This topic introduces Ingresses and describes how Ingress controllers and the NGINX Ingress controller work.
Introduction to Ingress
In a Kubernetes cluster, an Ingress functions as an access point that exposes Services in the cluster. It distributes most of the network traffic that is destined for the Services in the cluster. An Ingress is a Kubernetes resource object that is used to enable external access to Services in a Kubernetes cluster. You can configure routing rules for an Ingress to route network traffic to backend pods of different Services.
How an Ingress controller works
Ingress controllers are used to parse the forwarding rules of Ingresses in a Kubernetes cluster. After an Ingress controller receives a request that matches an Ingress rule, the Ingress controller routes the request to the corresponding Service. Then, the Service forwards the request to pods and the pods process the request. In a Kubernetes cluster, Services, Ingresses, and Ingress controllers work in the following process:
A Service is an abstraction of an application that is deployed in a group of replicated pods.
An Ingress contains reverse proxy rules. It controls to which Services HTTP or HTTPS requests are routed. For example, an Ingress routes requests to different Services based on the hosts and URLs in the requests.
An Ingress controller is a reverse proxy program that parses Ingress rules. If changes are made to the Ingress rules, the Ingress controller updates the Ingress rules accordingly. After an Ingress controller receives a request, it redirects the request to a Service based on the Ingress rules.
The changes to Ingresses in a Kubernetes cluster are updated to Ingress controllers through the cluster API server. The configurations of SLB instances are dynamically generated based on these changes. Then, Ingress rules are updated based on the configurations. 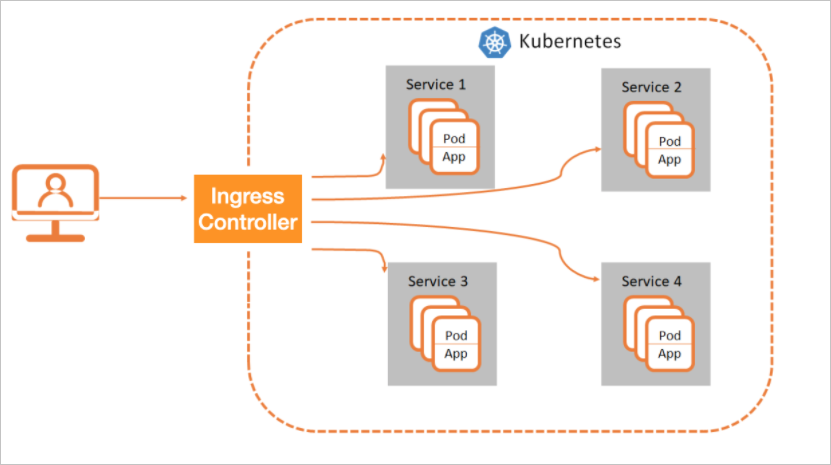
How to use the NGINX Ingress controller
ACK Serverless cluster provides the NGINX Ingress controller that is optimized based on the open source version. You can install the NGINX Ingress controller when you create an ACK Serverless cluster.