After you change the schema of a table in a database in Data Management (DMS), DMS adds the latest schema to the schema version list of the database. You can download and compare schema versions and restore an earlier schema version in the schema version list.
Background information
Schema versions are defined based on a database and store the schema information of all the tables in the database. If the schema of a table in the database is changed, a new schema version is saved. New schema versions are saved when the following operations are performed in DMS:
SQL statements are executed on the SQLConsole tab to change schemas.
SQL statements are executed to change schemas when you submit tickets for normal data modify, lock-free data change, schema design, or schema synchronization.
SQL statements are executed in SQL tasks by a DMS administrator to change schemas.
If the schema of a table in a database is changed in an environment other than DMS, you can synchronize the metadata of the database in DMS to obtain and save the latest schema. For more information, see Synchronize the data dictionary of a database instance.
If the database instance in which the database resides is managed in Security Collaboration mode, you can also click the
 icon on the SQLConsole tab to synchronize the metadata of the database.
icon on the SQLConsole tab to synchronize the metadata of the database.
Prerequisites
You have query permissions on the table or database that you want to manage.
Your database is of one of the following types:
MySQL: ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, PolarDB-X, AnalyticDB for MySQL, and OceanBase databases in MySQL mode
PostgreSQL: ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, PolarDB for PostgreSQL, and AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle)
SQL Server
MariaDB
Oracle
Limits
The following content shows the maximum number of schema versions that can be retained for each database in database instances that are managed in different control modes:
Flexible Management: 3
Stable Change: 20
Security Collaboration: unlimited
You cannot manage schema versions for the following databases:
Databases that contain more than 1,024 tables
System databases such as the information_schema and sys databases in a MySQL database instance
Procedure
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
Go to the Database version list page by using one of the following methods:
Method 1: Access from the Database Instances section on the homepage
In the left-side navigation pane of the DMS console, click Database Instances, find the database that you want to manage, right-click the database, and then select Version Management.

Method 2: Access from the SQLConsole tab
On the SQLConsole tab of the database that you want to manage, click the
 icon in the upper-right corner.
icon in the upper-right corner. 
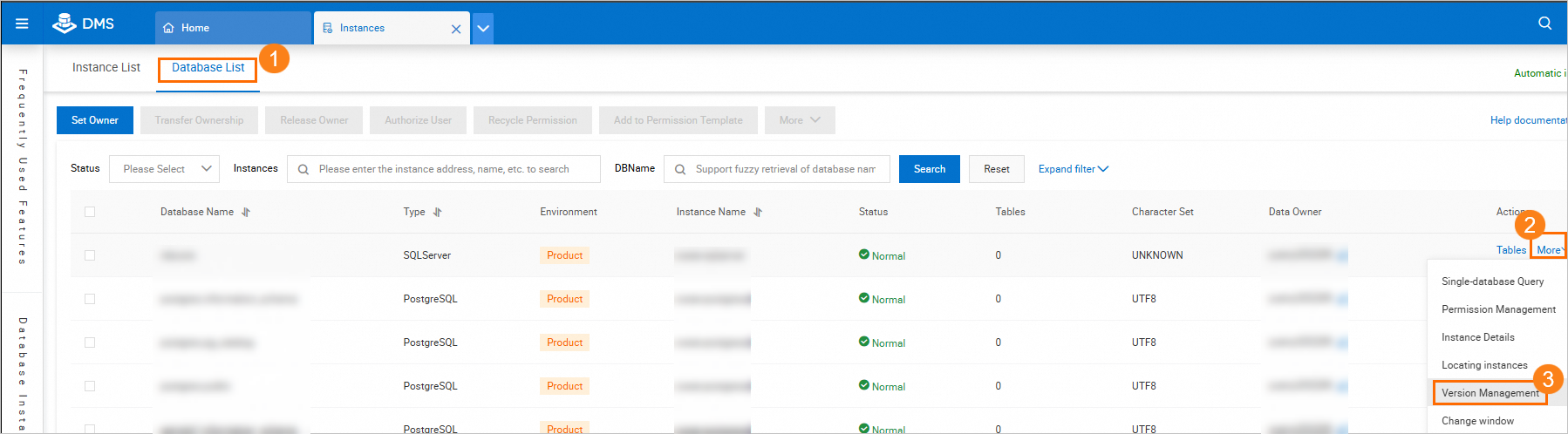
Method 3: Access from the Instances page
This method is applicable only to DMS administrators or database administrators (DBAs).
Move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . Note
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . NoteIf you use the DMS console in normal mode, choose in the top navigation bar.
In the Database List tab, find the database that you want to manage.
Choose More > Version Management in the Actions column.
On the Database version list page, find the version number of the schema that you want to manage. The following section describes the operations that you can perform:
Click Change Details to view the SQL script that is used to generate the schema version.
Click Rollback to roll back data to the previous schema version.
Select two schema versions and click Version Comparison.