This topic describes how to configure a route between Data Transmission Service (DTS) and VPN Gateway. You must configure this route if your source or destination database is connected to Alibaba Cloud by using a VPN gateway. After you configure the route, DTS can access the network in which the source or destination database is deployed.
Prerequisites
The network in which your on-premises database is deployed is connected to Alibaba Cloud by using a VPN gateway. For more information, see Connect a VPC to a data center in single-tunnel mode.
Procedure
Log on to the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Modify the configurations of an IPsec connection.
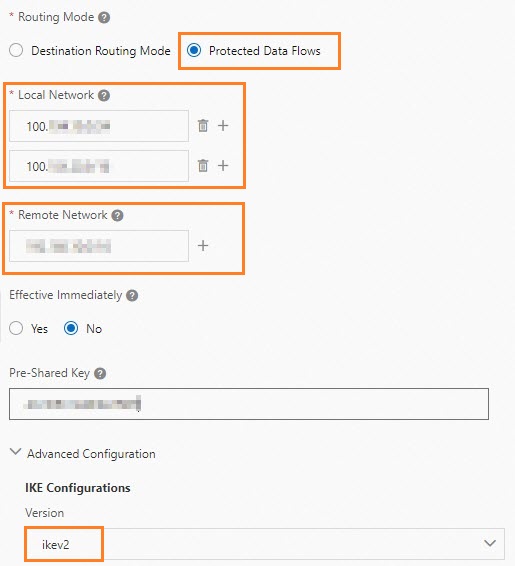
Set the Routing Mode parameter to Protected Data Flows.
Enter the CIDR blocks of DTS servers in the specified region in the Local Network field.
Enter the IP address of your data center in the Remote Network field.
Select ikev2 from the Version drop-down list in the IKE Configurations section.
NoteIf the VPN connection protocol is set to ikev1, you can enter only one CIDR block in the Local Network field. Therefore, you must set the VPN connection protocol to ikev2.
Add CIDR blocks of all DTS servers in the specified region to the Local Network field. For more information, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
Download the modified configurations of the IPsec-VPN connection and modify the configurations of the gateway device in the data center. For more information, see Step 4: Load the configuration of the IPsec-VPN connection to the gateway device in the data center.
NoteWhen you modify the VPN configurations of the gateway device in the data center, you need to add the CIDR blocks of the VPC and your data center to the VPN configurations. You do not need to add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the VPN configurations. For example, if an H3C firewall is used as the gateway device, enter the CIDR blocks of the data center and the VPC in the Source IP Address and Destination IP Address fields. You do not need to enter the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
Add a static route entry to the gateway device in the data center. The destination addresses are the CIDR blocks of DTS servers. The next hop is the new IPsec-VPN tunnel interface.
For information about how to troubleshoot the issue if an IPsec connection fails, see IPsec-VPN connection FAQ.
What to do next
When you configure data migration, data synchronization, or change tracking, select Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway as Access Method. Select the VPC that is connected to the source database from the drop-down list. You can select an on-premises database as the source or destination database. For more information, see Overview of data synchronization scenarios or Overview of data migration scenarios.