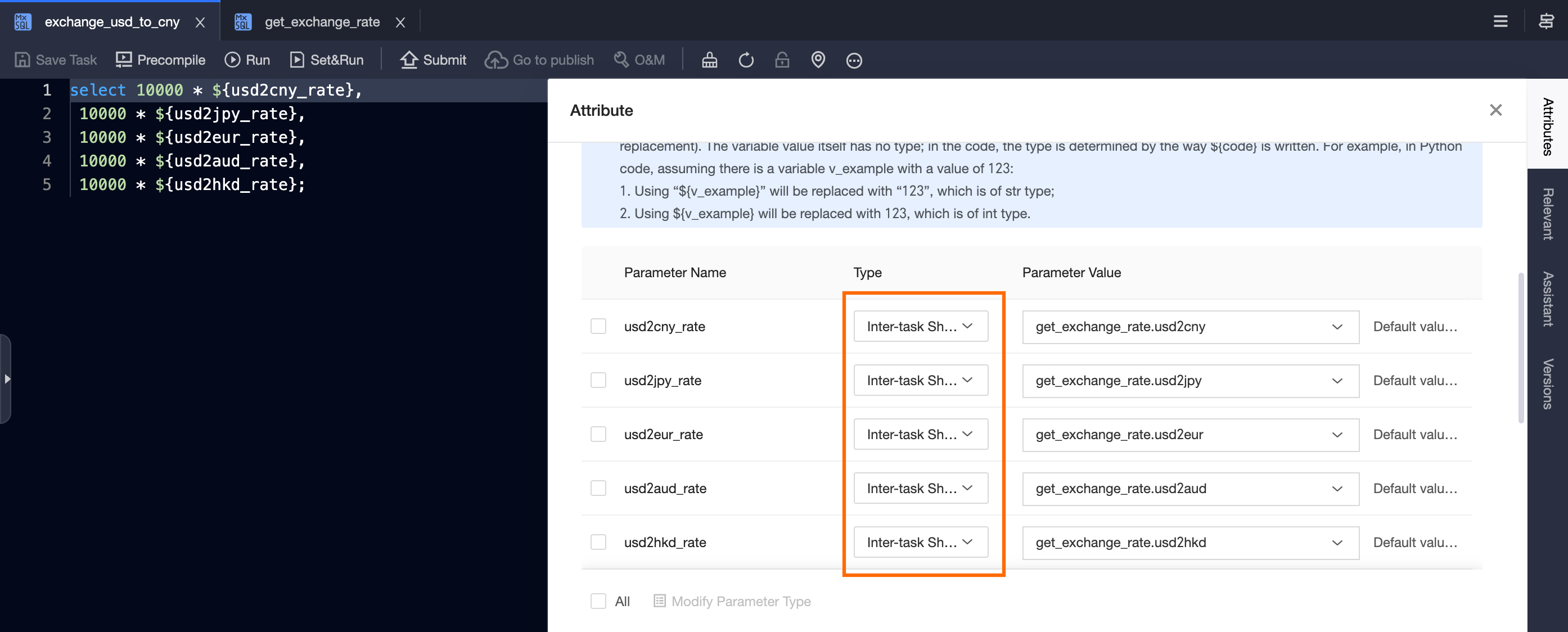
Select the corresponding cross-node output parameter of
get_exchange_ratein the parameter value of each cross-node variable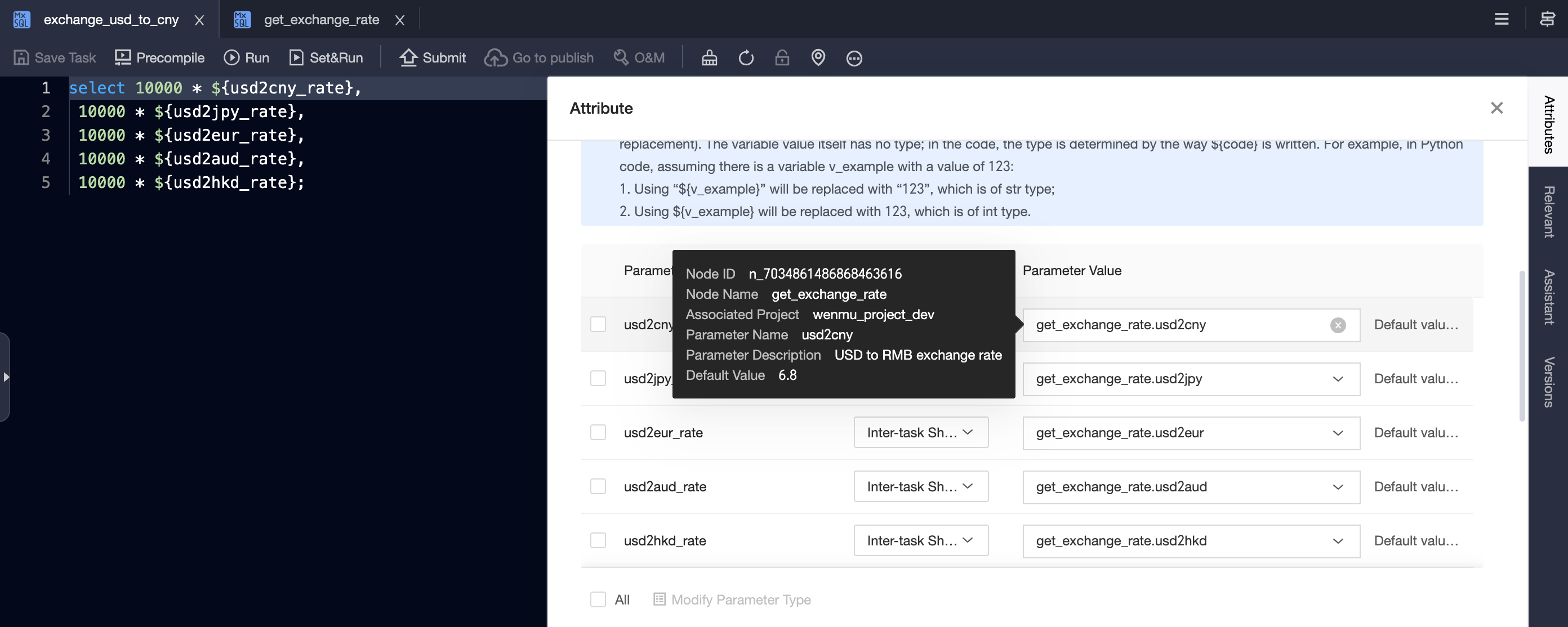
Data backfill
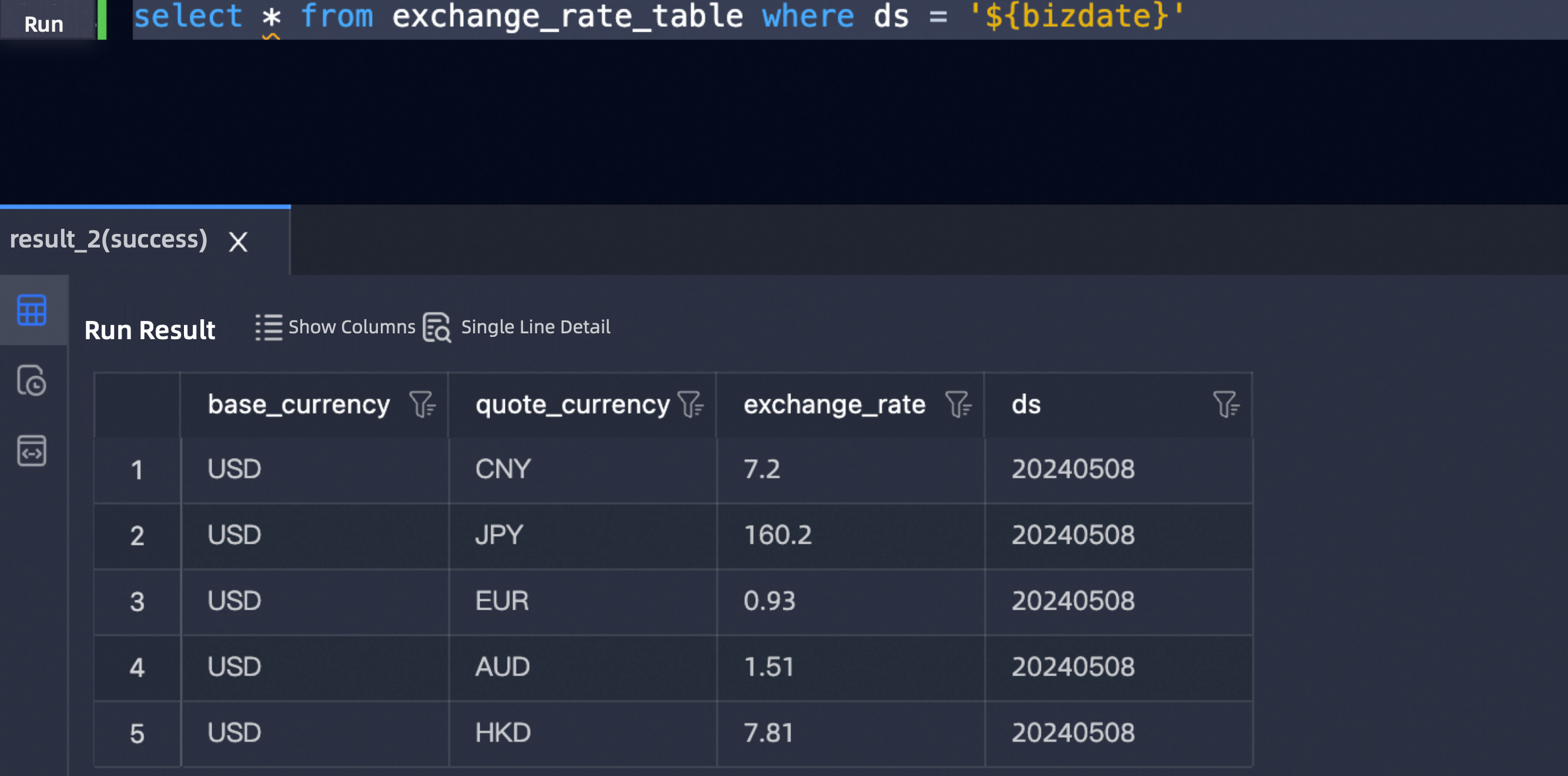
Confirm the exchange rate for the current day in the table.
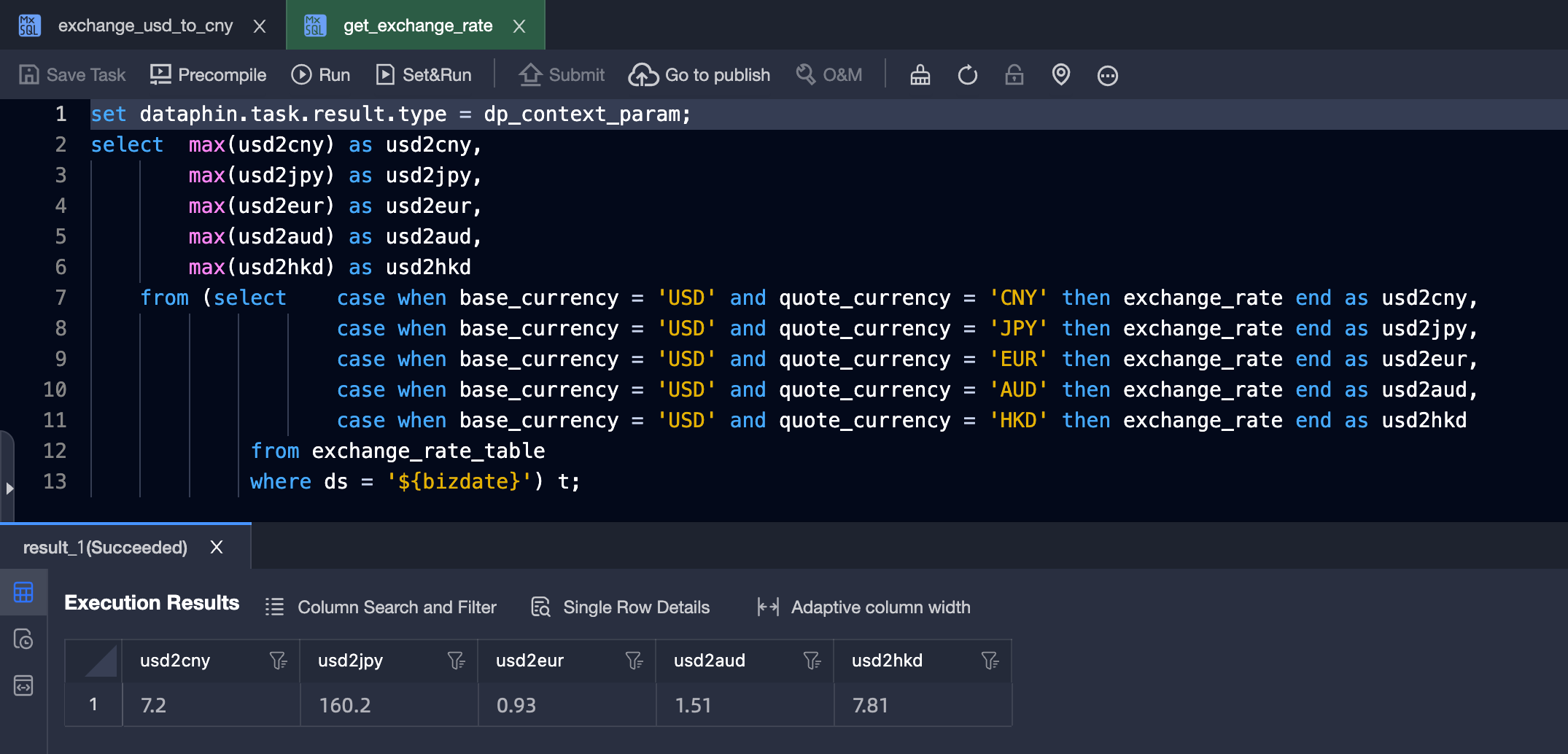
Go to the Operations Center, click Data Backfill in the
get_exchange_ratenode, select Backfill Current And Upstream/downstream Tasks, and select the downstreamexchange_usd_to_cnyto backfill data together.NoteWhen backfilling data for input nodes, you must also backfill the output nodes. Otherwise, the input nodes will use the default values of the cross-node parameters.
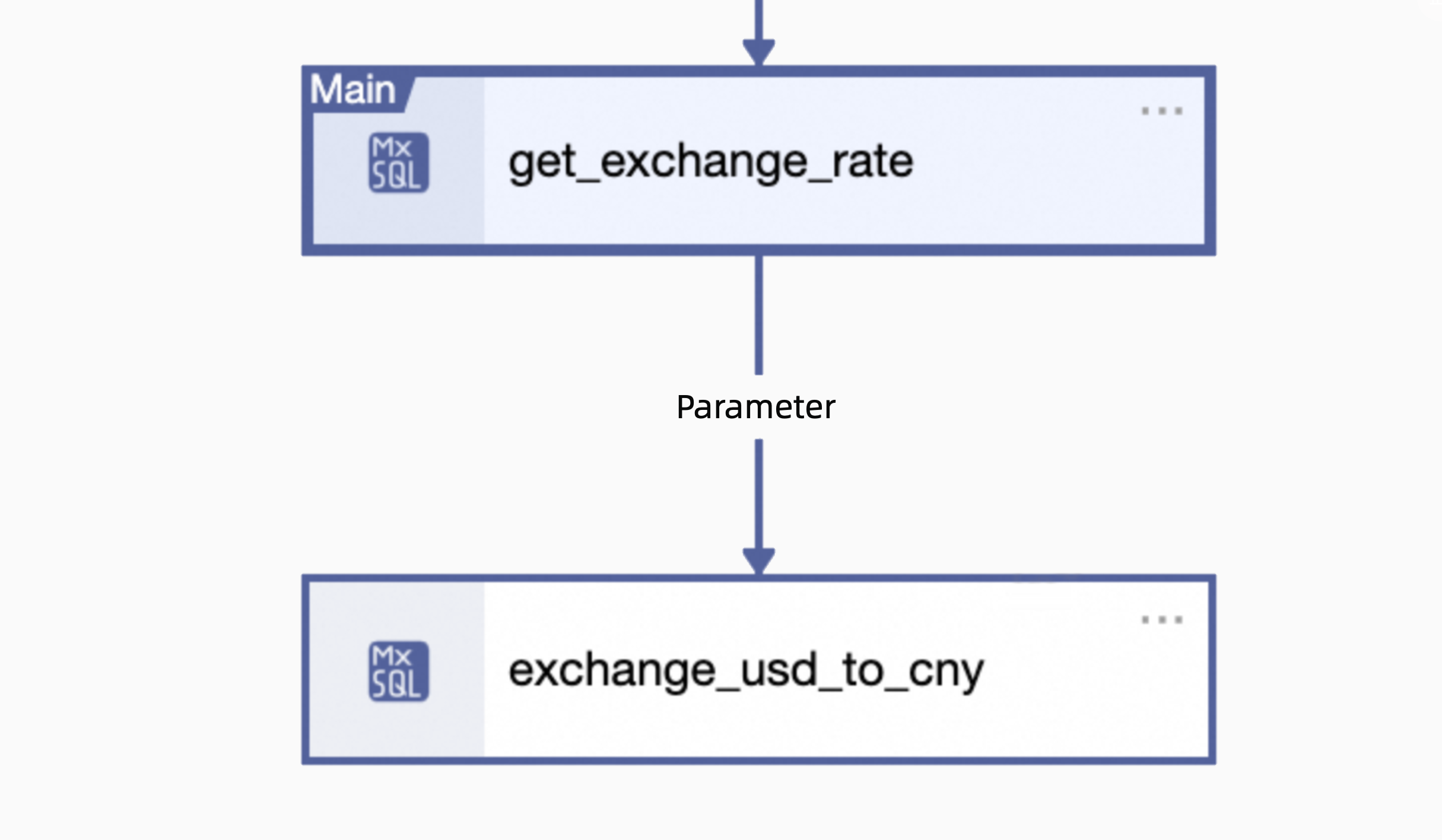
The runtime log of
exchange_usd_to_cnyis as follows. You can see that the system reads the data from the table, assigns it to the cross-node output parameters, and passes it to the downstream task.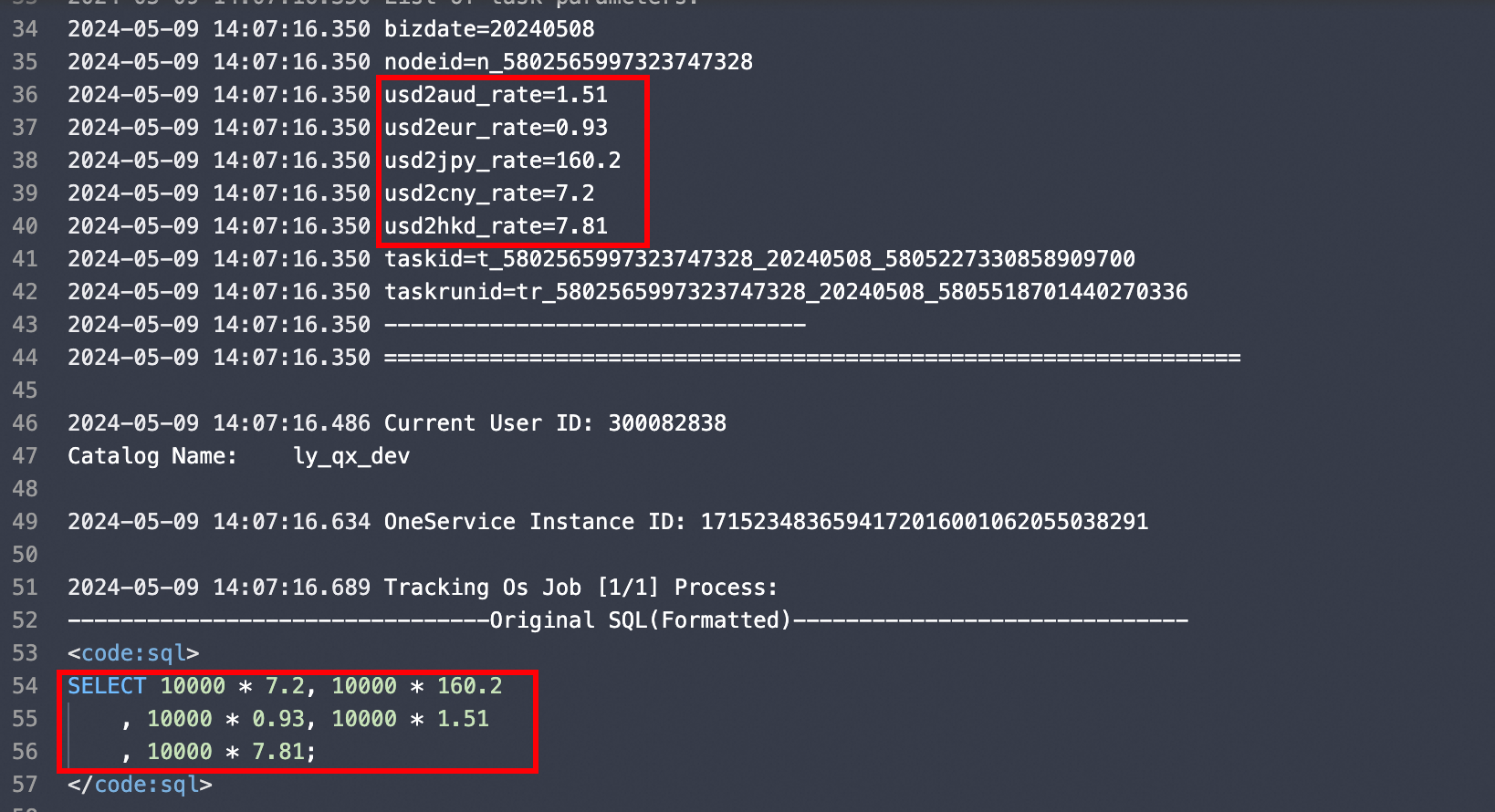
Example 2: Confirming update status
Output node
Create an analog Python task to detect update status, and add the cross-node output parameter
update_status.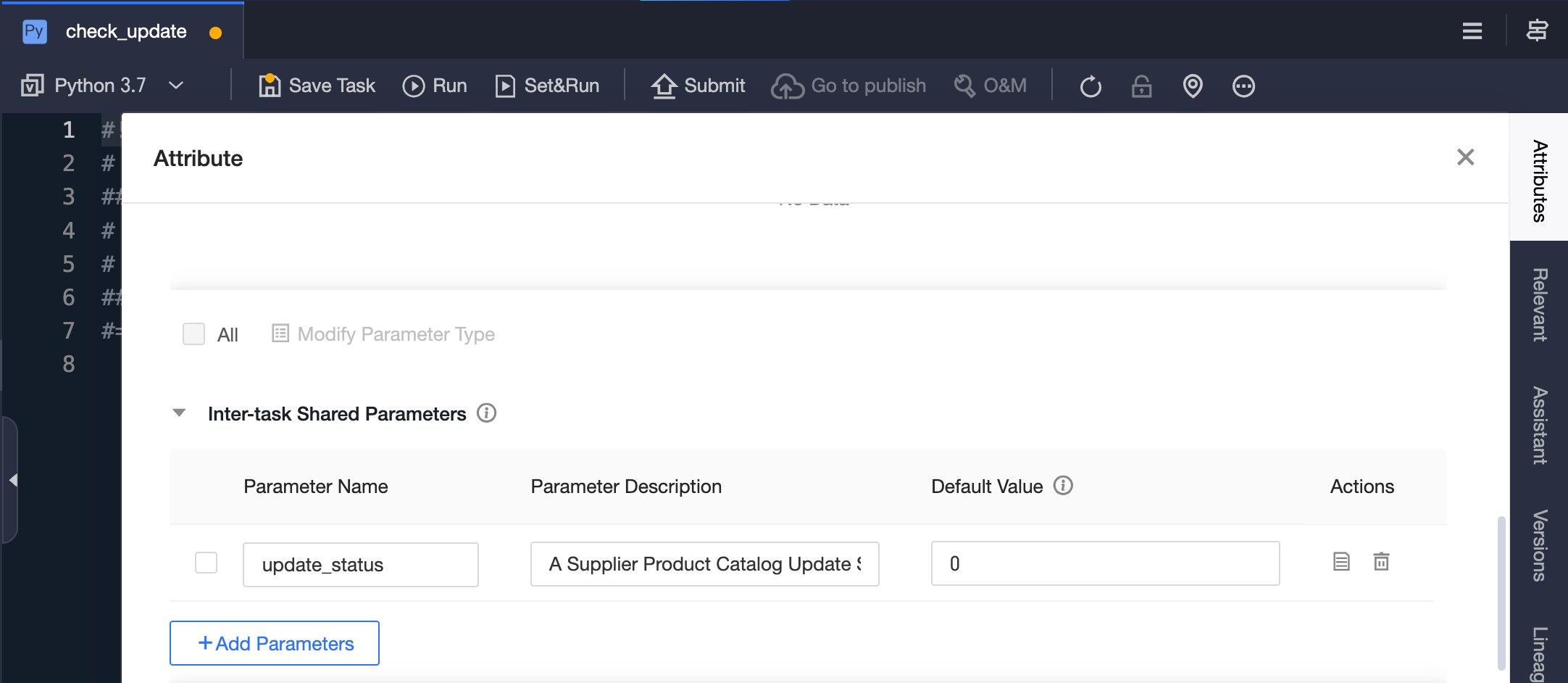
Enter the code, using a random function to return the status. Right-click, select Set Cross-node Parameters, and then submit the task.
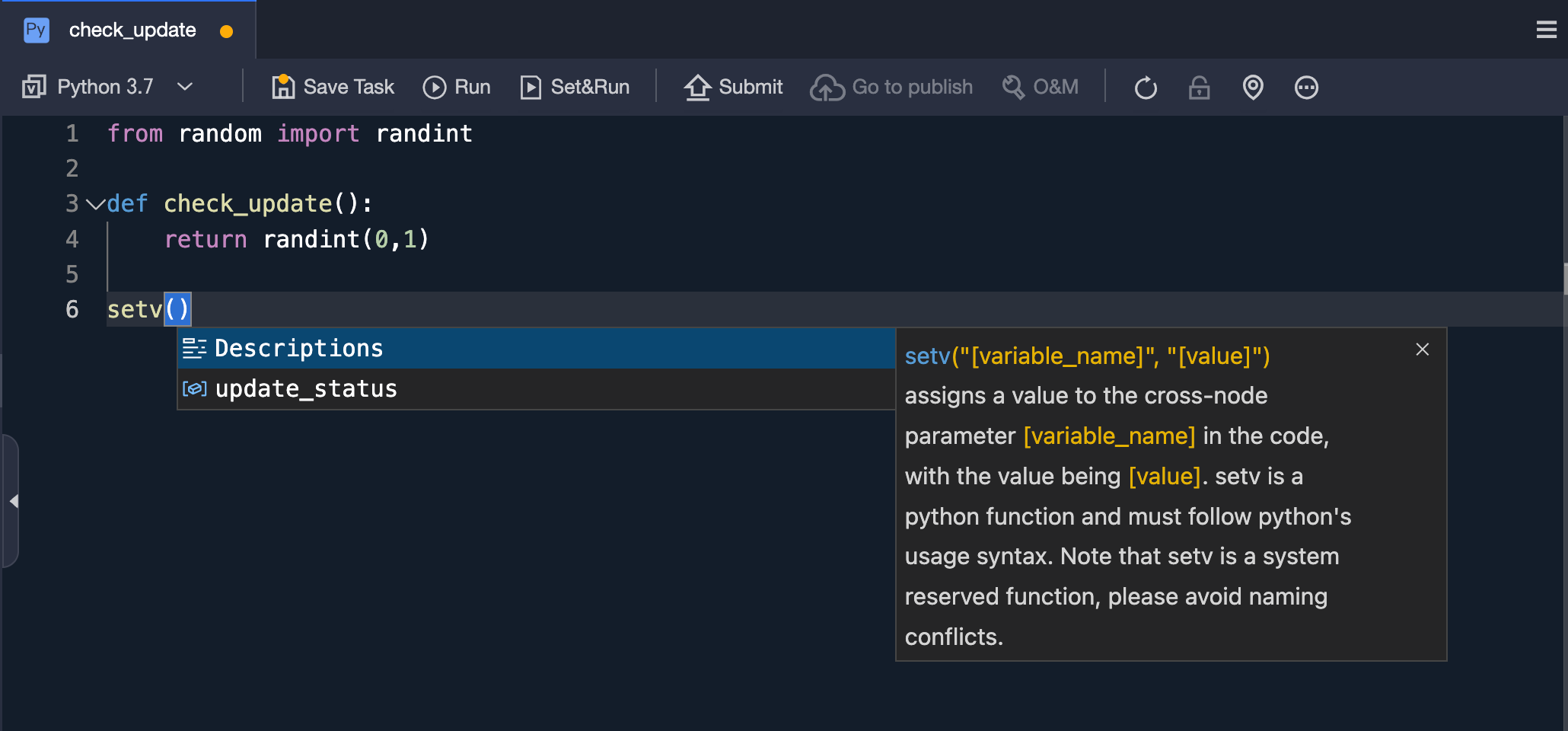
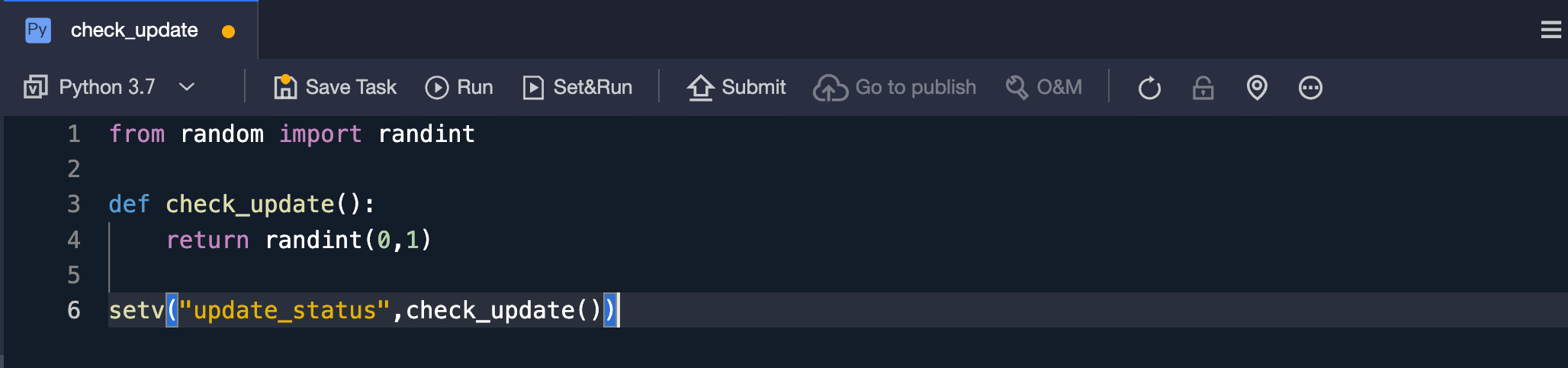
from random import randint def check_update(): return randint(0, 1) setv("update_status", check_update())
Input node
Create an offline pipeline task
imp_product_catalog, and addcheck_updateas its upstream task.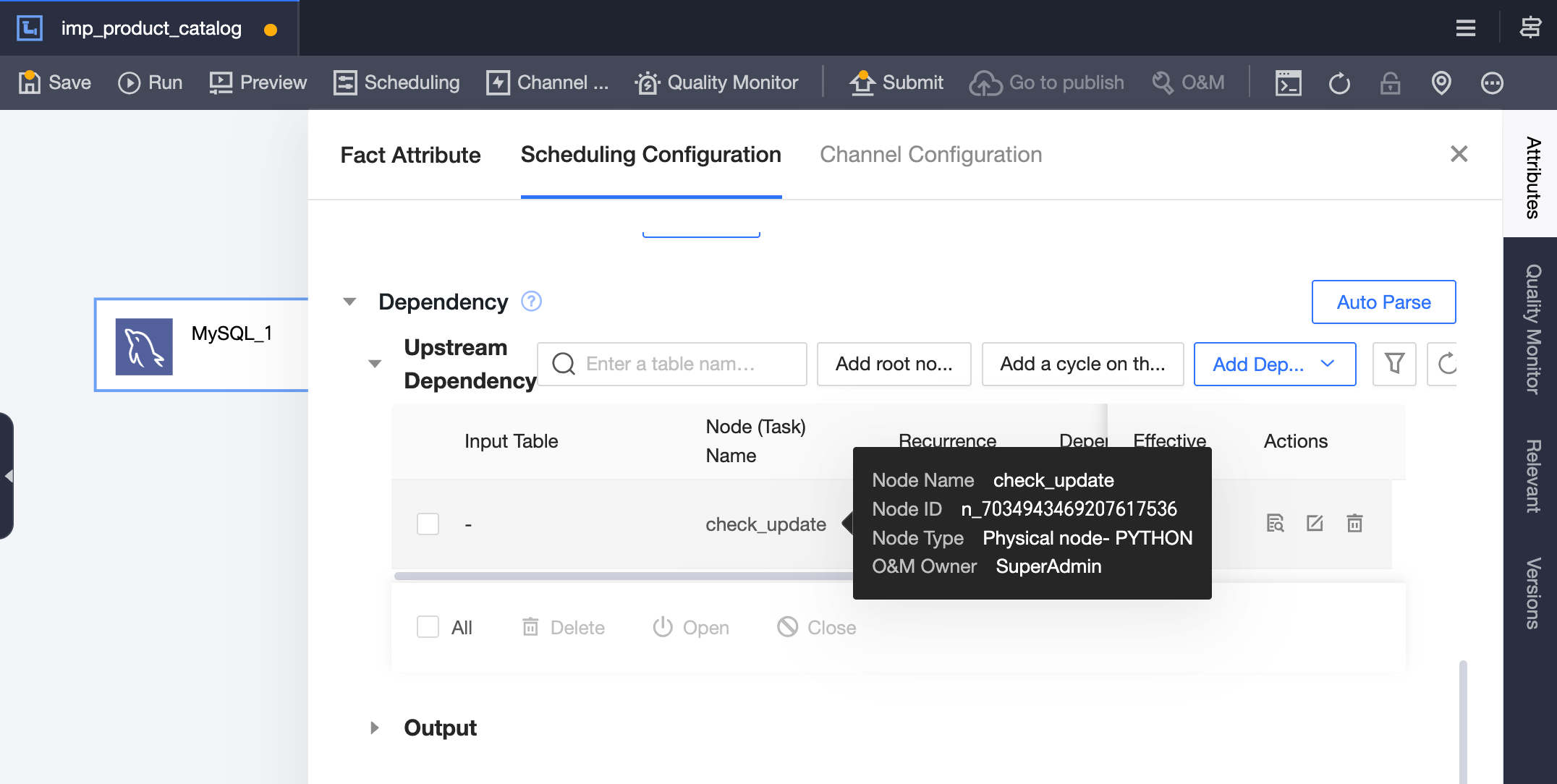
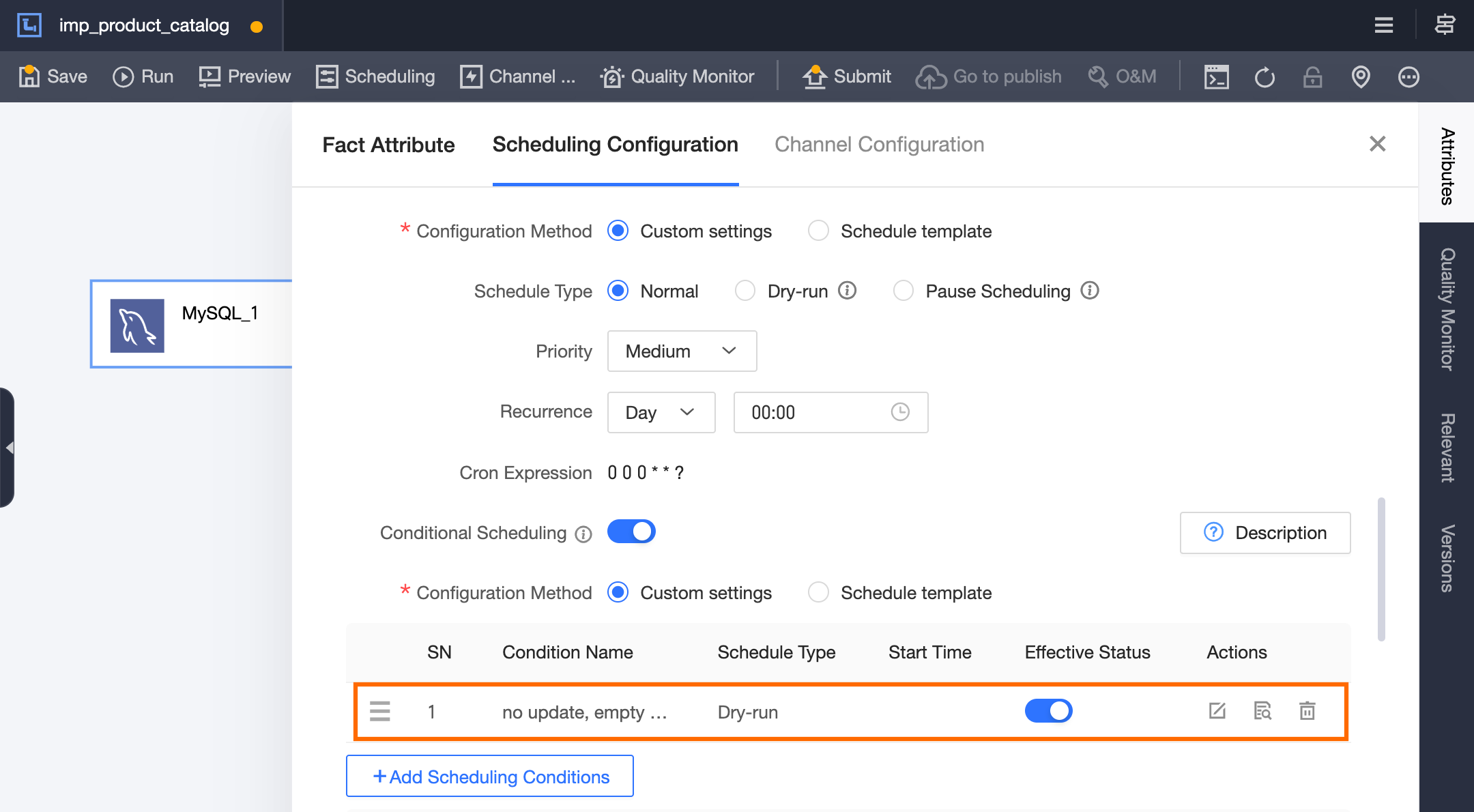
Enable conditional scheduling for the
imp_product_catalogtask.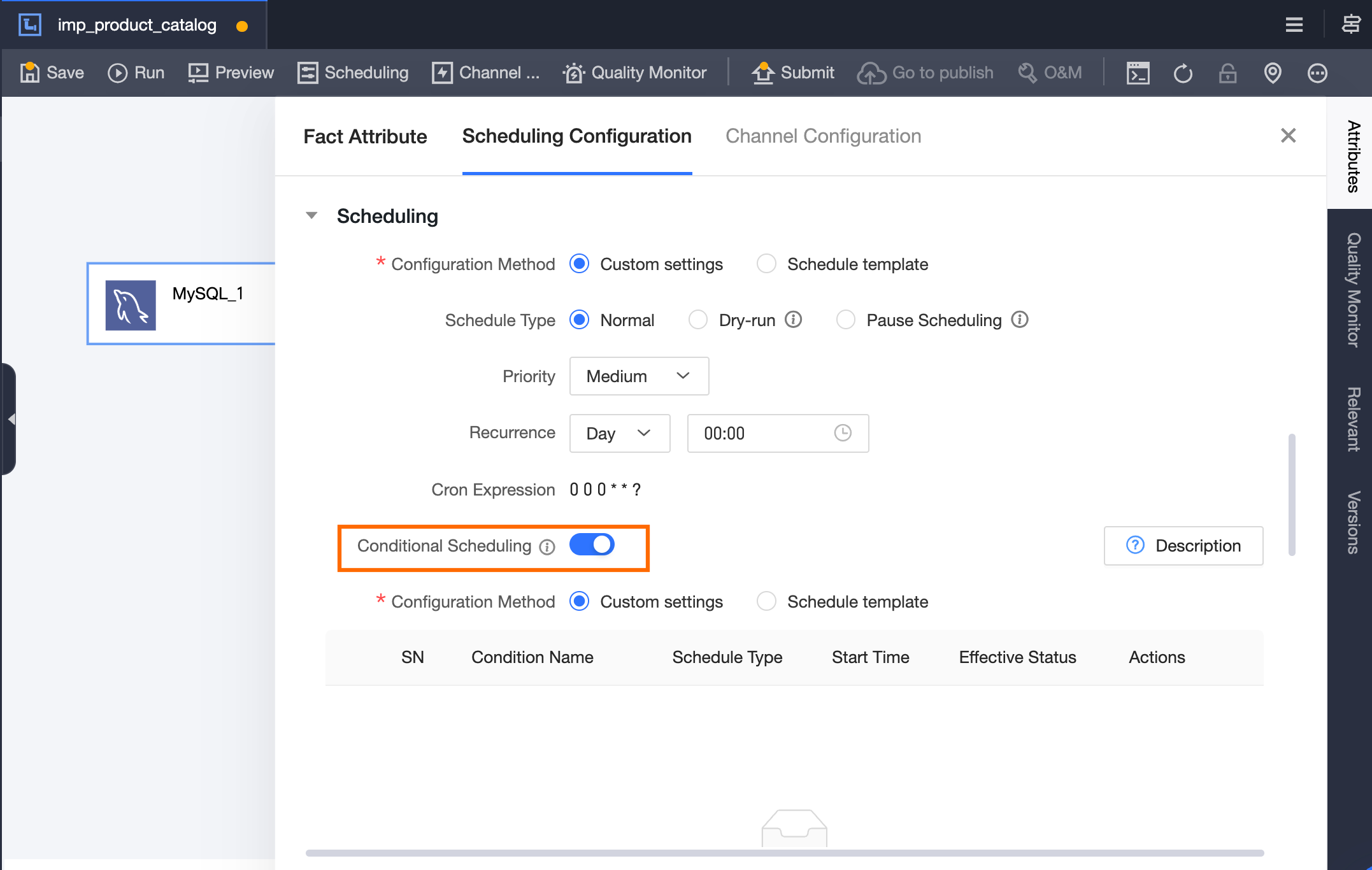
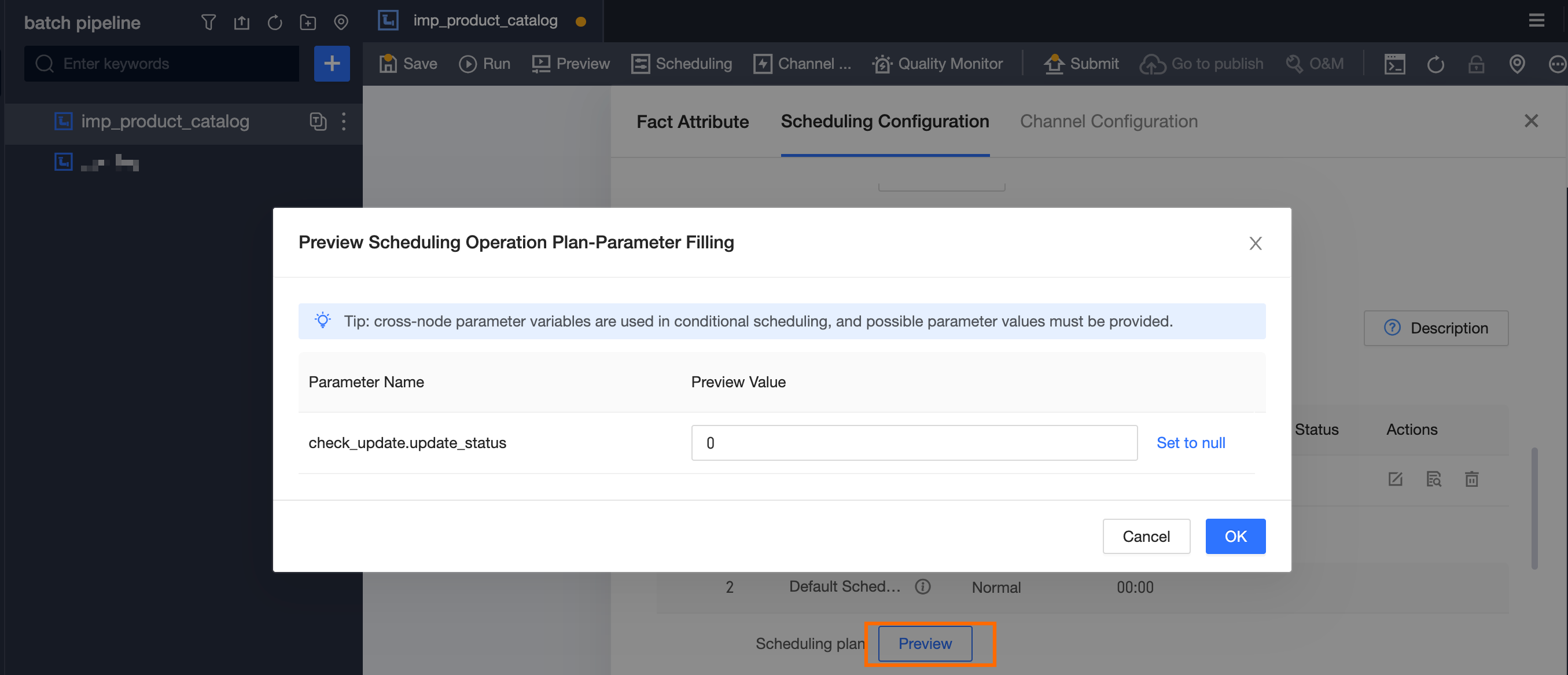
In conditional scheduling, add the condition
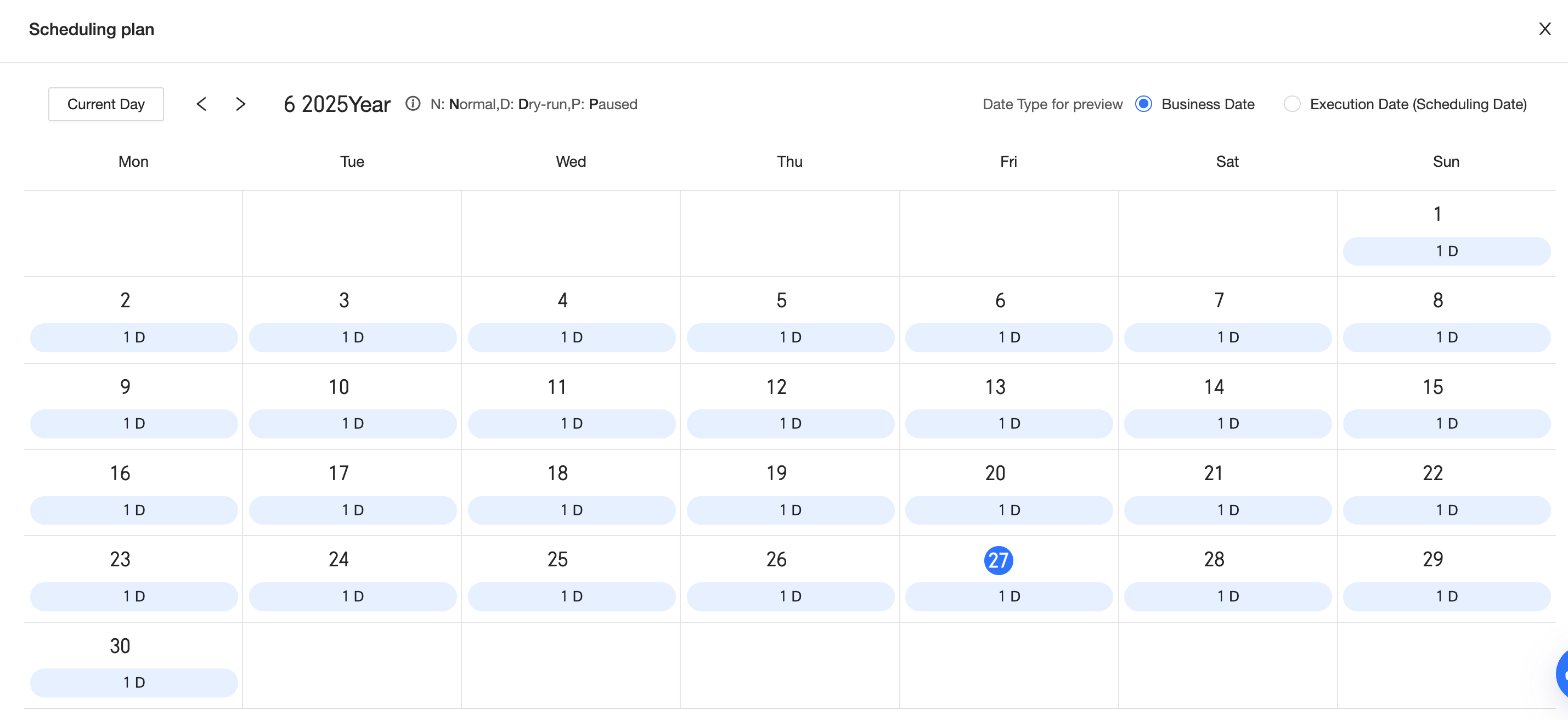
Cross-node parameter-check_update.update_status = 0(meaning no update) for dry-run scheduling. If this condition is not met, the default condition is hit (normal scheduling).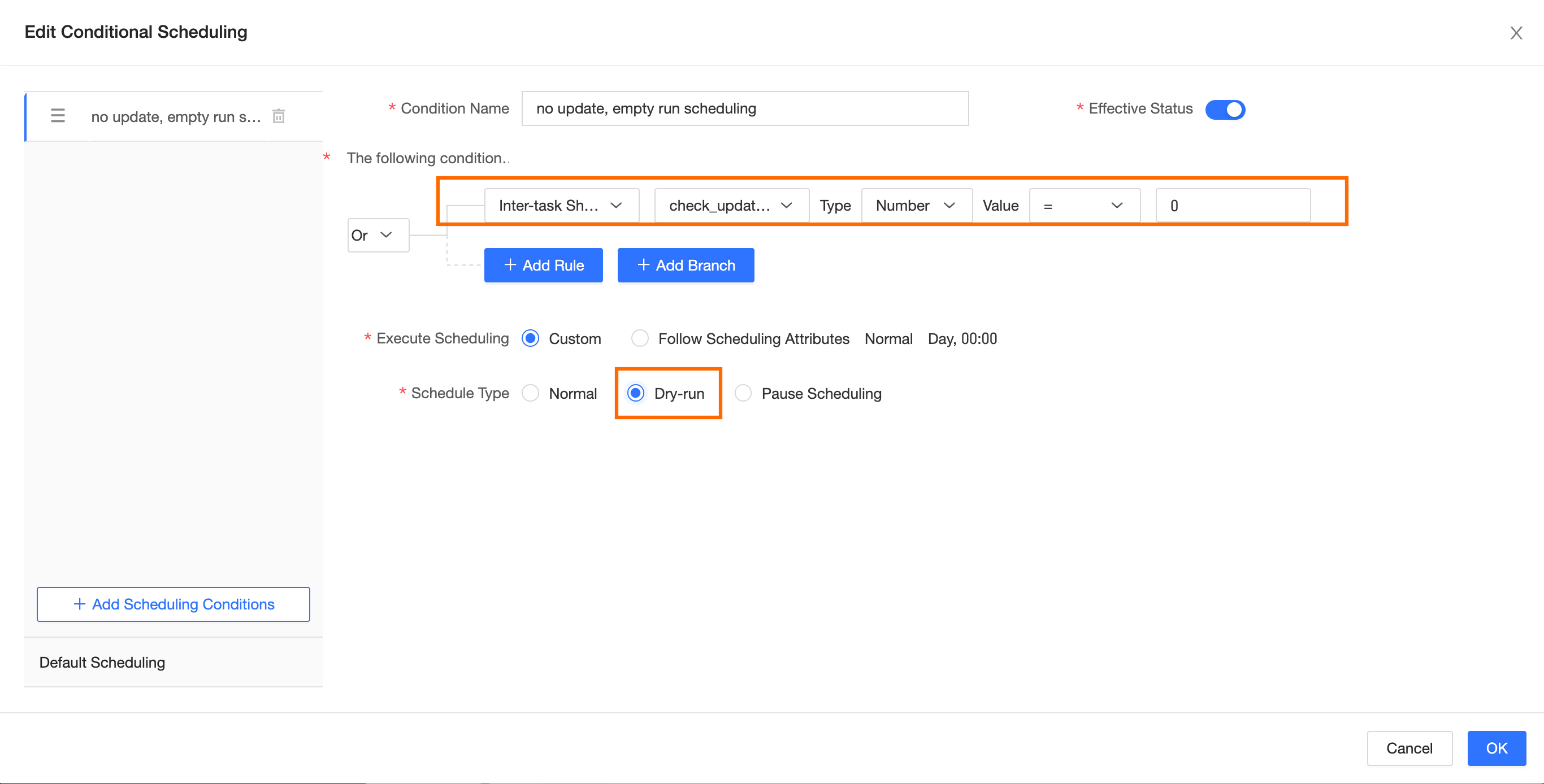
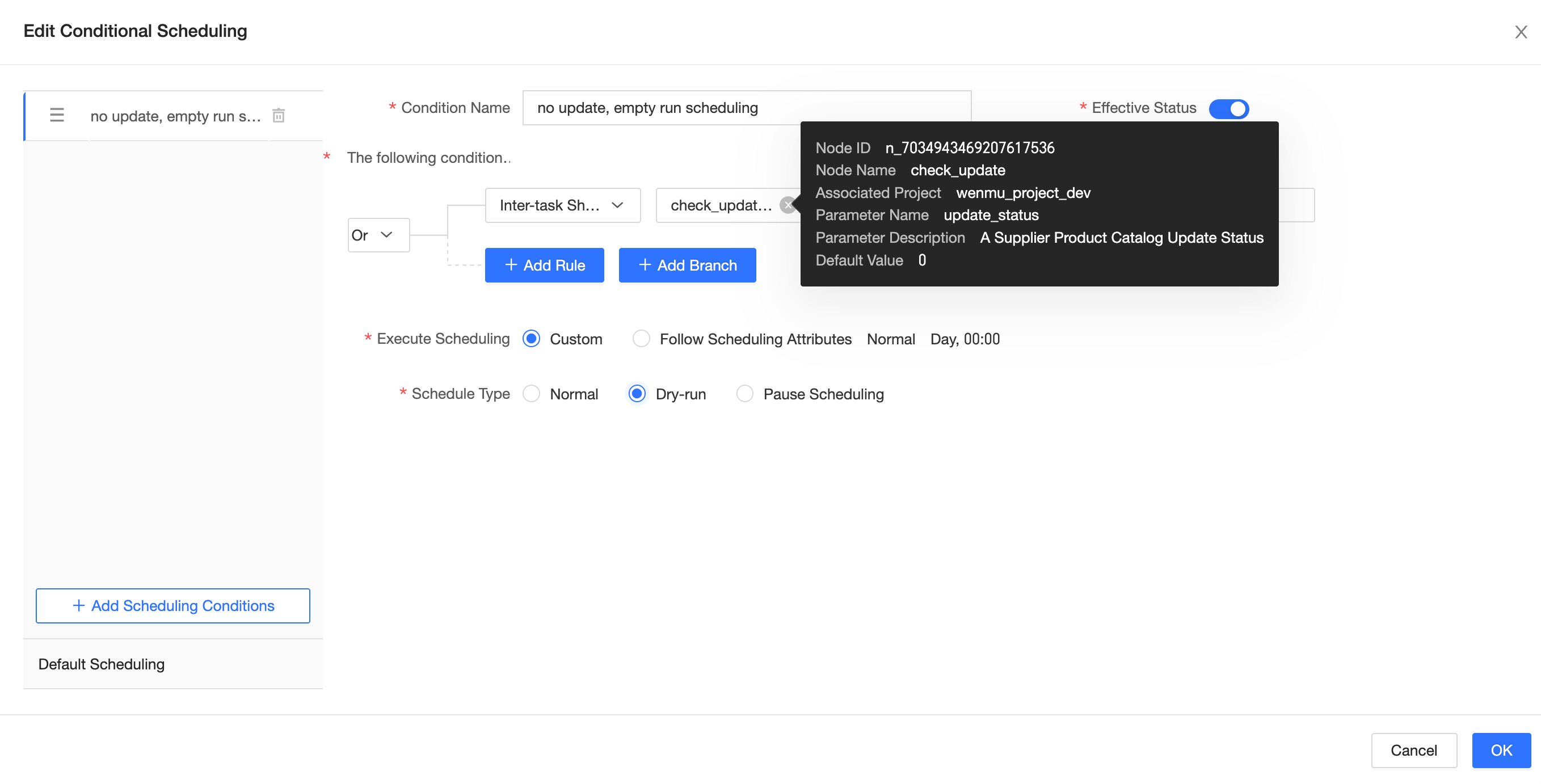
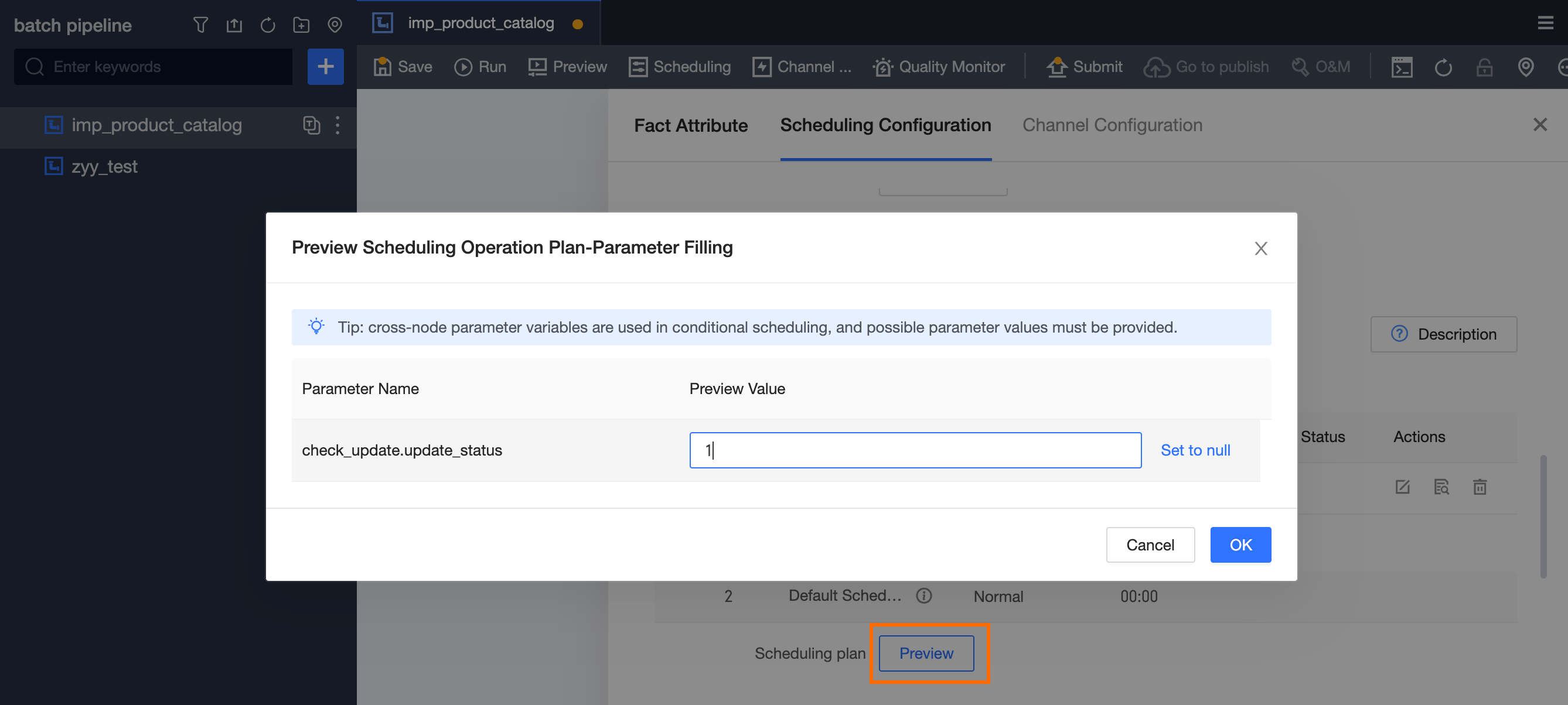
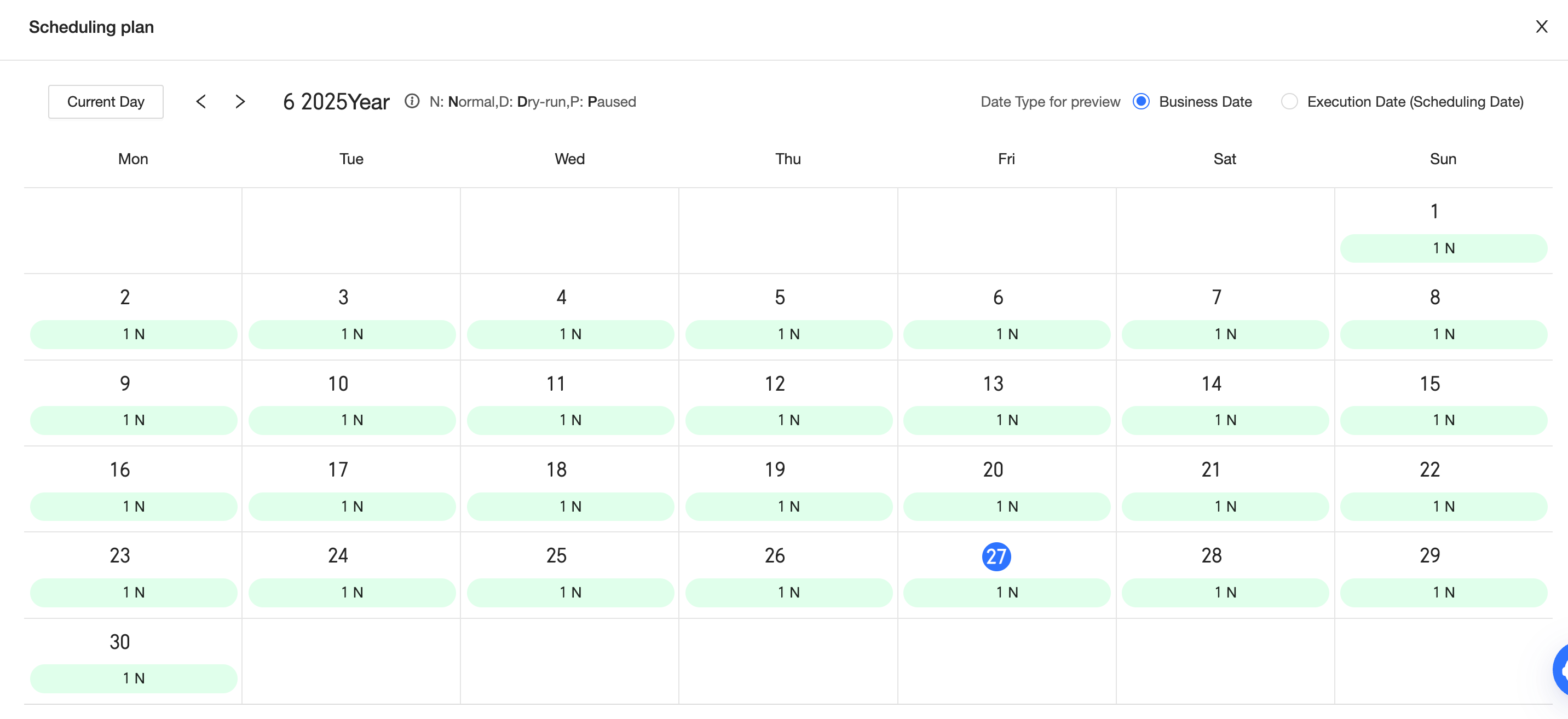
Enter different cross-node parameter values to preview the scheduling plan.