After you use the VMware backup and disaster recovery feature to restore a VMware virtual machine (VM) as an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance on the cloud, you can perform a failback from the ECS instance to on-premises VMware by performing the following operations: Create a custom image for the ECS instance and export the image as a VMDK file. Use the VMDK file to create a VM in the on-premises VMware environment.
Prerequisites
A backup VMware VM is restored as an ECS instance on the cloud. For more information, see Restore a VMware VM to an ECS instance.
ImportantThis feature applies only to failback of VMware VMs from Linux ECS instances to on-premises VMware. For CentOS 7, if the system cannot be started after the failback, manually switch the disk controller to the IDE controller and then start the system again.
An Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket is created in the region where the custom image resides. You can use the OSS bucket to temporarily store the custom image and then download the image to your computer. For more information, see Create buckets.
Usage notes
Due to copyright restrictions, you cannot export Windows Server custom images or custom images that are derived from Alibaba Cloud Marketplace images. For more information about the limits on image export, see Export a custom image.
The ECS instance from which an image is exported (the ECS instance for which you want to perform a failback to on-premises VMware) must be an ECS instance that is backed up and restored by using the VMware backup and disaster recovery feature of Cloud Backup. Otherwise, the VM created by using the VMDK file in the on-premises VMware environment fails to be started.
Procedure
This procedure includes the steps of creating a custom image, exporting the image, and using the image to create a VM. The time consumed by these steps depends on the data size of the disk. Evaluate the time required in advance to ensure that the steps are performed smoothly.
The failback requires careful planning and testing to ensure smooth system migration and prevent data loss and service interruption.
Create a custom image for the ECS instance. For more information, see Create a custom image from an instance.
Export the custom image to the OSS bucket. For more information, see Export a custom image.
If the format of the exported image does not meet the requirements, you can use the qemu-img tool to convert the format of the image. For more information, see Convert the format of an image.
Create a VMware VM by using the VMDK file.
Step 1: Create a custom image from the ECS instance and export the image to the OSS bucket
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group to which the resource belongs.

Find the instance from which you want to create a custom image. Choose in the Actions column.
In the Create Custom Image dialog box, enter a name for the custom image, retain the default settings of other parameters, and then click OK.
ImportantSnapshots are automatically generated when you create a custom image. You are charged for the snapshots if you retain the custom image. For more information, see Snapshots.
You can export the image only if the image is in the Available state.

In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Custom Images tab, find the image that you want to export and click Export Image in the Actions column.
ImportantYou can use an OSS bucket to download the image to your local computer.
The exported image is stored in an OSS bucket. Therefore, when you export a custom image, you are charged for OSS storage and the traffic generated for image download. For more information about the OSS billing, see Billing overview.
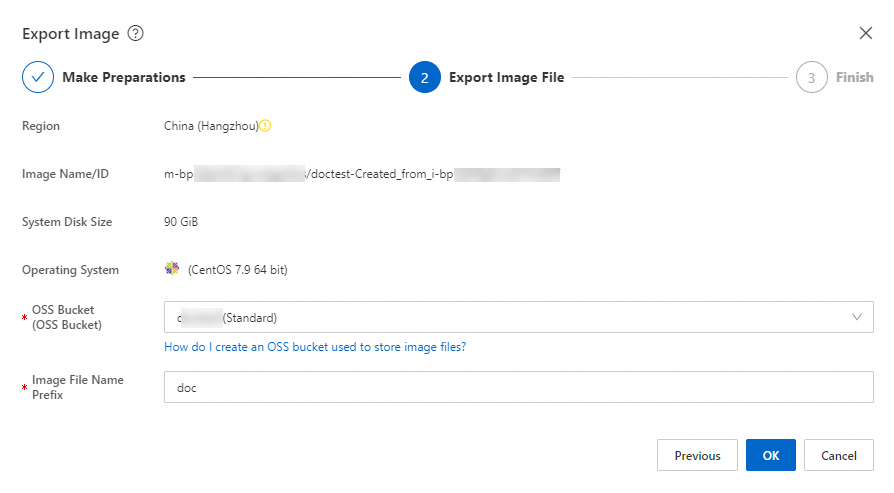
In the Export Image dialog box, read the notes and limits and click Next. For more information about the limits, see Export a custom image.
Specify the OSS Bucket and Image File Name Prefix parameters and click OK.
 Important
ImportantYou can export a custom image in one of the following formats: RAW, VHD, QCOW2, VDI, and VMDK. By default, custom images are exported in the RAW format in regions where the Image Format parameter is unavailable. For more information about how to export a custom image, see Export a custom image.
If the exported image is in the RAW format, you must convert the RAW format to the VMDK format when you create a VMware VM.
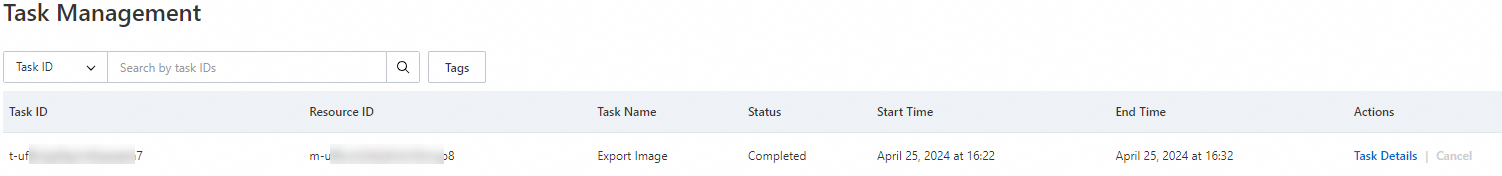
In the left-side navigation pane, move the pointer over Maintenance & Monitoring and select Tasks. On the Task Management page, view the progress of the image export task. You can cancel the image export task at any time.
NoteThe amount of time required to export a custom image varies depending on the size of the image files and the number of concurrent export tasks in the queue. You can click Task Details to view the task progress.
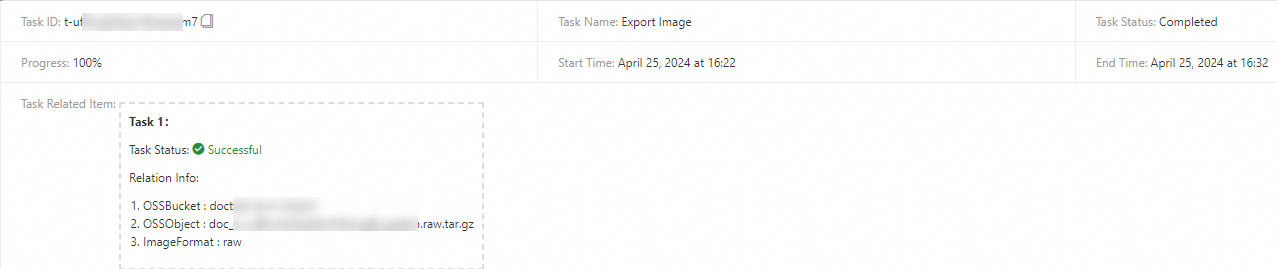
After the export task is complete, view the details of the export task. The image is saved in the specified OSS bucket.
Step 2: Export the image from the OSS bucket to your local computer
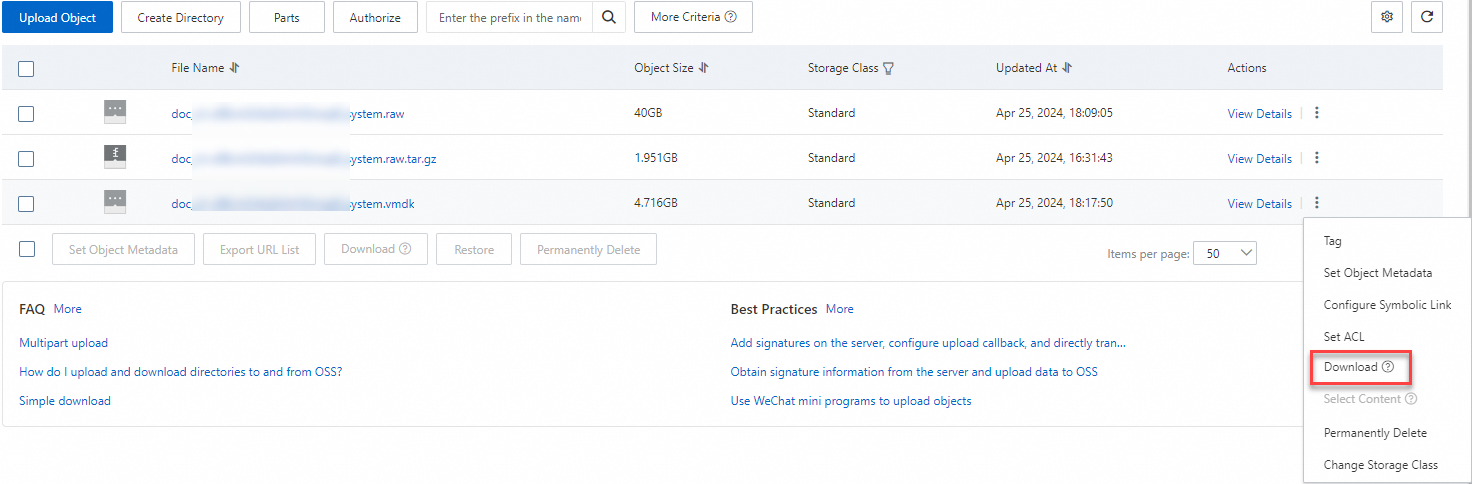
Download the exported image to your computer. For more information, see Download objects.
If you selected the RAW format when you exported the image, the default name extension of the exported image file is .raw.tar.gz and the name extension of the decompressed image file is .raw.
(Optional) Step 3: Convert the custom image from the RAW format to the VMDK format
If the name of the exported custom image is doc_system.raw.tar.gz, perform the following steps to convert the format.
If the format of the exported image does not meet the requirements, you can use the qemu-img tool to convert the format of the image. For more information, see Convert the format of an image.
Before you decompress the image file, you must plan sufficient storage space to prevent decompression failure caused by insufficient space.
Decompress the
doc_system.raw.tar.gzfile to thedoc_system.rawfile. The exported file isdoc_system.raw.tar -xvzf doc_system.raw.tar.gzConvert the format of the custom image to the VMDK format. For CentOS, you can run the
yum install qemu-imgcommand to install the qemu-img tool. The converted file isdoc_system.vmdk. After you run the command, wait until the conversion is complete. After the conversion is complete, adoc_system.vmdkfile is added to the corresponding directory.qemu-img convert -f raw -O vmdk doc_system.raw doc_system.vmdk
Step 4: Upload the VMDK file to VMware
Log on to the vSphere Web Client.
Find the desired datastore.
Go to the details page of the datastore and click UPLOAD FILES to upload the image. It takes an extended period of time to upload a large file. Wait until the upload is complete.
Step 5: Use the VMDK file (image) to create a new VMware VM
Log on to the vSphere Web Client.
Right-click a data center, host, or resource pool and choose New Virtual Machine, and then click NEXT.
In the New Virtual Machine wizard, select Create a new virtual machine for the creation type and click NEXT.
Specify Virtual machine name, select the location for the VM, and then click NEXT.
Select the compute resources and click NEXT.
Select a storage location to store the VM file and click NEXT.
Select compatibility and click NEXT.
Select an operating system and an operating system version, and then click NEXT.
Configure the VM hardware, including the CPU, memory, network, and other hardware options.
Delete the default new hard disk and select the uploaded VMDK file as the new hard disk.
Click Add NEW DEVICE and select Existing Hard Disk.
Browse and select the uploaded VMDK file, select IDE 0 for Virtual Device Node of the new hard disk, and click NEXT.
If multiple disk image files are available, upload the VMDK files in sequence. Select IDE 0 as the virtual device node to complete the upload.
In the Ready to complete wizard, review the configuration.
Click FINISH. The VM is created.
Now, you have completed failback of the ECS instance to the on-premises VMware environment. The username and password of the newly created VM are the same as those of the ECS instance. You can perform subsequent testing and other tasks as planned.
 > Disks and Images > Create Custom Image
> Disks and Images > Create Custom Image