Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) allows you to create volume snapshots from disks and use the volume snapshots to restore application data. This topic describes the basic terms related to volume snapshots and how to use volume snapshots in ACK clusters. This topic also describes how to dynamically and statically create volume snapshots.
Prerequisites
ACK clusters that run Kubernetes 1.18 and later support volume snapshots. To use volume snapshots that are created from disks, make sure that Kubernetes V1.18 or later is used in your ACK cluster. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster.
Log on the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console and select the region where your cluster is deployed. Make sure that the volume snapshot feature is enabled. For more information, see Activate ECS Snapshot.
Background information
When you deploy stateful applications in an ACK cluster, disks are commonly used to store application data. You can create snapshots from disks and use these snapshots to restore application data. ACK also allows you to use snapshots to back up and restore data. You can back up and restore data in your ACK cluster in the following ways:
Create backups (volume snapshots) from disks by using VolumeSnapshots.
Restore data by setting dataSource to the related persistent volume claim (PVC).
Usage notes
To enable volume snapshots, you can use CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs) to define the following resources in your ACK cluster:
Resource name | Description |
VolumeSnapshotContent | A snapshot that is created from a volume in the ACK cluster. It is created and managed by administrators. A VolumeSnapshotContent does not belong to any namespace. A VolumeSnapshotContent is a cluster resource similar to a persistent volume (PV). |
VolumeSnapshot | A request for a volume snapshot. It is created and managed by users. A VolumeSnapshot belongs to a specific namespace. A VolumeSnapshot is a cluster resource similar to a PVC. |
VolumeSnapshotClass | Specifies the attributes of a VolumeSnapshot, such as the parameters and controllers that are used to create snapshots. A VolumeSnapshotClass is a cluster resource similar to a StorageClass. |
To use volume snapshots, you must associate these resources with each other based on the following rules:
Before you can use volume snapshots, associate a VolumeSnapshot with a VolumeSnapshotContent in the same way that you associate a PV with a PVC.
After you specify a valid value in the VolumeSnapshotClassName field for a VolumeSnapshot, the ACK cluster automatically creates a VolumeSnapshotContent for the VolumeSnapshot. If you specify an invalid value or do not specify a value in the VolumeSnapshotClassName field, the VolumeSnapshotContent cannot be automatically created. In this case, you must manually create a VolumeSnapshotContent and associate the VolumeSnapshotContent with the VolumeSnapshot.
Each VolumeSnapshotContent can be associated with only one VolumeSnapshot.
When you delete a VolumeSnapshotContent, the associated snapshot is also deleted.
Dynamically create a volume snapshot
The following figure shows the procedure to dynamically create a volume snapshot from the disk that is used in an ACK cluster. 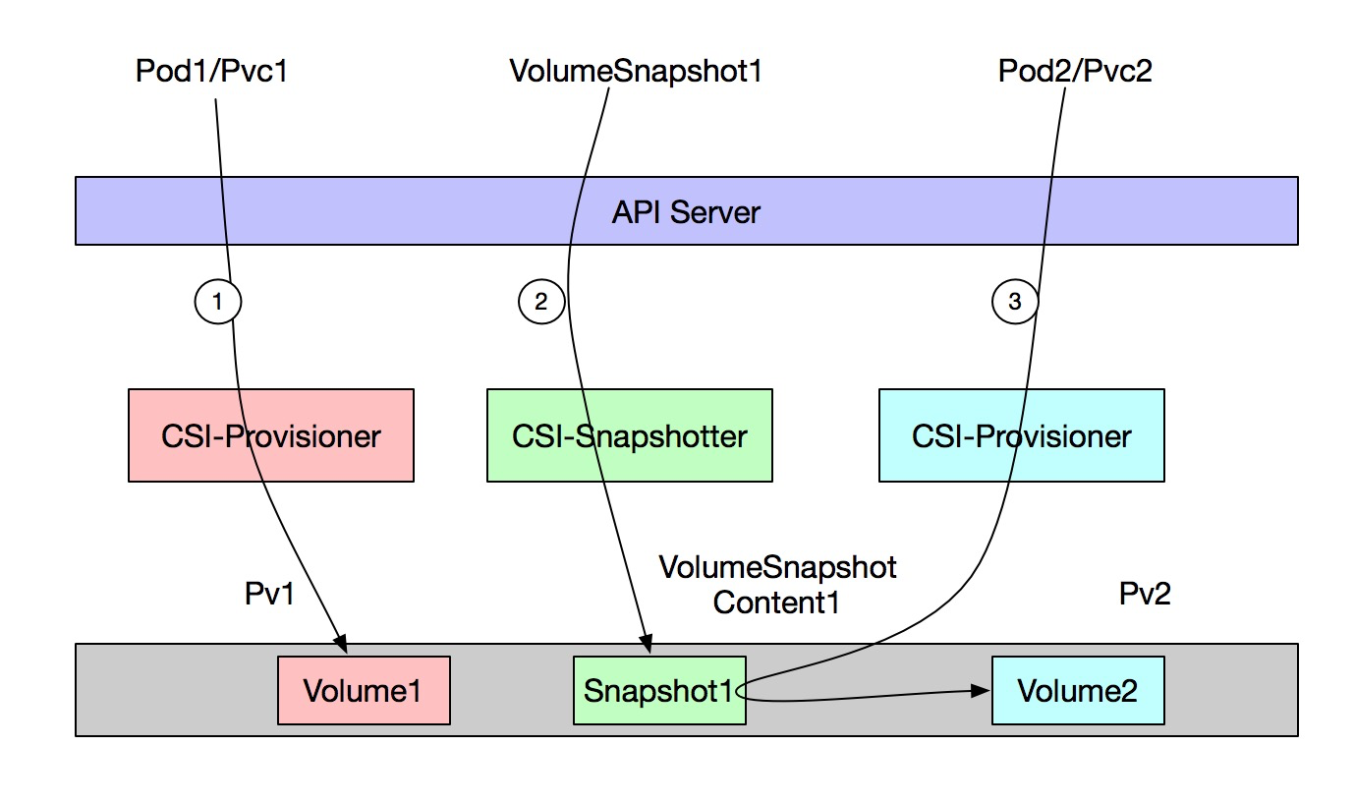
The following table describes the steps that are performed in the procedure.
Step | Description |
① | Create an application and create a disk volume to store application data. |
② | Create a VolumeSnapshot. Then, the ACK cluster automatically creates a VolumeSnapshotContent and a volume snapshot. |
③ | Create another application, create a PVC for the application, and then specify the volume snapshot that is created in Step 2 as the source of the PVC. |
The preceding steps are performed to enable the following features:
Backup: Snapshot 1 is created to back up data in Volume 1.
Restoration: Snapshot 1 is used to restore data in Volume 1 to Volume 2.
The following example shows how to create an MySQL application and restore the data of the application by using a volume snapshot. The following procedure demonstrates how to use a volume snapshot to restore the data of an application.
Create a VolumeSnapshotClass.
Create a file named volumesnapshotclass.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: VolumeSnapshotClass metadata: name: default-snapclass driver: diskplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com parameters: snapshotType: "xxx" instantAccessRetentionDays: "1" deletionPolicy: DeleteParameter
Description
deletionPolicy
If the value is set to Delete, the corresponding VolumeSnapshotContent and snapshot are deleted when you delete a VolumeSnapshot.
If the value is set to Retain, the corresponding VolumeSnapshotContent and snapshot are retained when you delete a VolumeSnapshot.
parameters.snapshotType
If the value is set to InstantAccess, the instant access mode is enabled to dynamically create snapshots. This feature is applicable to only enhanced SSD (ESSD)s. For more information, see Enable or disable the instant access feature.
The default value is normal, which indicates that a normal snapshot is created.
parameters.instantAccessRetentionDays
You must set this parameter if parameters.snapshotType is set to InstantAccess. This parameter specifies the retention period of snapshot that is created in instant access mode. After the feature is disabled, the snapshot that is created in instant access mode is converted to a normal snapshot.
parameters.forceDelete
Set forceDelete to "true" to forcefully delete snapshots. By default, this parameter is not specified.
If you set the value to "true", all snapshots are deleted.
If you do not specify this parameter, only snapshots that are not in use are deleted. If you want to delete snapshots that are in use, set the value to "true".
Run the following command to create a VolumeSnapshotClass:
kubectl apply -f volumesnapshotclass.yaml
Create an application and write data to the application.
Create a file named mysql.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: mysql spec: selector: matchLabels: app: mysql serviceName: "mysql" replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: mysql spec: containers: - name: mysql image: mysql:5.7 env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: mysql-pass key: password imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent volumeMounts: - name: disk mountPath: /data volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: disk spec: accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] storageClassName: "alicloud-disk-topology-alltype" resources: requests: storage: 20Gi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: mysql-pass type: Opaque data: username: dGVz**** password: dGVzdDEt****Run the following command to create an MySQL application:
kubectl apply -f mysql.yamlRun the following command to write data to pod mysql-0:
kubectl exec -it mysql-0 -- touch /data/test kubectl exec -it mysql-0 -- ls /dataExpected output:
lost+found test
Create a VolumeSnapshot.
NoteIf the version of the Container Storage Interface (CSI) plug-in used by your cluster is V1.22.12-b797ad9-aliyun or later, you can create a snapshot from a disk volume regardless of whether the PVC of the disk volume is used by a pod that is in the Running state. For more information about CSI versions, see csi-provisioner.
If the version of the CSI plug-in used by your cluster is earlier than V1.22.12-b797ad9-aliyun, you can create a snapshot only from a disk volume that is mounted to a pod. This means that the PVC of the disk volume must be used by a pod.
Create a file named snapshot.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: VolumeSnapshot metadata: name: new-snapshot-demo namespace: default spec: volumeSnapshotClassName: default-snapclass source: persistentVolumeClaimName: disk-mysql-0Run the following command to create a VolumeSnapshot:
kubectl apply -f snapshot.yamlRun the following command to check whether the VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent are created. You can also log on to the ECS console to view the snapshot.
Run the following command to view the VolumeSnapshot:
kubectl get volumesnapshots.snapshot.storage.k8s.ioExpected output:
NAME AGE new-snapshot-demo 36mRun the following command to view the VolumeSnapshotContent:
kubectl get VolumeSnapshotContentExpected output:
NAME AGE snapshotcontent-222222 36m
Restore data.
Create a file named mysql-restore and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: mysql-restore spec: selector: matchLabels: app: mysql serviceName: "mysql" replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: mysql spec: containers: - name: mysql image: mysql:5.7 env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: mysql-pass key: password imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent volumeMounts: - name: disk mountPath: /data volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: disk spec: accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] storageClassName: "alicloud-disk-topology-alltype" resources: requests: storage: 20Gi dataSource: name: new-snapshot-demo kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.ioNoteIn the dataSource field of the volumeClaimTemplates section, set kind to VolumeSnapshot and set name to new-snapshot-demo. The new-snapshot-demo snapshot is created in Step 3.
Run the following command to restore the application data:
kubectl apply -f mysql-restore.yaml
Run the following command to view the application data in pod mysql-restore-0:
kubectl exec -it mysql-restore-0 -- ls /dataExpected output:
lost+found testThe output shows that the same application data is returned. This indicates that the application data is restored.
Statically create a volume snapshot (import an existing snapshot from an ECS instance)
The following procedure demonstrates how to import an existing snapshot from an ECS instance to an ACK cluster.
Use the following YAML template to create a VolumeSnapshotContent:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: VolumeSnapshotContent metadata: name: new-snapshot-content-test spec: deletionPolicy: Retain driver: diskplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com source: snapshotHandle: <your-snapshotid> volumeSnapshotRef: name: new-snapshot-demo namespace: defaultParameter
Description
snapshotHandle
Enter the snapshot ID that is generated on the ECS instance page.
volumeSnapshotRef
Enter the following information for the VolumeSnapshot that you want to create:
name: the name of the VolumeSnapshot.namespace: the namespace to which the VolumeSnapshot belongs.
Use the following YAML template to create a VolumeSnapshot:
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: VolumeSnapshot metadata: name: new-snapshot-demo namespace: default spec: source: volumeSnapshotContentName: new-snapshot-content-testParameter
Description
metadata.name
The name of the VolumeSnapshot. The name must be the same as the VolumeSnapshot name that is specified in the preceding VolumeSnapshotContent.
spec.source.volumeSnapshotContentName
The name of the VolumeSnapshotContent that is associated with the VolumeSnapshot. The name must be the same as the name of the VolumeSnapshotContent that is created in the preceding step.
Restore data.
Create a file named mysql-restore and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: mysql-restore spec: selector: matchLabels: app: mysql serviceName: "mysql" replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: mysql spec: containers: - name: mysql image: mysql:5.7 env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: mysql-pass key: password imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent volumeMounts: - name: disk mountPath: /data volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: disk spec: accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] storageClassName: "alicloud-disk-topology-alltype" resources: requests: storage: 20Gi dataSource: name: new-snapshot-demo kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.ioNoteIn the dataSource field of the volumeClaimTemplates section, set kind to VolumeSnapshot and set name to new-snapshot-demo. The new-snapshot-demo snapshot is created in Step 2.
Run the following command to restore the application data:
kubectl apply -f mysql-restore.yaml
Run the following command to view the application data in pod mysql-restore-0:
kubectl exec -it mysql-restore-0 ls /dataExpected output:
lost+found testThe output shows that the same application data is returned. This indicates that the application data is restored.