This topic describes the scenarios, implementation, and billing of the backup management feature of Compute Nest, and how to use this feature to back up and restore data for service instances.
Background information
Customers often need to back up data of their service instances. For example, they need to back up data in the following scenarios:
Game server: A game server may crash and the save data of users is lost. To resolve this issue, you need to regularly back up data of a game server.
Database service: To ensure data security and prevent possible losses, you need to back up your databases.
Service upgrade: During a service upgrade, data may be lost. Therefore, data backup is required before the upgrade.
In the past, customers needed to back up data of their service instances in the consoles of the corresponding cloud services. For example, if a service instance is deployed on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, you need to log on to the ECS console, find the ECS instance, and manually create snapshots for the disks of the ECS instance. If you want to restore data, you need to find the required disk snapshot and roll back the data in the ECS console. Obviously, if a large number of disks or ApsaraDB RDS instances need to be backed up, the operations are cumbersome and inconvenient. In addition, you must record the name of the required disk snapshot or ApsaraDB RDS instance backup to ensure that the correct data is restored. This is error prone. To resolve the issues, Compute Nest provides the backup management feature. This feature allows you to back up or restore cloud resource data of service instances with a few clicks in the Compute Nest console.
Implementation
The backup and restoration features of Compute Nest depend on backup and restoration capabilities of underlying cloud resources. Therefore, Compute Nest supports backup and restoration for a cloud service only if the following conditions are met: The backup and restoration features are developed for the cloud service in Compute Nest, and the cloud service supports data backup and restoration. Compute Nest supports backup and restoration for the following cloud service resources:
Elastic Block Storage (EBS) devices
ApsaraDB RDS instances that run MySQL, SQL Server, or PostgreSQL
Backup
Before data backup, Compute Nest generates an empty backup record. This record is used to store the start time and end time of the backup task, overall backup result, and ID and backup status of each cloud service resource involved in the backup task.
During data backup, Compute Nest filters all cloud resources of the service instance based on the ID of the service instance and the tags added to the cloud resources to find EBS devices and ApsaraDB RDS instances that run MySQL, SQL Server, or PostgreSQL. Then, Compute Nest calls the API operations of cloud services to back up data. After the API operations are called, Compute Nest cyclically scans the cloud services for backup results. When the overall backup result is obtained, regardless of whether it is success or failure, Compute Nest records the result to the backup record and displays the result to customers. In most cases, one Compute Nest backup operation involves multiple instances of multiple cloud services. As long as an instance is being backed up, the backup record of Compute Nest is marked as backing up. If an instance of a cloud service fails to be backed up, the backup record of Compute Nest is marked as backup failed. If all instances of all cloud services are backed up, the backup record of Compute Nest is marked as backup successful.
Restoration
Before data restoration, Compute Nest generates an empty restoration record. This record is used to store the start time and end time of the restoration task, backup ID, overall restoration result, and ID and restoration status of each cloud resource involved in the restoration task.
During the restoration of a disk, the ECS instance to which the disk is attached must be stopped. Therefore, Compute Nest stops a service instance before data restoration. After the service instance is stopped, Compute Nest queries the resource IDs and calls the API operations of cloud services to restore data. After the API operations are called, Compute Nest cyclically scans the cloud services for restoration results. When the overall restoration result is obtained, regardless of whether it is success or failure, Compute Nest records the result to the restoration record and displays the result to customers. In most cases, one Compute Nest restoration operation involves multiple instances of multiple cloud services. As long as an instance is being restored, the restoration record of Compute Nest is marked as restoring. If an instance of a cloud service fails to be restored, the restoration record of Compute Nest is marked as restoration failed. If all instances of all cloud services are restored, the restoration record of Compute Nest is marked as restoration successful. When the restoration is complete, Compute Nest starts the service instance. Take note that databases and tables of ApsaraDB RDS instances that run MySQL or PostgreSQL are renamed during restoration due to the restoration mechanism. As a result, the original databases and tables cannot be found. To resolve this issue, when an ApsaraDB RDS instance that runs MySQL or PostgreSQL is restored, Compute Nest uses Function Compute to execute an SQL statement on the ApsaraDB RDS instance to change the names of databases and tables of the instance to the original names. Therefore, if your service instance contains an ApsaraDB RDS instance that runs MySQL or PostgreSQL, Function Compute fees may be generated during the restoration.
Billing
The backup management feature of Compute Nest is free of charge. This feature depends on backup and restoration capabilities of cloud services. Therefore, you are charged for the backup and restoration by the cloud services. The following billable items are involved:
Snapshots of EBS devices. For more information about the billing of snapshots of EBS devices, see Snapshots.
Backup of ApsaraDB RDS instances. For more information about the billing of backup of ApsaraDB RDS instances, see the following topics:
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL: Backup storage fees
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server: Backup fee
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL: Backup storage fees
Function Compute. For more information about why Function Compute fees are generated, see the "Implementation" section of this topic. For more information about the billing of Function Compute, see Billing overview.
Procedure
If the backup management feature is enabled for your deployed service, you can perform the backup and restoration operations on a service instance on the details page of the service instance.
Backup
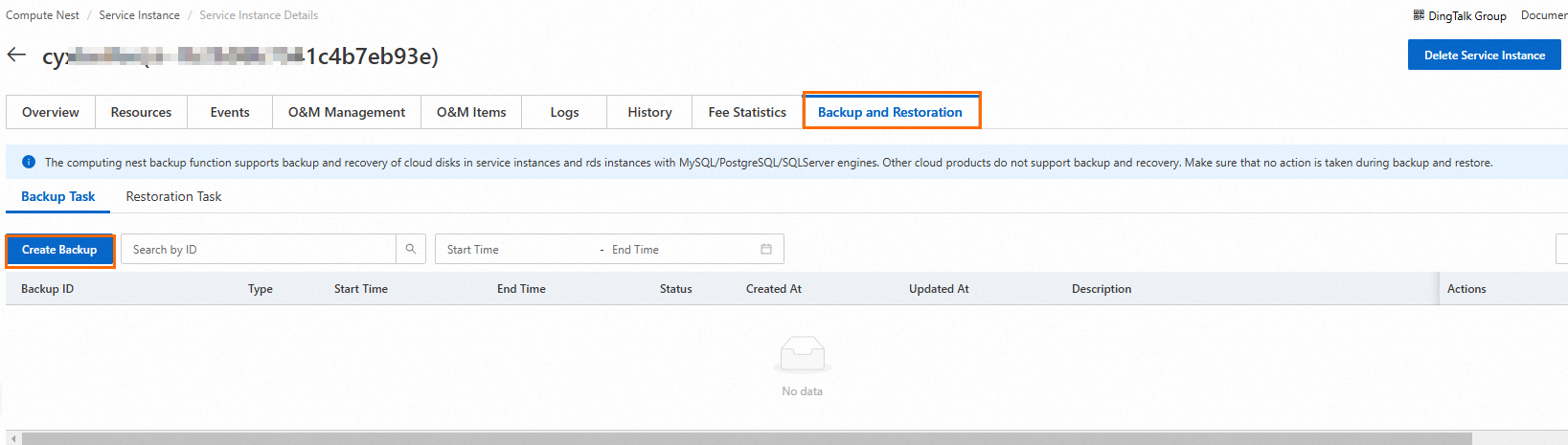
Log on to the Compute Nest console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Service Instance. On the My Service Instance tab of the Service Instance page, find the service instance and click its ID to go to the Service Instance Details page.
Click the Backup and Restoration tab. On the Backup and Restoration tab, click Create Backup.
 Warning
WarningDuring the backup, do not perform operations on the service instance or modify data.
Wait until the backup is complete. If the backup fails, move the pointer over the backup record to view the failure cause.
Restoration
On the Backup and Restoration tab, find the backup task and click Restore in the Actions column.
Click Confirm to restore data. On the Restoration Task tab, view the restoration task list.
WarningThe restoration operation will cause a service instance to stop. We recommend that you perform a backup operation again before the restoration.
During the restoration, do not perform operations on the service instance or modify data.
Wait until the restoration is complete. If the restoration fails, move the pointer over Restore Failed in the Status column to view the failure cause.